Summary
Bruxism refers to a disorder, which is characterised by grinding, gnashing or clenching of the teeth, generally seen during the night time when the individual is asleep. Bruxism is a common disorder, affecting over 31% of the adults with the most common cause of grinding being undue stress or anxiety. It has also been related to certain neurological disorders and may even be seen as a side effect of certain drugs or an effect of trauma to the dentition.
Over time, clenching disorders are likely to cause dental pain and may hamper the integrity of dental restorations along with wearing off of the occlusal surface of the teeth (the grinding or chewing surface of the teeth). It can also lead to jaw pain due to the manifestation of temporomandibular disorders. When this happens, there is a reduction in the functional capacity of the teeth or reduction in the masticatory forces. Disturbances in sleep pattern and facial pain may be some other effects of bruxism.
Stress management, alcohol reduction and cessation of smoking are some of the measures to prevent bruxism. Teeth grinding can be treated with the help of intraoral devices, splint therapy, orthodontic treatment, patient education and pharmacological therapy to reduce pain and manage anxiety. Let’s learn more about the symptoms, causes, treatment, prevention and complications of bruxism through this article.

 Doctors for Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
Doctors for Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)  Bruxism (Teeth Grinding) articles
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding) articles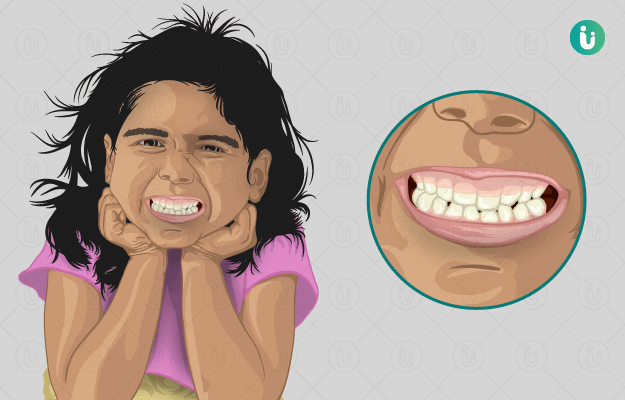
 Homeopathic Treatment of Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
Homeopathic Treatment of Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)

























 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria











