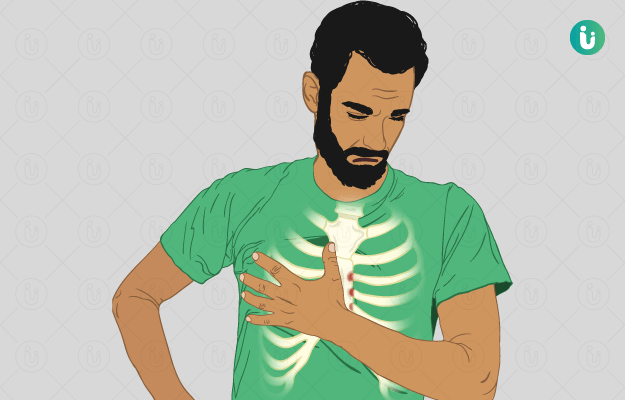
What is Costochondritis?
Costochondritis is characterised by an inflammation in the cartilages attached to the breastbone. Except for the last two ribs, all the ribs are attached by cartilage to the breastbone. This self-limiting inflammation results in chest pain, which is a common symptom of costochondritis.
Costochondritis is also known by the following terms:
- Costo-sternal Syndrome
- Parasternal Chondrodynia
- Anterior Chest Wall Syndrome
What are the main signs and symptoms?
Important signs and symptoms of costochondritis include pain with the following characteristics:
- Pain often occurs on the left side of the breastbone
- Pain felt maybe described as sharp and aching
- Patient may experience a pressure-like feeling of pain
- Deep breath, cough, exertion, and upper body movement aggravate the pain
- More than one rib is affected
What are its main causes?
Costochondritis is the most common cause of anterior chest wall pain. It usually has no specific underlying cause. The ribs joined by cartilage to the breastbone get inflamed leading to costochondritis.
Frequent causes include
- Injury or blow to the chest
- Over-exercising or severe chronic episodes of cough
- Arthritis-related (Read more: Arthritis treatment)
- Certain infections affecting the rib joint, for example, tuberculosis and syphilis
- Metastatic spread of lung, breast, or thyroid cancer to the chest region
Costochondritis is linked with Tietze’s syndrome, which involves only one area with associated painful, localised swelling.
People over 40 years of age are at a higher risk of costochondritis. It is more prevalent in women than in men.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis of costochondritis is based on the medical history and physical examination of the rib area. Your doctor will ask about any history of a severe cough or strenuous physical training. Anterior chest X-ray may be required to look for underlying causes including
- Arthritis in the shoulder joints and joints in the chest region
- Destruction of costal cartilage by infections or neoplasm
- Fibromyalgia
- Herpes zoster of the thorax
Treatment of costochondritis involves
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs
- Local anaesthetic or steroid injections if needed in severe cases
- Gentle stretching exercises as advised by the doctor
Self-Care
- Warm or cold compresses
- Avoidance of any strenuous physical activities or stress
(Read more: Inflammatory disease treatment)

 Doctors for Costochondritis
Doctors for Costochondritis