What is bronchitis?
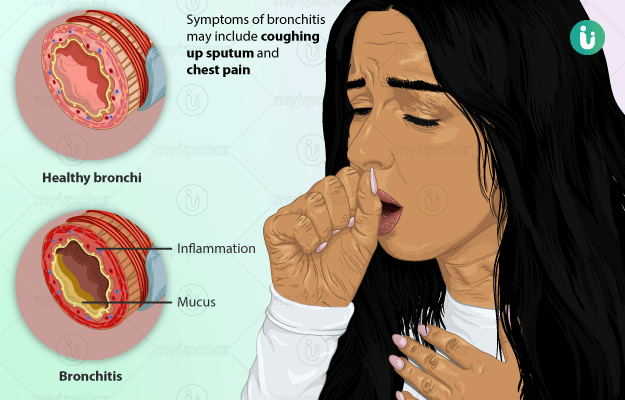
Bronchitis is a common lung condition wherein the lining of the bronchial tubes is inflamed. These tubes carry air into and out of the lungs, and their inflammation leads to difficulty in breathing due to narrowing of the airways. Cough in bronchitis is typically associated with the production of thick mucus. Bronchitis may either be acute or chronic.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Symptoms of bronchitis differ based on the stage of the condition. While certain symptoms remain common to acute and chronic bronchitis, some specific symptoms can be noted in the chronic stage.
Generalised symptoms:
- Chest tightness and shortness of breath
- Mild fever and chills
- Cough with mucus which may be clear, greenish or pale yellow, and may sometimes have streaks of blood
Acute bronchitis:
Most symptoms usually improve within a week, although the cough may last longer
Chronic bronchitis:
- Recurring bouts of cough
- Cough may be mild or may worsen
- Lasts for at least three months
What are the main causes of bronchitis?
Common viruses that cause cold and flu, like influenza virus, are responsible for bronchitis as well. However, chronic bronchitis can be the result of gastric reflux, exposure to lung irritants and chemicals at home or at the workplace, lowered immunity or cigarette smoking.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Bronchitis may be difficult to differentiate from a common cold, especially in the initial stages. Doctors usually use the following tests to diagnose the condition:
- Testing of sputum for allergies or signs of other ailments
- Chest X-ray to rule out pneumonia or other problems that may explain the cough, especially in smokers
- Pulmonary function tests to assess the lung capacity and look for signs of emphysema and asthma
Since most cases of acute bronchitis are caused by viruses, antibiotics are not prescribed. Most often, the disease resolves on its own in a couple of days. However, doctors may prescribe cough syrups to help ensure sound sleep and medications to reduce inflammation and widen the narrowed airways. Medications may also be given in case of asthma or other lung diseases. Breathing exercises, oxygen therapy, quitting smoking, increased intake of fluids, and steam inhalation are other important measures that can help relieve symptoms Precautions taken include:
- Wearing a mask when outdoors
- Using a humidifier indoors
- Staying away from pollutants and irritants
- Taking the flu vaccine to prevent recurrence
(Consult a doctor with online treatment app)

 Doctors for Bronchitis
Doctors for Bronchitis  OTC Medicines for Bronchitis
OTC Medicines for Bronchitis
 Bronchitis articles
Bronchitis articles News for Bronchitis
News for Bronchitis
 Diet for Bronchitis
Diet for Bronchitis
 Home Remedies for Bronchitis
Home Remedies for Bronchitis








 Editorial Team
Editorial Team

 Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Dt. Akanksha Mishra











