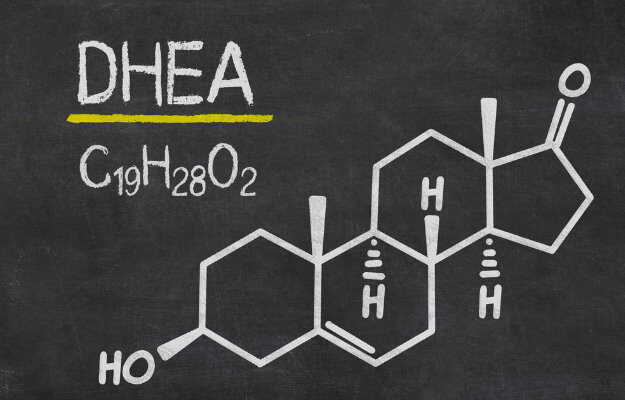
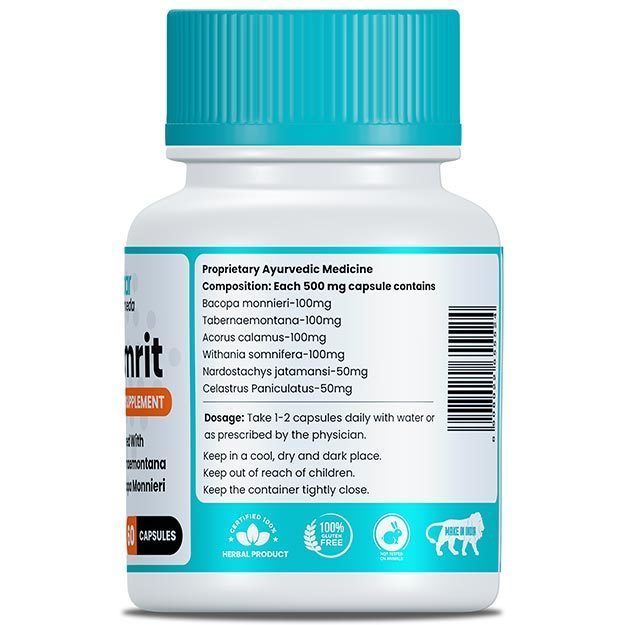
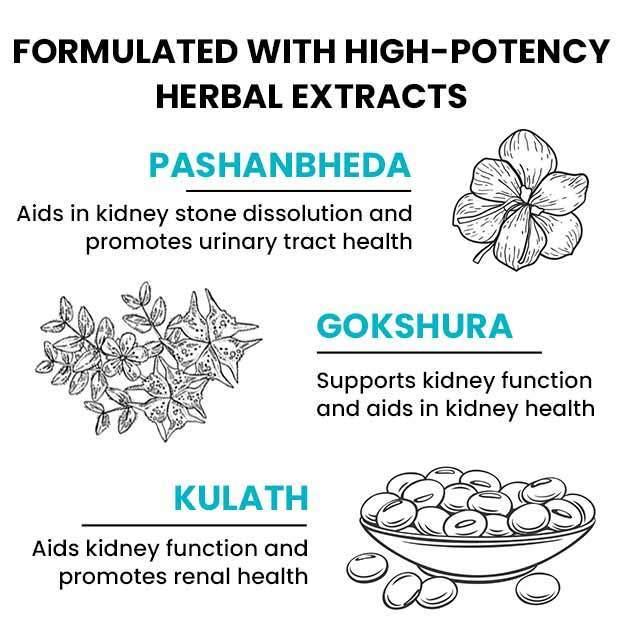
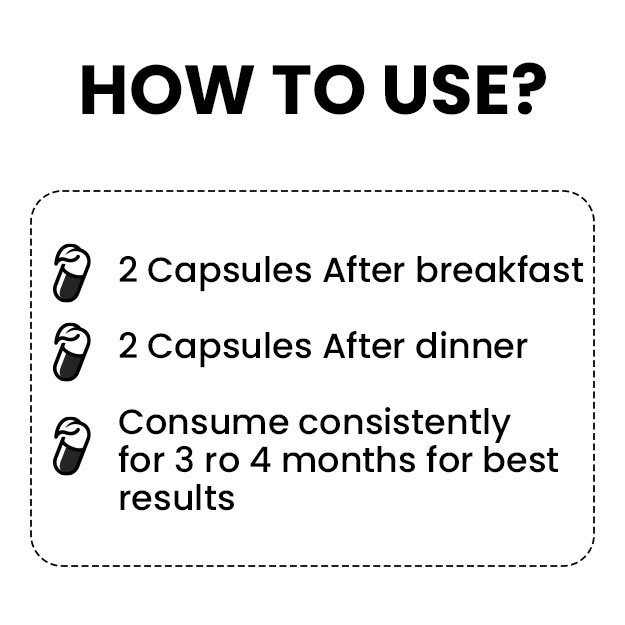
While DHEA offers some health benefits, its prolonged use can have serious drawbacks. Here are some potential risks and precautions:
Increased Risk of Bleeding: DHEA can slow down blood clotting, raising the risk of excessive bleeding. Taking it alongside foods like garlic, ginger, ginkgo, and Panax ginseng may further increase this risk.
Hormonal Imbalances: DHEA can cause oily skin, acne, and excessive hair growth in women (hirsutism).
Mental Health Concerns: This supplement may worsen symptoms of mental disorders.
Impact on Diabetes: DHEA can interfere with insulin function, making it unsuitable for diabetic patients. Those taking DHEA should monitor their blood sugar levels closely.
Not Recommended for Mood Disorders: Individuals with mood-related conditions should avoid DHEA.
Worsening of PCOS Symptoms: Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may experience worsening symptoms with DHEA intake.
Liver Health Risks: Long-term use may negatively affect liver function.
Not Safe for Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: Women who are pregnant or nursing should avoid DHEA.
Effect on Cholesterol Levels: DHEA may reduce levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL or "good" cholesterol).
Increased Cancer Risk: Long-term use can elevate the risk of hormone-sensitive cancers, including breast, ovarian, and prostate cancer.
Heart Disease Concerns: Individuals with high cholesterol or heart conditions should avoid DHEA due to its potential impact on blood circulation.
(Read more – Hormone replacement therapy for menopause)