What is an abscess?
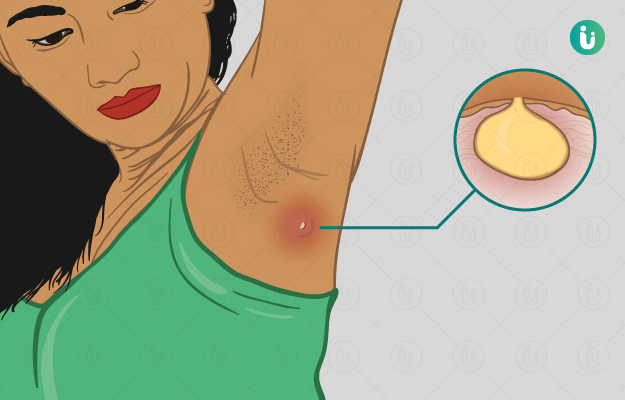
An abscess is the formation and accumulation of pus in an organ or tissue. It is filled with micro-organisms, dead cells, fluid and other debris. An abscess can occur on any part of the body, such as the face, mouth, teeth, organs like the kidneys and stomach. However, skin abscesses are the most common.
What are its main associated signs and symptoms?
- Common symptoms of skin abscess are redness, pain, swelling and a small skin eruption filled with a yellowish fluid.
- If you have an abscess in the internal organs, you are likely to experience pain over that area, with the possibility of developing a fever due to the infection.
- If the abscess is in the lungs, the person has difficulty in breathing, fatigue, and cough. Based on where the abscess is, it might disrupt the functioning of the organ.
- Similarly, when an abscess forms around the tonsils, a person has pain while talking and swallowing.
What are the main causes?
- An abscess is generally formed when there is some form of infection caused by bacteria, or other micro-organisms, such as viruses, fungi and parasites.
- A foreign body in any organ can also cause an abscess to develop.
- People with a weakened immunity are more likely to develop an abscess. Conditions that cause a weak immune system include:
- It is not necessary that an abscess occurs in the presence of some other disease. Healthy individuals can also have an abscess.
- Ingrown hair follicles can become infected and cause an abscess around them, called a furuncle or boil.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
- Your physician can diagnose a skin abscess by simple clinical examination. To confirm the cause, a thorough medical history and check-up are a must for abscesses in other locations.
- If an infection is suspected, the clinician may order blood investigations or culture of the fluid from the centre of the abscess.
- An X-ray or CT scan of the affected organ helps to check for the presence of an abscess, which is not visible to the naked eye.
- Treatment varies based on the size and location of the abscess. If it is a single, small skin abscess, home care like hot compress along with antibiotics is sufficient.
- For a larger abscess in the organs, surgical drainage might be the treatment of choice. Under anaesthesia, the doctor opens through the cavity of the abscess to drain out the contents. Along with this, antibiotics will be given to completely clear the infection.
- There are many modifications to the conventional surgery of incision and drainage. The physician performs the surgery in accordance with the part of the body involved and the size of the abscess.
(Get online doctor consultation for any health issue)

 Doctors for Abscess
Doctors for Abscess  OTC Medicines for Abscess
OTC Medicines for Abscess