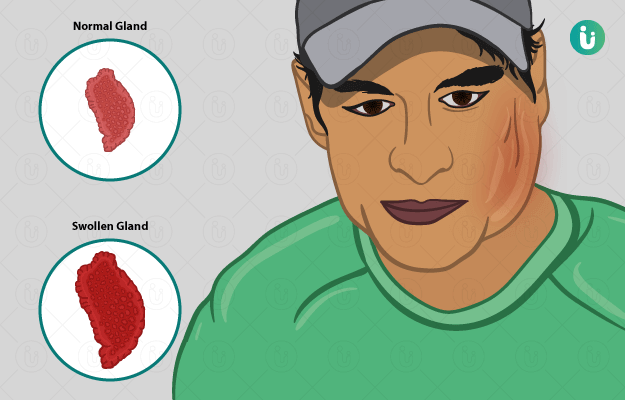
What is Mumps?
Mumps is a communicable viral infection that is common among children. It is a condition affecting the salivary glands present at the side of the face under the ears causing painful swelling.
What are the main signs and symptoms?
The symptoms develop 14 to 25 days after the infection with the mumps virus. A few symptoms are mentioned below:
- Swollen, tender jaw
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- Swelling in the jaw region
- Dry mouth
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Weakness
- Testicular pain
- Confusion
- Irritability
What are the main causes?
Mumps is caused by a virus that belongs to the family of paramyxoviruses. The virus enters through air droplets via the nose or mouth. Thus, spread occurs via air. It is important for the infected person to cover their mouth and nose while sneezing and coughing to prevent spread to other people.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis
- History of vaccination against mumps is noted
- Physical examination especially of the throat and ears
- Blood test to detect the virus and antibodies against the virus
- Oral/buccal swab for detecting the virus
- Urine test
Treatment
Antibiotics are ineffective as it is caused by a virus. The treatment is focused on relieving symptoms until the body’s immunity fights the virus. The steps to ease discomfort are as follows:
- Isolation from others to prevent the spread of infection
- Paracetamol for fever
- Ibuprofen for swelling
- Warm or cold compress for swelling
- Avoidance of food that requires chewing; soft food is preferable
- Plenty of fluid intake
Prevention
The Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) vaccine is recommended. According to the CDC recommendations, all children should receive two doses of the MMR vaccine: the first dose at 15 months of age and the second dose at 4-6 years of age. It is given 28 days after birth because antibodies transferred from the mother to the baby can provide protection against certain diseases.

 Doctors for Mumps
Doctors for Mumps  OTC Medicines for Mumps
OTC Medicines for Mumps