The menstrual cycle is a very important part of woman’s reproductive health. It’s a complex biological process driven by hormones that leads to regular bleeding from vagina , known as periods. A common misconception is that the menstrual cycle refers only to the days when a woman is bleeding. But , the cycle is much more than that—it includes four distinct stages, each preparing the body for a possible pregnancy.
Read more – (What does your period say about your health?)
- What is the Menstrual Cycle?
- Stages of the Menstrual Cycle
- Causes Of Changes In Menstrual Cycle
- Benefits Of Tracking Periods
- Summary
What is the Menstrual Cycle?
The word menstruation comes from the Latin word mensis, meaning month. Menstrual cycle or reproductive cycle, is a series of changes a woman’s body goes through each month to prepare for pregnancy. On average, it lasts between 21 to 35 days, although the length can vary from woman to woman. This cycle is regulated by various hormones that rise and fall at different stages. These hormonal changes don’t just affect physical health but also impact a woman’s mood, energy levels, emotions, and even sex drive.
.Each month, an egg is developed and released from the ovaries. Meanwhile, the uterus builds a thick, blood-rich lining that would serve as a cushion or “bed” for a fertilized egg in case pregnancy occurs. That’s why during pregnancy, periods stops—the lining is retained to support the growing baby. However, if pregnancy doesn’t occur, this lining sheds and exits the body in the form of menstrual blood.
Read more – (Irregular periods)
Stages of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is divided into four main phases:
- Menstrual Phase
- Follicular Phase
- Ovulation Phase
- Luteal Phase
Each phase varies in length and may shift slightly over time. Let’s take a closer look at each stage:
Menstrual Phase (Period Phase)
This is the first phase of the menstrual cycle, beginning when the egg from the previous cycle is not fertilized and estrogen and progesterone levels drop, signaling the body to shed the blood lining.
The result is menstrual bleeding, period blood also contains mucus and tissue from the uterus. During this phase, many women experience common symptoms such as:
- Abdominal cramps
- Breast tenderness
- Bloating
- Mood swings
- Irritability
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Lower back pain
Read more – (Menarche (First Period))
Follicular Phase
The follicular phase begins on the first day of your period, overlapping with the menstrual phase, and continues until ovulation. It starts when the hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). FSH stimulates the ovaries to produce 5 to 20 small sacs called follicles, each containing an immature egg.
Out of these, the healthiest follicle matures into a fully developed egg, while the others are absorbed by the body itself . The mature follicle releases estrogen, which helps thicken the uterine lining to create a nutrient-rich environment in case of pregnancy.
The follicular phase typically lasts around 16 days, but it can range from 11 to 27 days, depending on the individual.
Ovulation Phase
As estrogen levels rise during the follicular phase, the pituitary gland is triggered to release luteinizing hormone (LH) , which causes ovulation. During this phase, the ovary releases a mature egg that travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus, where it may be fertilized by sperm. This is the most fertile stage of the cycle. Signs of ovulation may include:
- Changes in body temperature
- Thick, white cervical discharge
If your cycle is 28 days long, ovulation typically occurs around day 14 and lasts about 24 hours. If the egg is not fertilized within this window, it ends . However, sperm can survive in the female body for up to 5 days, meaning you can still conceive even if intercourse occurs several days before ovulation.
Read more – (Light periods)
Luteal Phase
After ovulation, the follicle that released the egg transforms into the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone and a small amount of estrogen also . These hormones maintain the thickened uterine lining to support a possible pregnancy.
If fertilization occurs, the body produces human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) , the hormone detected by pregnancy tests which helps sustain the corpus luteum and uterine lining.
If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum breaks down, leading to a drop in estrogen and progesterone levels. This hormonal decline triggers menstruation, and the uterine lining is shed. The luteal phase lasts about 11 to 17 days. If pregnancy does not happen, you may experience PMS symptoms, such as:
- Bloating
- Breast tenderness or swelling
- Mood swings
- Headaches
- Weight gain
- Changes in libido
- Appetite changes
- Trouble sleeping
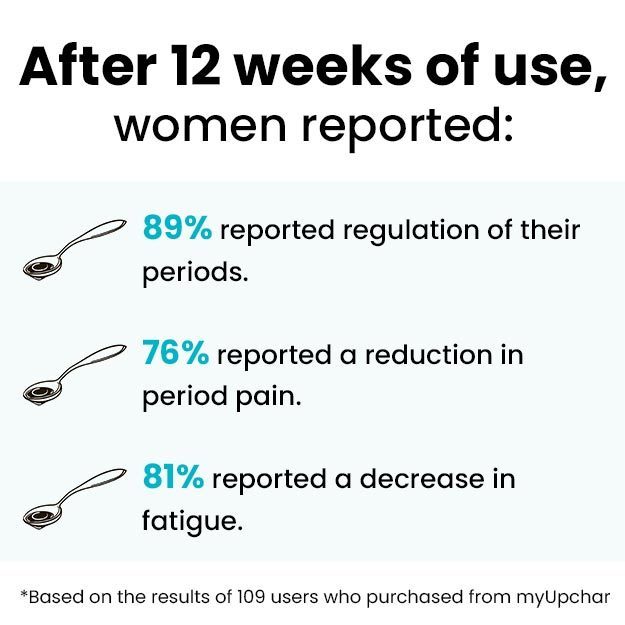
Every menstrual cycle is different. Some women have their period at the same time every month. Some women bleed more heavily or for longer days than other women. One way to find out the problem with your menstrual cycle is to track your periods every month .
Read more - (2 periods in one month)
Causes Of Changes In Menstrual Cycle
- Contraception - Taking the contraceptive pill can make your period longer or shorter.
- Pregnancy - Your periods should stop during pregnancy. Missing a period is the most obvious sign that you are pregnant.
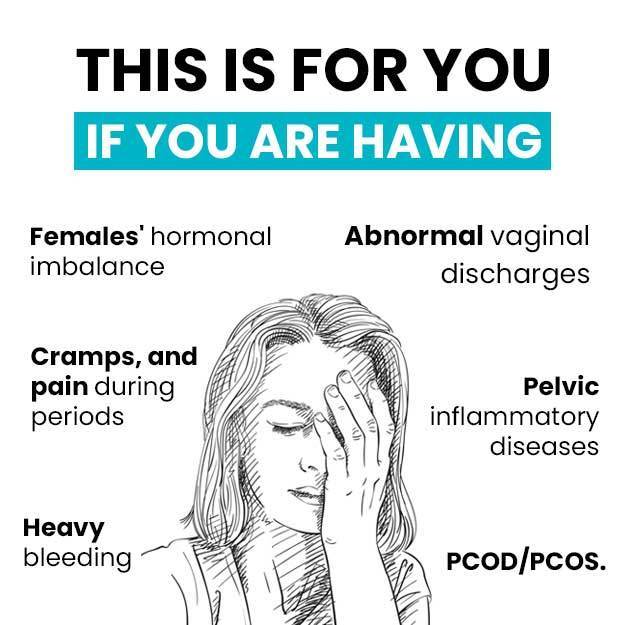
- Polycystic ovary syndrome - This hormonal imbalance prevents eggs from developing normally in the ovaries. PCOS causes menstrual cycles to become irregular and periods may not occur.
- Uterine fibroids - These noncancerous growths in your uterus can make your periods last longer than normal and cause heavy bleeding.
If you have missed periods, stopped completely, have irregular periods, bleed for more than 7 days, or have these or other problems with your menstrual cycle or periods, talk to your doctor.
Read more - (How late can your period be - myUpchar)
Benefits Of Tracking Periods
Tracking your periods can be beneficial for your reproductive health. There are so many benefits to tracking your menstrual cycle.
- Tracking your cycle helps you know when your next period is coming.
- Periods can tell a lot about health. By keeping track, we can easily know if there is any change that needs attention.
- If you are thinking about starting a family someday or want to avoid pregnancy, tracking your menstrual cycle can help you identify your ovulation days.
Read more - (What to do when periods are late?)