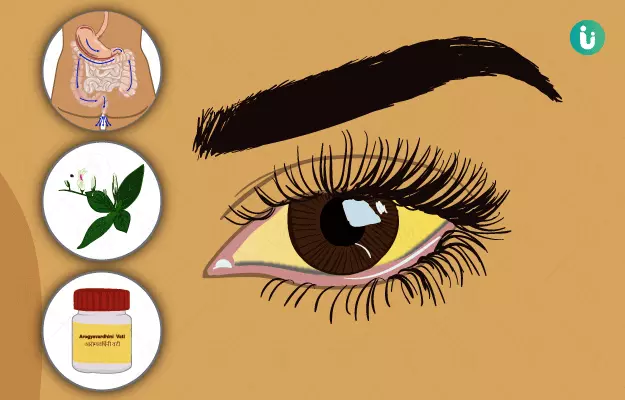
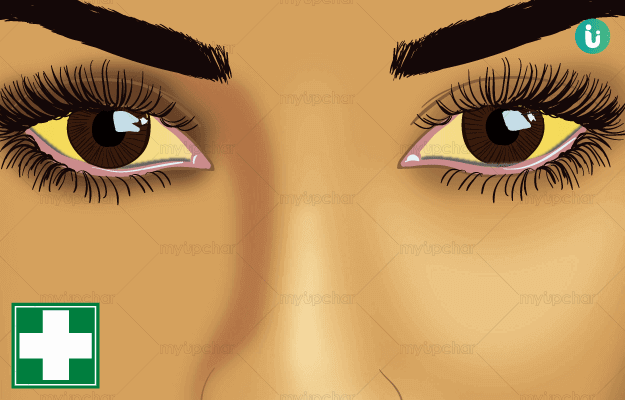
Jaundice is a liver disease that is caused due to excess levels of bilirubin, a pigment present in the body. The most commonly observed jaundice symptom is yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes. Excessive bilirubin levels can either be inherited or acquired. Inherited factors that are responsible for jaundice include glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and acquired factors include trauma and vitamin B 12 deficiency. Jaundice is diagnosed by measuring the bilirubin level in plasma. Consuming low-fat meals and plenty of water can help manage jaundice.
(Read more: How many glasses of water to drink in a day)
Jaundice is classified into three types based on the cause: pre-hepatic jaundice, hepatic jaundice and post-hepatic jaundice. Ayurvedic treatments have been traditionally used to treat various types of liver disorders successfully, including all types of jaundice, and even now, more than 50% of the Indian population relies on Ayurveda for the treatment of liver diseases. This is because toxicity levels of medications used in Ayurveda are low as compared to conventional medicines. Plenty animal and clinical research are now available to prove the effectiveness and safety of herbo-mineral and medicinal plants in treating liver diseases. One of the Ayurvedic medicines highly advocated for liver diseases is arogyavardhini vati (tablet), which also works on kamala (jaundice). Herbs like haridra (turmeric) and amalaki (Indian gooseberry) are some of the commonly used single herbs that are used to relive jaundice symptoms. Virechana (purgation), among all the five panchakarma (five treatments) procedures, is seen to be beneficial in treating jaundice.
- Ayurvedic view of jaundice
- Ayurvedic treatment for jaundice
- Ayurvedic herbs and medicines for jaundice
- Dietary and lifestyle changes for jaundice as per ayurveda
- How effective are ayurvedic medicines and treatments for jaundice
- Side effects and risks of ayurvedic medicine and treatments for jaundice
- Takeaway
Ayurvedic view of jaundice
Kamala is a disease caused due to altered pitta dosha, which affects the yakrit (liver). This disease is characterised by yellow discolouration of the skin, urine, stools, sclerae, and mucous membranes. Ayurveda classifies kamala as an apratyaksa (indirect) disease. Jaundice has been included in the group of diseases that are caused when pitta dosha is situated in rakta dhatu. The occurrence of jaundice due to other conditions or on its own is due to the aggravated pitta levels in the body. Foods and lifestyle factors that increase pitta levels tend to burn muscles and blood, which results in jaundice. Daha (burning sensation), haridra-netrata (yellowing of the eyes), daurbalya (weakness), haridra-anana (yellowing of the face), rakta-pitta shakrit (yellow stools with blood), avipaka (indigestion) and bheka varna (a frog-like complexion) are some of the symptoms seen in jaundice. Jaundice is usually associated with other conditions like malaise, indigestion and anorexia. Swelling and enlargement of the liver also occur in some cases of jaundice. Ayurveda suggests shamana chikitsa (pacification therapy) and samshodana or shodhan chikitsa (purification therapy) for jaundice treatment.
Ayurvedic treatment for jaundice
- Nidana parivarjana (avoiding the causative factors)
This therapy aims at keeping an individual free from disease by avoiding the causative factors of the disease and it is an essential part of Ayurvedic treatment in all diseases. The two-fold benefits of nidana parivarjana are a) halting disease progression and b) prevention of relapse. Based on the nidana (cause) of jaundice, preventive measures like avoiding eating at places with unclean food and water, using clean towels and good hygiene habits should be practised.
- Virechana
The process of virechana helps in getting rid of the excess pitta from the body. Bitter purgatives like vibhandi (senna), ghrit kumari (aloe) or amlaparni (rhubarb) are especially recommended in liver diseases like jaundice. They clean the liver, decongest bile and remove any obstructions in the passage from which the bile flows. Virechana is beneficial in people with kapha dosha as they have high levels of bile in their body. Virechana is not always recommended in people with vata dosha as it weakens the digestive fire, which is naturally less strong in such people. It is also unadvisable in pregnant, old or weak individuals and those with a prolapsed stomach or uterus. Eraṇḍa taila (castor oil) may be used in the virechana process to treat jaundice.
Medicines for pachana (digestion), deepana (increasing hunger), snehana (lubrication), and pittashamaka (pacifying pitta) are given as shamana chikitsa. The herbs used in the shamana chikitsa are mentioned in the next section.
Ayurvedic herbs and medicines for jaundice
Ayurvedic Herbs for Jaundice
- Katuki (kutki)
Katuki is known to have pittaghna (pitta-destroying) and kaphaghna (kapha-destroying) properties. Katuki is used in the deepena process of shamana chikitsa. It also stimulates liver function and helps in pitta removal and purgation. This is useful in reducing pitta and bile levels, thereby treating jaundice. Katuki is used in the form of a churna (powder) which can be taken with water, sugarcane juice, or honey or as recommended by your doctor.
- Kalamegha (king of bitters, green chirayta)
Kalamegha is also used in the deepana process of shamana chikitsa. The properties of kalamegha are useful in treating chronic fever, removing pitta, inducing purgation and destroying worms. It also helps improve the function of spleen and digestive system. Kalamegha is available in the form of churna, which can be taken with water, sugarcane juice, or honey or as per the suggestion of your doctor.
- Bhumyamalaki (Indian plum)
Bhumyamalaki is known to be useful in many liver disorders like jaundice. It improves the overall health of liver and prevents hepatitis B virus infection. Bhumyamalaki can be taken in the form of juice or churna, which can be taken with water, sugarcane juice, or honey as per the recommendation of your doctor.
- Garijara (wild carrot)
Garijara is known to be a blood purifier and a nervine tonic in Ayurveda. It has been in use for jaundice treatment since a long time. Garijara is used in the snehana and deepana process of shamana chikitsa. It helps reduce pitta in the rakta dhatu and also pacifies vata dosha.
Ayurvedic Medicines for Jaundice
- Phalatrikadi kwatha
Phalatrikadi kwatha is a decoction made from eight herbs including haritaki (chebulic myrobalan), nimba (neem), bhunimba (clearing nut tree), vibhitaki (belleric myrobalan), katuki, amalaki (amla), guduchi (giloy, heart-leaved moonseed) and vasa (malabar nut). The kwatha (decoction) is bitter to taste and has pitta-rechaka (pitta removing), choleretic (stimulates the secretion of bile from the liver), cholagogue (promoting the discharge of bile from the system), and kapha-pitta shamaka (pitta and kapha pacifying) properties. It is useful in treating anaemia as well as jaundice. These properties help strengthen and stimulate the liver tissue thereby making phalatrikadii kwatha an excellent hepatoprotective (liver-protecting) drug. The ingredients also have antiviral and antioxidant properties, which just add to its protective and preventive action. Phalatrikadi kwatha can be taken for as long as two to three weeks or as directed by your physician.
- Vasaguduchyadi kwatha
Vasaguduchyadi kwatha is a renowned medicine in Ayurveda, which is used to treat many diseases including kamala. It is also used for the treatment of alcoholic liver disease and panduroga (anaemia). Vasaguduchyadi kwatha is a combination of haritaki, vasa (Malabar nut), nimb (neem), katuki, guduchi, chirayata (bitterstick), amalaki (Indian gooseberry), and vibhitaki. All of these herbs are rich in phytoconstituents like flavonoids, tannin-gallic acid, triterpenoids, coumarin glycosides and phenolic components, which have hepatoprotective properties. Vasaguduchyadi kwatha can be taken for as long as two to three weeks or as recommended by your ayurvedic doctor.
- Punarnava mandoora
Punarnava (spreading hogweed) mandoora can be taken for two to three weeks along with buttermilk or as directed by your physician. This medicine is known to have cough and fever-reducing, rejuvenating, anti-inflammatory (reduces inflammation), and diuretic properties. It is also used as a swedopaga medicine (as an adjunct to sweating therapy). Punarnava can also be used as a vegetable.
- Arogyavardhini vati
Arogyavardhini vati is one of the multidrug formulations used in treating liver disorders. The medicine aims to improve good health by achieving the balance in all doshas of the body.
This medication has antioxidant and hepatoprotective properties that help improve liver function. It clears body channels, stimulates digestive fire, balances fat distribution in the body and draws out toxins from the digestive system. Arogyavardhini vati is also available in the form of churna. The vati or churna can be taken for as long as two to three weeks with water, sugar cane juice, or honey as advised by your physician.
Dietary and lifestyle changes for jaundice as per ayurveda
Do’s
- Include green gram, sugarcane juice, draksha (dried grapes), anjira (figs), khichadi prepared from purana shali (old rice), parwal (pointed gourd), haridra, barley, arahara (pigeon pea), wheat, pomegranates, papaya, potatoes, amla, buttermilk, grapes, mango, apple, cow’s milk and adrak (ginger) in your diet.
- Have shritasheeta jala (boiled and cooled water).
- Take complete rest.
Don’ts
- Do not eat fried foods or pungent foods like chillies.
- Do not eat matar (peas), mustard oil, tambula (betel leaves), sesame, excess oil and clarified butter, and urad (black gram).
- Do not drink excess water.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not suppress natural urges.
- Do not sleep during the day.
- Avoid overexposure to the sun.
- Do not do excessive physical exercise.
(Read more: Foods to improve liver health)
How effective are ayurvedic medicines and treatments for jaundice
According to a research conducted among 180 patients with liver disorders, kalamegha proved to be effective in 90%, 83.3% and 22.2% of the patients with jaundice, chronic hepatitis and obstructive jaundice, respectively. No side effects were noted in any of the patients.
In another study, Vasaguduchyadi kwatha administration showed zero toxic effects and no gross changes in the body.
Arogyavardhini vati has been found to be antioxidant and hepatoprotective. It acts as a natural detoxifying agent for the liver and is an excellent remedy for fatty liver. It also maintains the proper functioning of liver and improves pachana.
Side effects and risks of ayurvedic medicine and treatments for jaundice
There are no side effects or risks associated with any of the herbs and medicines mentioned in this article. As treatments vary according to the type of jaundice and an individual’s prakriti, consult your doctor for the appropriate medications.
Arogyavardhini vati contains heavy metals like mercury, excess doses of which can lead to severe poisoning in the body. This formulation should strictly be avoided in lactating and pregnant women and in children.
Takeaway
Herbs like kalamegha that cut down excess pitta in the body help in treating jaundice. The medicinal ingredients of Ayurvedic combinations like vasaguduchyadi kwatha and phalatrikadi kwatha are not only useful in treating jaundice but also they protect the liver from diseases and improve liver function.
Other than medications, lifestyle and dietary changes suggested by the physician help manage jaundice better and lead to a faster recovery. Conventional medicines used to treat liver diseases may develop serious side effects. The herbs and medicines used in Ayurveda help treat all the types of jaundice effectively without causing any adverse effects on the body.
Find Ayurvedic Doctor in cities
Doctors for

Dr. Megha Sugandh
Ayurveda
6 Years of Experience

Dr. Nadeem
Ayurveda
3 Years of Experience

Dr.Ashok Pipaliya
Ayurveda
12 Years of Experience

Dr. Harshaprabha Katole
Ayurveda
7 Years of Experience
References
- Panda AK, Bhuyan GC, Rao MM. Ayurvedic Intervention for Hepatobiliary Disorders: Current Scenario and Future Prospect. Current Scenario and Future Prospect. J Tradit Med Clin Natur 6:210.
- Ministry of AYUSH, Govt. of India. Ayurvedic Standard Treatment Guidelines. [Internet]
- Girendra Singh Tomar. A Review Of Ayurvedic Hepatology And Inferences From A Pilot Study On Kalmegh ( Andrographis Paniculata) Intervention In Hepatic Disorders Of Variable Etiology. Annals Ayurvedic Med. 2012: 1 (1 & 2) 44-52.
- Nambuhewagw Dhammika Namal Jayawardhane, Sri Kanth Tiwari. Ayurvedic Herbo-Mineral Approach in Management of Hepatitis (Kamala). International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences, Volume 2, issue 2 (2013),24-31.
- Ashutosh Chauhan, Deepak Kumar Semwal, Satyendra Prasad Mishra, Ruchi Badoni Semwal. Ayurvedic research and methodology: Present status and future strategies. An International Quarterly Journal of Research in Ayurveda : Volume : 36 Issue : 4, 2015.
- Deepthi Viswaroopan et al. Undernutrition In Children: An Updated Review. International Journal Of Research IN, 8(suppl 2), 2017.
- S Kamalakar Puripanda, Mahesh raju B, Mallika KJ, Tripathy TB. Understanding The Concept Of Sankramika Dadru Kusta- A Case Study. International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research, August 2016, Volume 4 Issue 8 -81.
- Surendra K. Sharma, M. A. Sheela. Pharmacognostic evaluation of leaves of certain Phyllanthus species used as a botanical source of Bhumyamalaki in Ayurveda. Ayu. 2011 Apr-Jun; 32(2): 250–253, PMID: 22408311.
- Abbi Charu et al. Punarnava ( Boerhavia Diffusa) : A Promising Indigenous Herbal Drug . International Research Journal Of Pharmacy; 2013,4 (3).
- Pramod Kumar Mishra, Deepika Dwivedi, N.P. Rai. [link]. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2016; 4(5): 260-263.
- Kalpu N. Kotecha, B.K.Kotecha, Vinay J. Shukla, Pradipkumar Prajapati, B.Ravishankar. Acute toxicity study of Vasaguduchyadi Kwatha: A compound Ayurvedic formulation. Ayu. 2013 Jul-Sep; 34(3): 327–330, PMID: 24501533.
- Kalpu N Kotecha, BK Ashok, VJ Shukla, PK Prajapati, B.Ravishankar. Hepatoprotective Activity Of Vasaguduchyadi Kwatha- Acompound Herbal Fromulation Against Paracetamol Inducedhepatotoxicity In Albino Rats. Pharma Science Monitor 6(4), Oct-Dec 2015, 157-167.
- Santosh Pal, A Ramamurthy, Bidhan Mahajon. Arogyavardhini Vati: A theoritical analysis. Journal of Scientific and Innovative Research 2016; 5(6): 225-227.
- Kalpu N. Kotecha et al. Acute toxicity study of Vasaguduchyadi Kwatha: A compound Ayurvedic formulation. Ayu. 2013 Jul-Sep; 34(3): 327–330, PMID: 24501533.