Summary
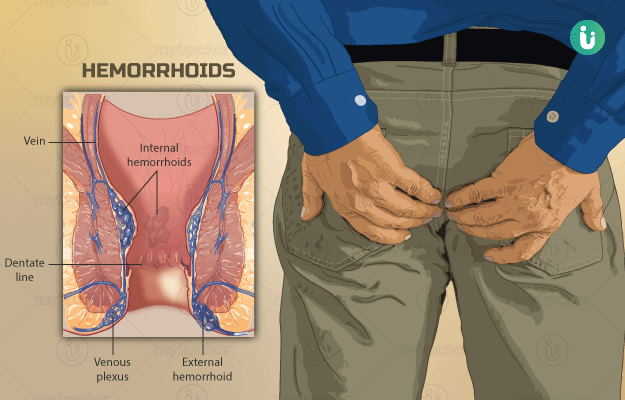
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen and distended veins in the lower rectum and the anus. Simply put, they are ‘varicose veins of the anus and the rectum’. Piles can be internal (develop inside the rectum) or external (under the skin around the anus).
Hemorrhoids can be caused due to several reasons, although the exact cause may often be unknown. They could be the result of overstraining during bowel movements or due to increased pressure on the rectal veins during pregnancy. The symptoms vary from mild itching and discomfort to bleeding and prolapse depending on the severity of piles. The treatment depends on the symptoms and the severity of piles. Treatment could be as simple as incorporating some lifestyle changes such as consuming fibrous foods to use of topical pain relievers or even surgery. The complications of piles are usually rare. If left untreated, piles or hemorrhoids can become chronic and inflamed and be prone to thrombosis (clot formation) and ulceration.
Hemorrhoids are usually not dangerous and need to be treated only if they are bothersome. Those occurring during pregnancy usually improve on their own after delivery. For hemorrhoids caused due to constipation, important changes to diet and lifestyle ensure a good prognosis. Surgical correction of piles also yields satisfactory results.



 Doctors for Piles
Doctors for Piles  OTC Medicines for Piles
OTC Medicines for Piles
 Lab tests for Piles
Lab tests for Piles Piles articles
Piles articles
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Piles
Ayurvedic Treatment of Piles
 First Aid for Piles
First Aid for Piles
 Home Remedies for Piles
Home Remedies for Piles
 Homeopathic Treatment of Piles
Homeopathic Treatment of Piles




































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team
















