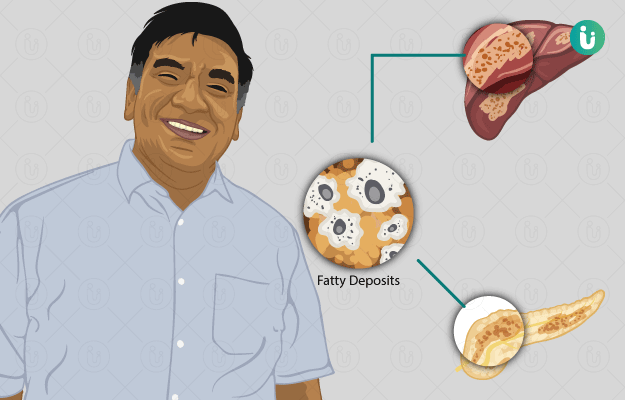
What is metabolic syndrome?
A syndrome is a collection of medical conditions and symptoms which occur together and characterise a certain disease or condition. Metabolic syndrome is a condition where high blood pressure, high triglyceride levels, diabetes and obesity occur together, resulting in an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The signs and symptoms of metabolic syndrome are not so specific and definitive. The most prominent and common signs of a person suffering from metabolic syndrome are:
- Increased blood pressure for a long period of time
- Increase in the waistline of the person
- Signs of diabetes and insulin resistance like recurrent infections, increased thirst and appetite, weight gain, increased urination, and others
What are the main causes?
The main cause for metabolic syndrome is obesity and lack of physical activity. Other causes which can lead to metabolic syndrome are as follows:
- High blood pressure
- Insulin resistance which is hereditary and the main cause of type 2 diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome can also occur in females who have developed diabetes or high blood pressure during pregnancy
How is it diagnosed and treated?
The diagnosis of metabolic syndrome is considered when the following signs are seen in a person:
- High level of cholesterol in the blood – Blood tests are performed to find the cholesterol content.
- Hypertension or high blood pressure – Persistent blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg or higher increases the risk of metabolic syndrome.
- Obesity – An increased waistline, taken as 94 cm or more in men and 80 cm or more in women, is an indication of abnormal metabolism.
- High glucose level in the blood.
People can incorporate several habits and lifestyle changes to control metabolic syndrome. Some of these are:
- No smoking – Smoking increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, cancer and other diseases.
- Controlled diet – Diet should be controlled to prevent overeating and obesity.
- Increase in physical activity – Adapting to an active and healthy lifestyle is the key to prevent obesity, high blood pressure and many other life-threatening conditions. Weight loss is important to control diabetes, high blood pressure, high triglycerides as well as insulin resistance.
Treatment of these conditions is similar to the steps taken for prevention. In addition, certain medications are also introduced to manage any condition which may result in an overall increase in the long-term effects of metabolic syndrome. Insulin shots may also be prescribed to control the increase in blood sugar levels. Blood pressure lowering medications will be prescribed to lower blood pressure.

 Doctors for Metabolic Syndrome
Doctors for Metabolic Syndrome  OTC Medicines for Metabolic Syndrome
OTC Medicines for Metabolic Syndrome