Diabetes is a chronic condition in which the patient's blood sugar levels rise above the normal range of under 100 millilitres per deciliter of blood (ml/dL) fasting and under 140 ml/dL after eating. Diabetes can be of two types: type 1 diabetes (insulin-dependent) and type 2 diabetes (non-insulin dependent). Diabetes can be managed properly by cutting down on sugar, taking medication on time, quitting alcohol and doing exercises for diabetics.
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to six major complications:
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Diabetic Neuropathy (nerve damage due to diabetes)
- Diabetic Nephropathy (kidney damage due to diabetes)
- Cardiovascular disease
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Periodontitis (the gums and tissues supporting the teeth become inflamed)
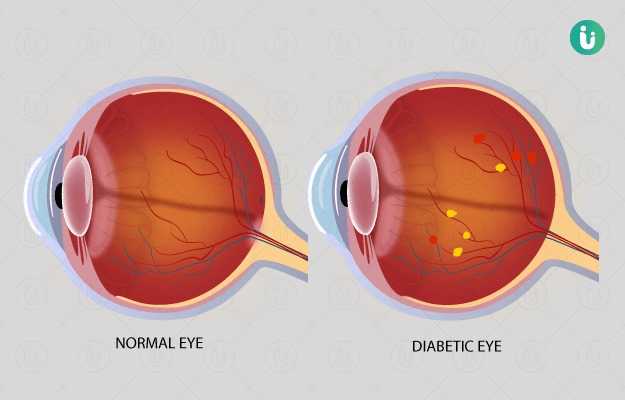
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes which damages the retina of the eye. The retina is a thin layer present at the back of the eye which converts any image your eyes see into electrical signals and sends it to the brain. The brain then processes the image and sends it back to the retina, which helps you to see things.
A person with diabetic retinopathy can complain of blurry vision, floaters and dark spots in the area of vision along with colour blindness and night blindness.
If caught early, diabetic retinopathy can be managed with the help of medications, manual eye surgeries and laser surgeries. If not treated or diagnosed on time, diabetic retinopathy can lead to a complete loss of sight.
Please check this page for complete diabetes treatment.
(Read More - Diabetic Nephropathy treatment)

 Doctors for Diabetic Retinopathy
Doctors for Diabetic Retinopathy  OTC Medicines for Diabetic Retinopathy
OTC Medicines for Diabetic Retinopathy