What is an Injury?
Any damage caused to your body by external factors is known as injury or trauma. Injury can occur to any part of the body from head to toe. Some injuries are easily curable, while major traumatic injuries can either be disabling or fatal. Injuries can be classified depending on a number of factors, such as location, severity and cause.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The signs and symptoms differ according to the site and severity of the injury. Common symptoms are as follows:
- Pain.
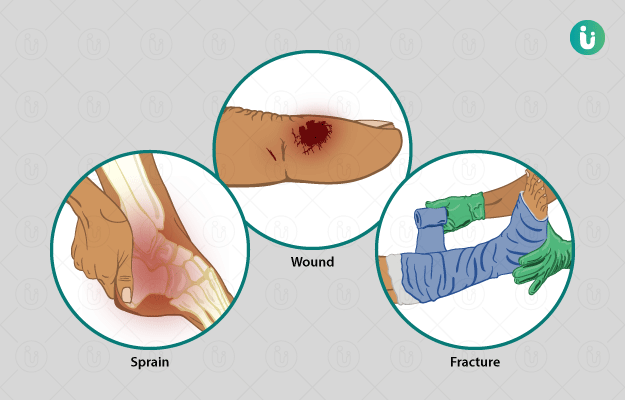
- Swelling and tenderness.
- Loss of motion or inability to continue a physical activity.
- A bleeding wound.
- Hematoma (accumulation of clotted blood in tissues).
- Vomiting.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Inability to see properly.
- Loss of coordination.
- Memory loss.
What are the main causes?
Following are the main causes of injury:
- Accidents
- Falls
- Burns
- Physical assault
- Suicidal attempt
- Sports injuries
- Violence or war
- Repetitive strain
- Drug toxicity
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis of the injury is done primarily by the signs and symptoms which can be superficial (visible) or internal (invisible). Grading of injury using the Injury Severity Score is a very important part of diagnosis as it indicates the severity of the trauma. Diagnosis involves the following:
- Physical Examination
Detailed physical examination of the site of injury is necessary to understand the severity and decide the treatment. For bone and muscle injury, the doctor will assess your gait and the range of movement of the affected part. - Neurological testing
The doctor will examine eye movements, sensation and control over muscles to assess nerve functioning. - Imaging
- X-ray.
- MRI.
- Ultrasound.
- CT scan.
- Blood test
A blood test is done to detect the presence of two important proteins (GFAP and UCH-L1) released in brain injury.
Treatment of an injury will begin primarily with an effective first aid, even before the person is taken to the hospital. The treatment regimen generally followed:
- Medications, such as painkillers, anti-inflammatory and anti-emetic drugs, and tranquillizers.
- Elevation of the affected body part.
- Elastic compression bandages, slings or casts in case of fractures.
- Physiotherapy.
- Surgery.
You may seek advice from experts in the case of an injury. Recovery from minor injuries is faster than that from a major trauma. Rehabilitation, gentle exercises, proper diet and seeking advice regularly from your doctor and physiotherapist will help in a speedy recovery.

 Doctors for Injury
Doctors for Injury  OTC Medicines for Injury
OTC Medicines for Injury
 Injury articles
Injury articles
 First Aid for Injury
First Aid for Injury
 Home Remedies for Injury
Home Remedies for Injury
 Homeopathic Treatment of Injury
Homeopathic Treatment of Injury







 Editorial Team
Editorial Team


 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria











