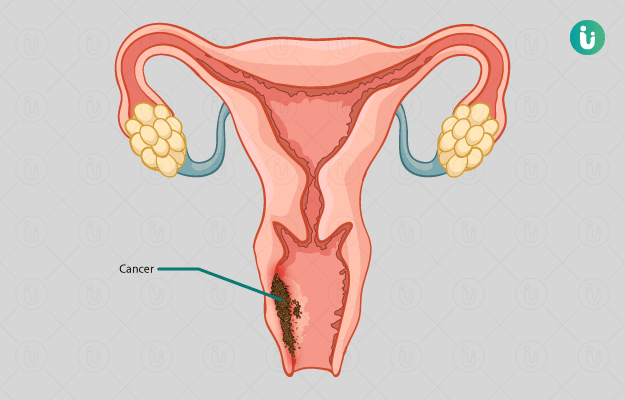
What is vaginal cancer?
A rare type of cancer found in the female reproductive system, vaginal cancer accounts for less than 0.2% of all cancers. Usually, it is seen in women above 60 years of age when sexual activity is ceased. This cancer starts in the vagina when the normal healthy cells undergo changes and grow uncontrollably, to forms a tumour. The most common type is the squamous cell carcinoma. The one that starts in the glands is known as adenocarcinoma. The connective carcinoma is extremely rare and is known as sarcoma.
What are the main signs and symptoms?
It is uncommon to have early symptoms, however, signs and symptoms that may be noticed by the individual are:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding during or after menopause
- Pain while urinating
- Pain while intercourse
- Pain in pelvic region
- Lump in vagina
- Vaginal discharge offensive or blood stained
- Vaginal itch
- Pain in back
- Pain in legs
- Swelling in legs
- Constipation
What are the main causes?
The exact cause of the vaginal cancer is unknown, but there are risk factors which can trigger the cancer growth, such as
- Age: the risk increases as age advances, it usually occurs in women above 60 yrs.
- Human Papilloma Virus (HPV infection)
- Diethylstillbestoral (DES): a drug used to prevent miscarriage in the first trimester.
- Previous radiation therapy
- Cervical cancer
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Smoking
- Alcohol
How it is diagnosed and treated?
When there are any of the above symptoms or causes are present, then it’s better to consult a doctor the earliest. The doctor will ask for a complete medical history and will discuss the symptoms and conduct a physical examination which includes pelvic examination and PAP smear test. Other tests that might be done are:
- Colposcopy: a sample of tissue is collected from the vagina to examine under the microscope.
- Biopsy: when other tests are indicative of cancer, biopsy is the only definitive test which confirms the diagnosis.
- Chest X-ray: this is done to see if cancer has spread to the lungs.
- Ultrasound sonography (USG) of pelvis and abdomen
- Computed tomography (CT scan)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Positron emission tomography (PET scan): it is done to detect malignant tumour cells in the body with the help of radioactive sugars.
- Cystoscopy: to look inside the bladder and the urethra
- Ureteroscopy: to look inside the ureters
- Proctoscopy: to look inside the rectum
There are three standard treatments available for vaginal cancer.
Surgery:
- Laser surgery: tumor is cut with help of laser beam
- Wide local excision: cancer lesion along with some healthy tissue surrounding is also cut.
- Vaginectomy: vagina is removed.
- Total hysterectomy: in this uterus and cervix both are removed.
Radiation therapy: high energy X rays or other radioactive substances are used.
Chemotherapy: drugs are used to stop the growth of cancer by killing the cancer cells, or stop them from dividing.
Most of the treatments are have side effects such as various pains and other symptoms uneasy feelings, nausea, appetite loss, diarrhoea, vomiting, hair loss, depression.

 Doctors for Vaginal Cancer
Doctors for Vaginal Cancer