What is a kidney infection?
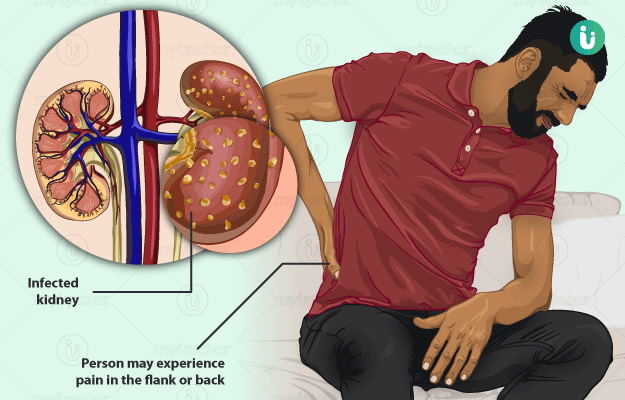
Kidney infection is the presence or invasion of the kidneys by bacteria, which begins in the urinary bladder and spreads to the kidneys. It is also referred to as pyelonephritis.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Kidney infections are common, and the following typical symptoms are observed:
- Pus or blood in urine.
- Burning sensation and pain while urinating.
- Foul-smelling cloudy urine.
- Frequent urination.
- Pain in the lower back and abdomen.
- High fever with chills.
- Upset stomach.
- Loss of appetite.
What are the main causes?
Kidney infections are typically caused by bacteria and rarely, occur after kidney surgery. The risk of infection is more in women than men, as the anus and the urethral opening are located closer to each other, making it easier for the bacteria to reach the bladder. Pregnant women are at an increased risk, as the baby puts pressure on the ureter and blocks the flow of the urine. The main causes of kidney infections are as follows:
- Kidney stone in the urinary tract.
- Enlarged prostate or its infection.
- A structural problem like a pinched urethra or ureters.
- Reflux, where urine backflows from the bladder to the kidneys.
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- Weakened immune system.
- Nerve damage in the bladder.
- Using a urinary catheter.
The commonest bacterium that causes kidney infections is E. coli.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Timely diagnosis and treatment of kidney infection are necessary, as it can be life-threatening if delayed.
- Urine examination to detect pus, blood and bacteria.
- Urine culture to know the type of bacteria.
- Ultrasound and CT scan to check for stones or structural abnormalities.
- Voiding cystourethrogram to rule out any blockages.
- DMSA (dimercaptosuccinic acid) scintigraphy to check the structure, morphology and function of the urinary system.
The following treatment regimen is suggested for a kidney infection:
- Oral antibiotics to control the bacterial infection and antipyretics to control fever. In case of severe infection, hospitalisation is necessary for the administration of intravenous (into the vein) antibiotics and fluids.
- For frequent infections, it is advisable to consult a urologist to find the underlying cause.
- Surgery may be suggested to correct a structural abnormality.
You can avoid kidney infections by following some healthy habits like drinking lots of water, avoiding deodorants on genitals, wiping from front to back after each bowel emptying and urinating as soon as you have the urge. In case the symptoms arise, it is best to consult your doctor promptly to avoid complications.

 Doctors for Kidney Infection
Doctors for Kidney Infection  OTC Medicines for Kidney Infection
OTC Medicines for Kidney Infection
 Kidney Infection articles
Kidney Infection articles
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Kidney Infection
Ayurvedic Treatment of Kidney Infection
 Diet for Kidney Infection
Diet for Kidney Infection






 Editorial Team
Editorial Team












