Summary
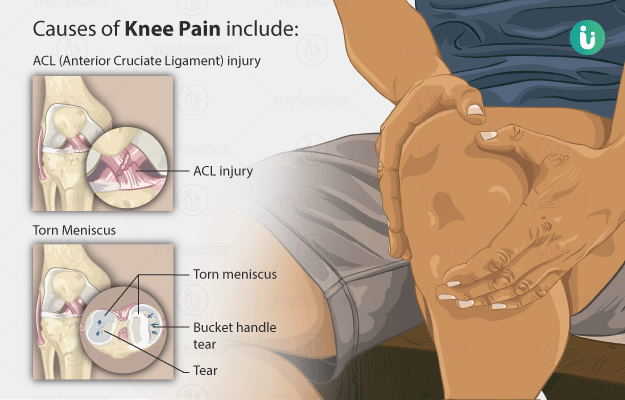
Knee pain is quite common in the elderly. It is the pain felt in the knee joint while at rest or walking or carrying out day-to-day activities. Most of the times, it is caused due to a damage to the surrounding tissues which happens because of an increased fragility of the tissue structure, as seen in old age. Also, knee pain can result from an injury caused by an accident or overuse of the knee joint. Knee pain can be easily diagnosed by a doctor on the basis of the person’s complete medical history, blood tests, and some radiological tests such as X-rays and ultrasonography. Knee pain can be treated by managing the underlying cause of the pain such as weight reduction in people who are obese along with symptomatic treatment with ice packs and rest. Other treatment options such as physiotherapy and acupuncture may also be recommended to treat knee pain. If knee pain persists despite these treatment modalities, then surgery may be needed. Prognosis of knee pain is quite good, however, if the cause is not diagnosed on time, it can lead to complications such as worsening of the pain or complete damage of the knee joint. The knee joint is important for various physical activities such as walking, running, playing a sport, and also for everyday chores. Hence, it is advisable to immediately consult the doctor to prevent permanent damage to the knee.

 Doctors for Knee Pain
Doctors for Knee Pain  OTC Medicines for Knee Pain
OTC Medicines for Knee Pain
 Lab tests for Knee Pain
Lab tests for Knee Pain Knee Pain articles
Knee Pain articles
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Knee Pain
Ayurvedic Treatment of Knee Pain
 Exercise for Knee Pain
Exercise for Knee Pain
 Home Remedies for Knee Pain
Home Remedies for Knee Pain
 Homeopathic Treatment of Knee Pain
Homeopathic Treatment of Knee Pain



































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team

 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria
 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla











