What is spondylosis?
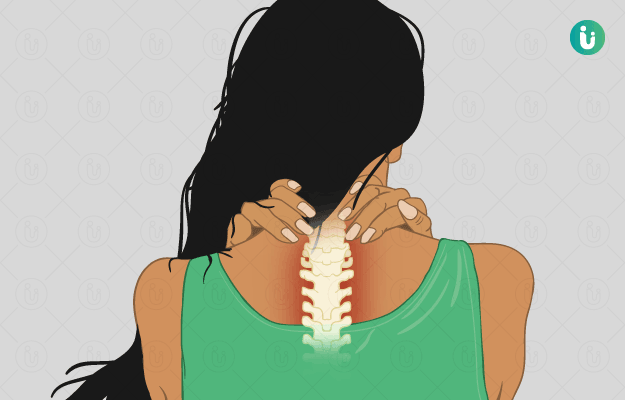
Spondylosis is a disease that causes changes in the bones of the spine as well as the cartilage and discs. Over time, spondylosis leads to breaking apart of the spine tissues (discs) that cushion the bones of the spine (vertebrae). Spondylosis ultimately can lead to stiffening of the spine or osteoarthritis. Typically it affects the vertebrae in the neck and the lower back i.e., the lumbar region.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The main signs and symptoms of spondylosis based on the type of spondylosis are:
Lumbar spondylosis
- Stiffness and back pain in the mornings
- Pain after sitting for a long time
- Pain with movements like bending and lifting
Cervical spondylosis
- A headache in the back of the head
- Weakness and numbness in the legs and arms
- Stiffness in the neck
- Feeling off balance
- Neck pain that might spread downwards to the shoulder
- Abnormal sensations in the legs or shoulders
- Difficulty in controlling the bladder and bowel
Thoracic spondylosis
- Pain in the middle back while bending backwards
- Pain when moving the spine forwards and backwards
What are the main causes?
The main causes of spondylosis are:
- Ageing
- A neck injury in the past e.g., a whiplash injury in a motor vehicle accident
- Severe arthritis
- Spine injury in the past
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Spondylosis is diagnosed using the following methods:
- Detailed history and physical examination for checking the flexibility of the back and neck
- Assessing the walking function
- Testing the strength and reflexes of the legs, arms and hands
- An X-ray, MRI or a CT scan may be ordered, if needed
Spondylosis is treated using the following methods:
- Over-the-counter medications for pain relief
- A brace or a soft collar
- Exercises to strengthen muscles of the region
- Physical therapy
- Injection of painkillers in case of severe pain
- Surgery in severe cases that do not respond to oral or injectable painkillers or where daily routine is significantly disturbed.

 Doctors for Spondylosis
Doctors for Spondylosis  OTC Medicines for Spondylosis
OTC Medicines for Spondylosis