What is hepatitis?
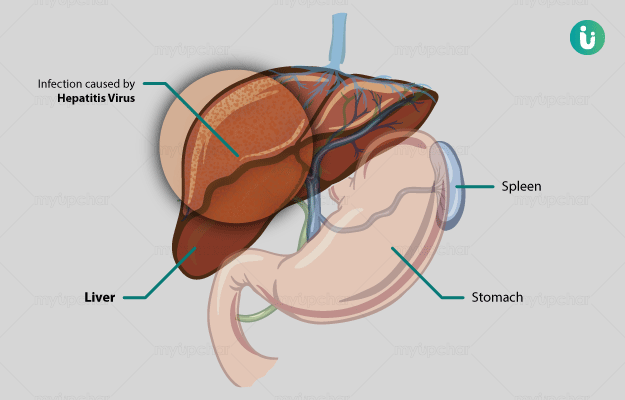
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the largest organ of the body, the liver. The liver is a vital organ which helps in digesting food, storing energy and removing toxins from the body. Acute hepatitis can last for up to 6 weeks, while chronic hepatitis may persist for a lifetime. There are several kinds of hepatitis, including:
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- Autoimmune hepatitis
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The main symptoms of hepatitis include:
- Muscle pain
- Pain in the joints (Read more: Joint pain treatment)
- Fever
- Headache
- Chronic fatigue
- Jaundice
- Depression
- Feeling unwell and lethargic
- Loss of appetite
- Repeated stomach pains
- Nausea
What are its main causes?
Hepatitis can occur due to a wide number of causes ranging from genetic to viral infections.
- Viral infection with hepatitis A, B, C, D or E viruses
- Alcohol consumption
- Autoimmune diseases due to genetic or environmental factors
- Metabolic diseases like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis due to excess fat accumulation on liver
- Excessive intake of pain-relief and fever-reducing medications
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Hepatitis is diagnosed using blood tests and liver biopsy (analysis of a tissue sample taken from the liver). Other tests may be performed to detect the presence of antibodies in the blood. Blood tests are specific for each kind of hepatitis.
Acute hepatitis is mostly eased with the help of bed rest and medications. Abstaining from alcohol and fat-rich diets will help in resolving the symptoms faster. In extreme cases, where much damage has been caused to the liver leading to liver cirrhosis or liver failure, liver transplant may be required.
It is important to note that viral hepatitis B, C are diseases which can spread through contact with infected bodily fluids. Hence, avoid sharing personal items belonging to the infected person (toothbrushes, razors, etc). Sexual contact (contact with vaginal fluid or semen) can also transmit the virus, and hence the use of condoms is important to prevent spread.
Vaccination is available for hepatitis B and is compulsory in our country for every new-born child. Hepatitis A vaccine is also compulsory.

 Doctors for Hepatitis
Doctors for Hepatitis  OTC Medicines for Hepatitis
OTC Medicines for Hepatitis
 Hepatitis articles
Hepatitis articles News for Hepatitis
News for Hepatitis
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Hepatitis
Ayurvedic Treatment of Hepatitis
 Homeopathic Treatment of Hepatitis
Homeopathic Treatment of Hepatitis