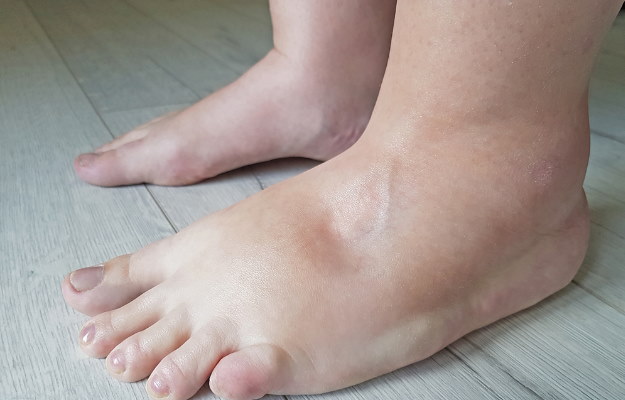
Swelling or oedema occurs due to fluid accumulation in tissues. It makes the organ look enlarged and the person often experiences tenderness and redness in the affected area. Swelling that affects the entire body is called generalised swelling, and swelling of a part of the body is called localised swelling. Swelling can be caused by various underlying conditions such as burns, nephrotic syndrome, nutritional deficiency, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, liver failure from liver cirrhosis, pregnancy, thyroid disease, inflammation, allergies, lower than normal level of albumin in the blood (hypoalbuminemia), excess salt or sodium and use of certain drugs. Some drugs that may lead to swelling include corticosteroids and medicines used for the treatment of heart disease, high blood pressure and diabetes. Doctors also classify swelling as pitting and non-pitting. Pitting oedema is when a dent occurs in the swollen area it is pressed for about 5 seconds. This dent slowly fills back in. Non-pitting oedema does not create a dent on pressing.
Homeopathy describes several remedies for the management of swelling. Some of the remedies are terebinthiniae oleum, strophanthus hispidus, lachesis mutus, kalium nitricum, kalium iodatum, helleborus niger, fluoricum acidum, crataegus oxyacantha, convallaria majalis, arsenicum album, apocynum cannabinum, apis mellifica, adonis vernalis and aceticum acidum.
A homeopathic doctor considers the disease symptoms along with the tendency of a person to suffer from certain conditions (Called miasm in homeopathy) before choosing a unique remedy for them. So, a homeopathic medicine that works for one person may not work for another. Additionally, homeopathic medicines are given on the basis of the principle like cures like, which means that any substance that causes certain symptoms in large doses in a healthy person, may heal the same symptoms when given in diluted doses to a sick person.
- Homeopathic medicines for swelling
- Dietary and lifestyle changes for a patient with swelling as per homeopathy
- How effective are homeopathic medicines and treatments for swelling
- Side effects and risks of homeopathic medicine and treatments for swelling
- Takeaway
Homeopathic medicines for swelling
- Terebinthiniae Oleum
Common Name: Turpentine
Symptoms: It is an effective remedy for the treatment of inflammation in kidneys, bleeding mucous membrane (makes the inner lining of some organs like the gut and nose) and oedema. Other symptoms that can be treated using this medicine are:
- Strophanthus Hispidus
Common Name: Kombe-seed
Symptoms: Kombe-seed is useful in the management of many symptoms, some of which are listed below:- Weakness of heart muscles
- Swelling and fluid accumulation in lungs
- Swelling of arms and legs
- Skin rashes
- Lachesis Mutus
Common Name: Bushmaster
Symptoms: Lachesis Mutus can help treat the following symptoms:- Swelling, boils and ulcers of the skin
- Difficulty breathing
- Pain in the lower leg
- Mottled, puffed and swollen face
- Allergic asthma
- Sense of suffocation on lying down
Symptoms aggravate on sleeping and after taking a warm bath. Symptoms improve on using warm applications on the affected area.
- Kalium Nitricum
Common Name: Nitrate of potassium
Symptoms: Kalium Nitricum is commonly used to treat asthma and sudden swelling all over the body. It can also help manage the symptoms listed below:- A feeling as if the nose (especially the right nostril) is swollen from inside
- Severe backache
- Burning sensation and pain in the chest
- Swelling in extremities
All the complaints worsen in the morning and afternoon. The person feels better after taking a few sips of water.
- Kalium Iodatum
Common Name: Iodide of potassium
Symptoms: Iodide of potassium is mainly used to treat swelling of the glands. It can also help in the management of the following symptoms:- Small boils on the skin
- Hives
- Swelling of the cranium (part of skull that covers the head)
Symptoms worsen with warmth and in damp weather. Symptoms get better on moving about in open air.
- Helleborus Niger
Common Name: Snow-rose
Symptoms: It is a useful remedy for treating muscular weakness that is accompanied by oedema. It can also be used to treat the following symptoms:- Sudden fluctuant (firm) swelling of the skin
- Itching accompanied by oedema of the skin
- Swelling and pain in the abdomen
- Painful and heavy limbs
Symptoms start to worsen in the evening and stay aggravated until morning, they also worsen on keeping the affected area uncovered.
- Fluoricum Acidum
Common Name: Hydrofluoric acid
Symptoms: This remedy increases the frequency of urination in patients with dropsy. It is also useful in treating the following symptoms:- Swelling of the scrotum
- Varicose veins
- Swelling in limbs
All complaints aggravate in warm climate and on consuming warm drinks. The symptoms get better on walking and with cold.
- Crataegus Oxyacantha
Common Name: Hawthorn berries
Symptoms: This medicine primarily acts on the heart. It treats oedema and the following associated symptoms:- Swelling in the heart
- Eruptions on the skin
- Diabetes
- Difficulty in breathing
- Insomnia
All the symptoms worsen in a warm environment and improve on taking rest or taking in some fresh air.
- Convallaria Majalis
Common Name: Lily of the valley
Symptoms: Lily of the valley is effective in the treatment of generalised swelling. It can also help in the management of:- Irritability
- Pain in the lower back region
- A bubbling feeling in the chest along with pain on deep breathing
- Soreness in the uterine area
- Inflammation of the innermost layer of heart tissue, the endocardium
- Fever, wherein the person feels thirsty and gets a headache along with chills
Symptoms worsen in a warm environment and get better on going out in open air.
- Arsenicum Album
Common Name: Arsenious acid
Symptoms: Arsenicum album is primarily used to treat burning pains and restlessness. It can also help in the treatment of:- Swelling and external inflammation around the eyes
- Swollen face that looks pale and yellow
- Ulceration along with stitching and burning pains in the tongue
- Swelling and burning in throat
- Itching, burning, swelling and eruptions on the skin
- Dry, rough and scaly skin
Symptoms worsen in rainy and cold weather, post-midnight and after consumption of cold food and drinks. Symptoms get better from warmth, keeping one's head in an elevated position and drinking warm beverages.
- Apocynum Cannabinum
Common Name: Indian hemp
Symptoms: Apocynum Cannabinum is used to treat oedema, fluid accumulation in the belly, and irritability of the stomach along with increased thirst. It can also treat the following symptoms:- Swelling of heart muscles
- Swelling and inflammation in kidneys
- Restlessness and reduced sleep
- Soreness and discomfort in anus that worsens after meals
The symptoms worsen in cold climate, on consuming cold drinks and keeping the affected region uncovered.
- Apis Mellifica
Common Name: The honey-bee
Symptoms: Apis Mellifica is best suited for individuals who have swelling in various parts of the body. It can treat inflammatory conditions of the kidney and fluid accumulation in different parts. Following are some other symptoms that can be managed using apis mellifica:- Swollen, inflamed and burning eyelids
- Redness and swelling of nose
- Swelling of throat due to tonsillitis
- Stinging pains along with constriction of throat
- Swelling of skin due to bites and allergies
- Sudden generalised swelling
- Swollen and stiff feet
Symptoms are aggravated late in the afternoon, after sleeping and in closed rooms; they worsen due to heat and warmth, and on touching or putting pressure on the affected area. Symptoms get better if the affected area is left uncovered, when the person goes out in the open air or takes a bath with cold water.
- Adonis Vernalis
Common Name: Pheasant's eye
Symptoms: This remedy is primarily used to treat oedema of the heart muscle. Few other symptoms that can be treated using this medicine are:- Swelling in hands and legs
- Stiffness and pain in the extremities
- Heaviness in the stomach
- Presence of the protein albumin in urine
- Restlessness
- Aceticum Acidum
Common Name: Glacial acetic acid
Symptoms: Glacial acetic acid is mainly used to treat swelling and weakness caused due to anaemia. It can also treat symptoms like:
Dietary and lifestyle changes for a patient with swelling as per homeopathy
Homeopathic remedies are prepared in diluted amounts, so, their action gets easily affected by various factors, especially medicinal or strong-smelling substances. To get optimal results from homeopathic treatment, the following modifications should be made in the diet and lifestyle of the patient:
Do’s:
- Eat healthy and nutritious food as advised by the doctor.
- Stay active and perform regular exercise.
Don’ts:
- Do not drink caffeinated beverages or drinks that have a strong odour.
- Do not stay in marshy or damp areas.
- Do not consume any food and drink that possess a medicinal quality. This includes some meats and dishes that contain medicinal herbs and roots.
- Avoid excess of salt and sugar.
- Avoid any emotion that may cause physical or mental exertion.
How effective are homeopathic medicines and treatments for swelling
Homeopathic medicines for swelling are prescribed on the basis of the underlying cause of the condition and the physical and mental make-up of the individual. When taken under the guidance of a doctor, these remedies can effectively help treat swelling and its associated symptoms.
There have been a few studies that indicate the positive effect of homeopathic remedies in swelling. For example, a case study published by the British Homeopathic Association showed the efficiency of homeopathic medicines in the treatment of asthma, eczema and severe inflammatory condition of the eye. As per the study, the 18-year-old male was on corticosteroids and cyclosporine therapy for several months but had experienced a flare-up in his eyes every few weeks. He was experiencing skin problems for the last 18 months with itching behind his ears and eyes and his symptoms aggravated during summer. The boy also had swelling in his face and eyelids and puffiness in his lips at the age of 2 years. Additionally, he had a history of corneal surgery at the age of 7 years and was prescribed steroid eye drops after this surgery until he was 14 years of age.
The boy was given natrium muriaticum at different potencies and doses daily. Within two months, he experienced complete relief from the swelling.
Side effects and risks of homeopathic medicine and treatments for swelling
Homeopathic remedies are being used for over two hundred years for their effectiveness in numerous conditions. These medicines are made from natural products such as herbs, animal or mineral products. These products are diluted extensively before using them as medicine. The dilution removes all the side effects of these products, but they retain their therapeutic properties.
Homeopathic remedies are considered to be safe and effective in children, pregnant women and elderly individuals. However, these remedies should only be taken after consulting a qualified doctor.
A doctor will guide you to the right medicine along with suggestions for appropriate diet and lifestyle that will ensure a speedy recovery.
Takeaway
Swelling is a common symptom associated with many different conditions. Depending on the cause, it can affect a part of the body or the whole body. Although many conventional treatments are available today to treat swelling, a lot of people prefer natural remedies. Homeopathic remedies are safe in a wide range of the population. A homeopathic doctor prescribes a remedy on the basis of the clinical status of the individual and their miasms. These medicines, along with appropriate dietary and lifestyle modifications can effectively help get rid of swelling and its associated symptoms.
Find Homeopathic Doctor in cities
References
- MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. [Internet] US National Library of Medicine; Swelling
- Oscar E. Boericke. Repertory. Médi-T; [lnternet]
- The European Comittee for Homeopathy. Benefits of Homeopathy. Belgium; [Internet]
- British Homeopathic Association. Allergies. London; [Internet]
- Wenda Brewster O’Reilly. Organon of the Medical art by Wenda Brewster O’Reilly . B jain; New Delhi
- Michigan Medicine: University of Michigan [internet]; Swelling