What is Liver Cirrhosis?
Liver cirrhosis is a condition where the liver gets scarred due to long-term liver damage. The liver shrinks and hardens. Therefore, it is not able to function properly and may ultimately cause liver failure. The condition also impacts the blood supply to the liver and creates a condition termed as portal hypertension.
Cirrhosis is a progressive disease and replaces the healthy tissue with fibrous bands. In response to natural defences, the liver nodules get ready to fight the trigger and get scarred and cover the whole peripheral surface of the liver. These scar tissues overtake the blood supply to the liver and may steer towards total liver failure or death.

 Doctors for Liver Cirrhosis
Doctors for Liver Cirrhosis  OTC Medicines for Liver Cirrhosis
OTC Medicines for Liver Cirrhosis
 Liver Cirrhosis articles
Liver Cirrhosis articles News for Liver Cirrhosis
News for Liver Cirrhosis
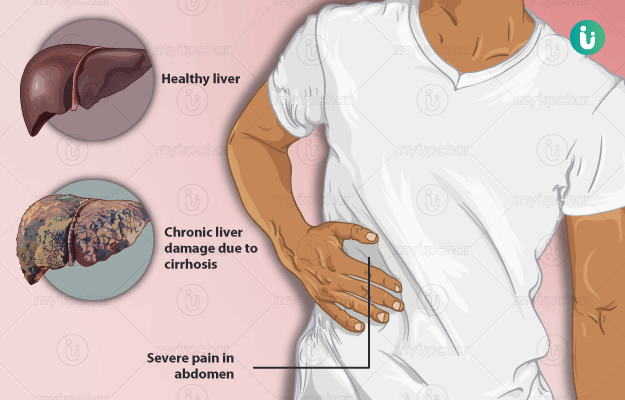
 Diet for Liver Cirrhosis
Diet for Liver Cirrhosis
 Home Remedies for Liver Cirrhosis
Home Remedies for Liver Cirrhosis

















 Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Dt. Akanksha Mishra











