What is Jock itch or dhobie itch?
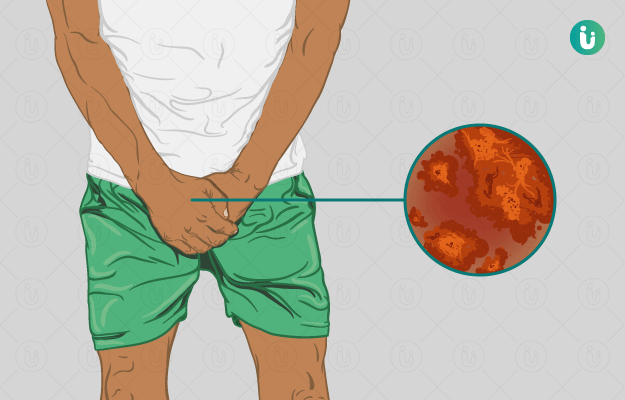
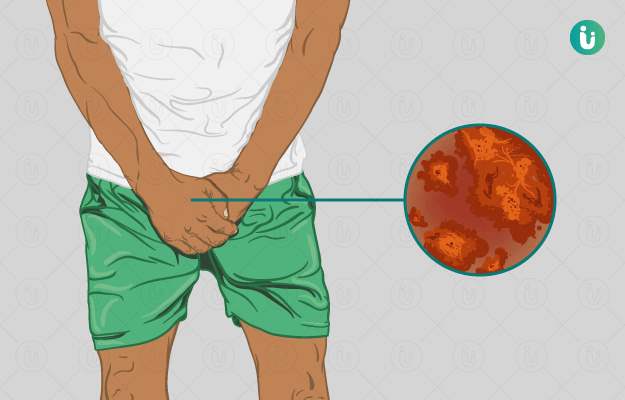
Jock itch or dhobie itch is a fungal infection of the skin around the groin area. It is also called ringworm or medically, Tinea cruris. It is a very common skin infection and affects the groin area superficially. It is not a life-threatening condition but may cause significant discomfort and social embarrassment.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Jock itch, also known as dhobi itch in tropical climates, affects the area around the groin. However, it may spread to the inner thighs, buttocks, and in some cases, to the abdomen. Genitals are generally not affected. It is more frequently seen in athletes or obese people. The following signs and symptoms may indicate Jock itch:
- Change in the colour of the affected skin, usually, a redness is seen in the affected area.
- A rash-like appearance, which is circular in shape. (Read more: Skin rash treatment)
- The borders of the lesion are sharply demarcated.
- There may be presence of normal looking skin within the concentric circles of the affected area
- The lesion will appear a bit raised
- Blisters may accompany the lesion
- Itching and discomfort are commonly seen
- Symptoms worsen on exercising
This is a recurring infection and if one has suffered from jock itch or dhobie itch in the past, they are likely to be affected in the future. Also, at times, the infection of the groin area is seen in combination with the infection of the feet.
What are its main causes?
It is a fungal infection, which is communicable. The fungi grow on skin surfaces that are moist and warm. Thus, wearing tight or wet undergarments may be a risk factor. Overweight people who have touching folds of skin are also at a greater risk. Jock itch or dhobie itch may spread through the use of infected towels, bedsheets, etc. Since it is highly contagious, it may also spread to other parts of your body through contact. The condition affects men more than women. The fungi that cause jock itch are Epidermophyton floccosum and Trichophyton rubrum.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
A diagnosis can be made using the patient’s medical history and examining the affected area. Still, a potassium hydroxide (KOH) slide may be prepared which can confirm the type of fungi in 4-6 weeks. As Tinea cruris is a mild infection, it can usually be treated with topical antifungals applied 2-3 times a day. The infection usually completely resolves in 3-4 weeks. Care must be taken to keep the area dry and maintain good hygiene practices.

 Doctors for Jock itch (Dhobie itch)
Doctors for Jock itch (Dhobie itch)  OTC Medicines for Jock itch (Dhobie itch)
OTC Medicines for Jock itch (Dhobie itch)
 Jock itch (Dhobie itch) articles
Jock itch (Dhobie itch) articles
 Home Remedies for Jock itch (Dhobie itch)
Home Remedies for Jock itch (Dhobie itch)






 Dr. Apratim Goel
Dr. Apratim Goel











