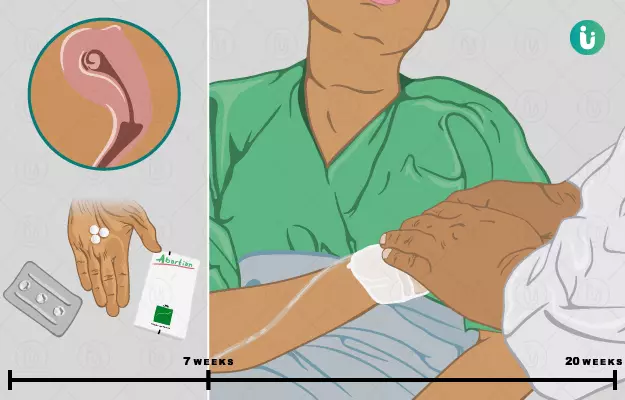
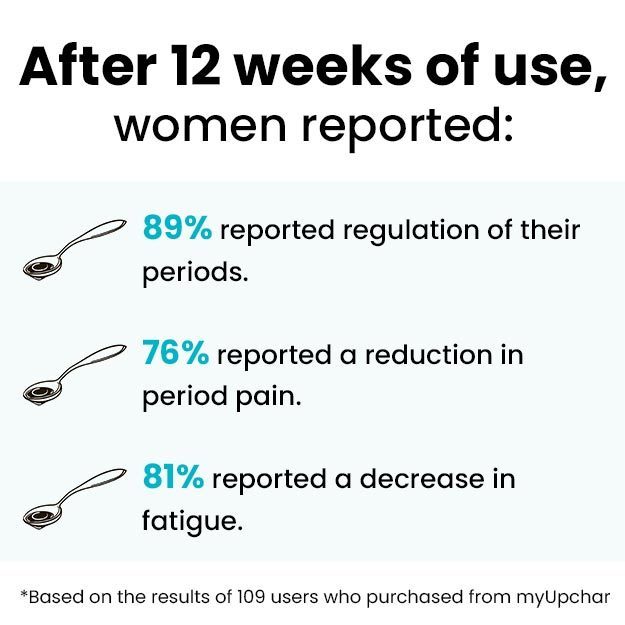
The decision to undergo an abortion is often one of the most profoundly personal and challenging choices a woman or couple may face. While emotionally complex, it's essential to understand that abortion is a medical procedure for the termination of pregnancy, which can be performed either medically or surgically. The safety and specific procedure depend significantly on the stage of pregnancy. Generally, the earlier an abortion is performed, the fewer complications are likely to arise. While common side effects such as bleeding, cramping, nausea, and vomiting can occur, severe symptoms like excessive blood loss, fever, or extreme pain warrant immediate medical attention. It's crucial to know that, when performed safely by a trained gynecologist, abortion typically does not affect a woman's future pregnancies or fertility, making it a medically sound option for those who choose it.
- What is An Abortion?
- What Are The Different Types of Abortion?
- What is The Minimum Time For Abortion?
- What is the Difference Between Safe and Unsafe Abortion?
- Causes of Abortion
- Abortion Procedure - When will periods start after Abortion in Hindi
- What Happens to The Body After An Abortion?
- When is The Best Time to Abort?
- How Many Abortions Can A Woman Have?
- Side Effects of Abortion
- What Happens to a Woman’s Body After An Abortion?
- Risks or Complications of Abortion
- Do Abortions Have Long-term Effects?
- Chances of Getting Pregnant After Abortion
- Survey Based On Abortion in India
- Precautions After Abortion
- Indian Law of Abortion
- Summary
What is An Abortion?
An abortion refers to the termination of pregnancy. It is carried out by the removal or expulsion of the fetus from the womb of the woman. It either results in or is done because of the death of the embryo or fetus.
What Are The Different Types of Abortion?
Based on whether the abortion has occurred normally or is being induced, it is of the following two types:
Spontaneous or natural abortion or miscarriage
A spontaneous or a natural abortion is when the embryo or the foetus dies due to complications of pregnancy. This is commonly termed miscarriage.
Induced abortion
Induced abortion is the one that is performed purposely to expel or remove the fetus from the uterus which may be done either medically or surgically. It is performed in cases where it poses a hazard to the health, safety or survival of the bearing mother.
Read more: Family planning
What is The Minimum Time For Abortion?
According to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, India, terminating a pregnancy is safe till the second trimester (20 weeks). Getting an abortion done beyond this time has very high risks of complications, which can occur during or after the procedure.
What is the Difference Between Safe and Unsafe Abortion?
As mentioned above, getting an abortion done is safe when it is conducted before 20 weeks or up to the second trimester of pregnancy. As the fetus grows further with the pregnancy continuing beyond the second trimester, the risks and complications associated with an abortion increase making it highly unsafe. Hence, it is recommended by doctors that a woman should take the decision of abortion before entering the third trimester.
The safety of abortion also depends on the healthcare facility where the surgical or medical abortion is performed. A procedure performed by a qualified doctor or gynaecologist who is authorised to prescribe abortion pills or conduct surgical abortion is often safe and must be the only centre visited for an abortion procedure. It must be ensured that the clinic follows all sterilisation procedures before conducting an abortion to ensure protection against infections.
Causes of Abortion
The different reasons for a spontaneous and an induced abortion have been listed below.
Induced abortion
Induced abortion is performed only when the mother and the doctor decide on it. Hence, it may have a lot of personal, social, and medical causes involved. As per a recent study conducted in 14 countries, the main reasons for an abortion are:
-
Child spacing
As it has been widely advised that couples must maintain a difference of at least three years between two pregnancies, women opt for an abortion when they have recently undergone childbirth and are looking for spacing.
-
Unwanted pregnancy
Some women who inadvertently get pregnant go for abortion more often than not. Such pregnancies usually result from having unprotected sex or due to the failure of contraceptives. This is one of the most common reasons that women go for an induced abortion.
-
Financial problems
Raising a child comes with a lot of responsibilities. It is important to have a regular financial source that is adequate enough to take the responsibility of being a parent. Hence, couples with financial issues go for an abortion. -
Career decisions
Pregnancy immensely alters the personal and professional life of a woman. Sometimes, it gets hard for her to modify her professional goals and aspirations. Sometimes at a crucial stage of life, women opt for an abortion for either further studies or a job or career. -
Issues with the partner
Many couples often say that they got pregnant together because having a child is a two-way street and it is the responsibility of both partners to be equally involved. In some cases where women have issues with their partners such as an unhappy married life, disagreement regarding pregnancy, financial insecurity, or a divorce, they are pushed to the decision of abortion. -
Very young age
Girls who get pregnant at a very young age and are not in a physical or mental state to continue a pregnancy or raise a child often get advised for an abortion by their doctors. -
Pregnancy before marriage
Many girls, especially in India, are not allowed to continue pregnancy out of wedlock or before marriage. There is a huge taboo around this. In cases where girls get pregnant before marriage, abortion is usually forced. In some cultures, it is considered shameful and a sign of 'bad character'. -
Health risks
If the continuation of pregnancy poses a serious health risk to the fetus or the mother, doctors advise going for an abortion. -
Family or peer influences
In some unfortunate instances where a woman is influenced by her relatives, friends, or family, she opts for an abortion. It is, therefore, suggested that pregnancy should always be discussed with a counsellor or a gynaecologist. -
Wanting a boy
To say the least, a criminal offence that is widespread in most Indian states and some Asian countries is committed by people who prefer to have a boy. This decision is usually made spontaneously without the consent of the mother or even the father.
Spontaneous abortions
There are certain cases in which the health of the woman may be affected, such as:
-
Genetic abnormalities
Parents who have a dormant or occult (hidden) genetic abnormality may transfer these genes to the fetus making it incompatible to survive. -
Immunological causes
A miscarriage may also occur when the mother's immune system starts acting against the fetus. -
Abnormal clots
Thrombophilia is a disorder in which abnormal clots may be formed in the placenta. As a result, the oxygen supply to the fetus is reduced and it becomes a reason for its demise. -
Hormonal disorders
Some hormonal disorders such as hypothyroidism (low thyroid hormone levels), high level of serum thyroid antibodies, and an absence of thyroid antibodies but a raised serum (TSH) thyroid-stimulating hormone, and PCOS (Polycystic ovarian syndrome) have been found to be associated with miscarriages.
-
Faulty embryo selection
If the embryo is defective or possesses a poor quality being less viable for implantation, the fetus fails to grow normally, which may lead to a miscarriage. -
Lifestyle
Women who do not eat a nutritious diet, drink alcohol, smoke, perform strenuous exercises, do not maintain proper hygiene or have very low to no physical activity may be responsible for unfulfilled nutritional and immunological requirements of the fetus resulting in its demise. -
Uterine malformations
Defects in the structure and function of the uterus may also lead to poor attachment, reduced transfer of nutrition, and decreased waste removal leading to its death after some time.
Read more: TSH test
Abortion Procedure - When will periods start after Abortion in Hindi
There are two ways by which an abortion is done - medical and surgical. Both the procedures are different for a first- trimester and a second-trimester pregnancy.
First Trimester
The abortion which is carried out within the first thirteen weeks of pregnancy is known as a first-trimester abortion. Most pregnancies are terminated during the first trimester as it is a lot safer than termination in the second trimester.
-
Medical abortion
A medical abortion includes the intake of 'abortion pills' as prescribed by your doctor. These medicines may either be taken orally or placed in the vagina or both. It is mostly done at a clinic to observe the immediate response of the body. However, you can also take these medications at your home as per the instructions of your gynaecologist. -
Surgical abortion
Surgical termination of pregnancy is done by a method called suction-curettage. You may be given a local or general anaesthesia, or sedatives, to reduce your sensitivity towards pain incurred during the procedure. In this method, your cervix (birth canal) is dilated either by using medicines or with the help of dilator instruments. When the cervix is dilated enough, a suction tube is entered through the vagina into the uterus. This tube is then connected to a vacuum which helps in sucking out and detaching the embryo or the foetus from the uterine wall.
Once the procedure is done, your doctor may prescribe a few painkillers to be taken at home. It is best that you see your doctor at least once within two weeks of the procedure. This will help in diagnosing if there are any remains of the fetus left after the procedure. It will also help in identifying any other side-effects or infections.
Second Trimester
When the pregnancy is terminated between the thirteenth and twentieth week, it is known as a second-trimester abortion. Just like a first-trimester pregnancy, it can also be conducted medically or surgically. Doctors suggest that surgical abortion has fewer complications as compared to medical in the case of second-trimester surgery.
-
Medical abortion
A medical abortion in the second-trimester is performed within the doctor’s clinic. The doctor may ask you to take abortion pills orally. Sometimes, vaginal pills or intravenous (administration of medicines through the veins) injections may be given. These medicines start showing their effect after twelve hours of administration. The mechanism of action of these pills can be explained on the basis of contraction of the uterine muscles which lead to the expulsion of the fetus.
Your doctor may prescribe a few painkillers because a medical abortion in the second trimester can cause severe cramping. -
Surgical abortion
A procedure called Dilatation and Evacuation is the choice of surgery to abort a second-trimester pregnancy. In this procedure, some medicines may be given a day before the surgery, which help in dilating the cervix. On the day of surgery, the cervix is further dilated using dilator instruments. If required, local or general anaesthesia is given to relieve pain. A suction tube is then used to remove the fetus from the uterus.
What Happens to The Body After An Abortion?
Hey there! Let's talk about what happens to your body after an abortion in a way that's easy to understand. It's a journey your body goes through, and everyone's experience can be a little different, just like no two people are exactly alike.
Immediately After
Right after the procedure, in the first few hours to days, you can expect some noticeable changes. Bleeding is very common, much like a heavy period, as your body sheds the uterine lining. You might see some small blood clots, and this can last anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, sometimes even stopping and starting again. It's usually advised to use pads instead of tampons during this time to help prevent any infection. Alongside the bleeding, you'll likely feel some cramping, which is similar to period cramps. This happens as your uterus contracts to shrink back to its usual size. Over-the-counter pain relievers can often help manage this discomfort. It's also completely normal to feel quite tired; your body has undergone a significant change, so rest is important. Emotionally, your hormones are shifting, and you might experience a range of feelings, from relief to sadness, or even anxiety. All these emotions are valid and a part of the healing process.
In the Weeks Following
As the weeks pass, your body continues to heal and adjust. The bleeding and cramping will gradually lessen, becoming less frequent and intense. You might experience some light spotting for a few more weeks. Your menstrual cycle will typically resume within four to eight weeks after the abortion. Your first period might feel a bit different from your usual, perhaps heavier or lighter, but it should regulate over time. Your ovaries will also begin their normal function of releasing eggs again, meaning it's possible to become pregnant again quite quickly after an abortion. If you're not planning another pregnancy, discussing contraception options with your healthcare provider is a good idea. Any breast tenderness or swelling you experienced during pregnancy should also start to disappear as your hormone levels return to normal.
Long-Term Outlook
For the vast majority of people, a safe abortion does not lead to any long-term physical health issues or affect their ability to have future pregnancies. It's considered a very common and safe medical procedure when performed by qualified professionals.
It's crucial to listen to your body and pay attention to how you're feeling. If anything seems concerning or not quite right, please don't hesitate to contact your healthcare provider. They will likely schedule a follow-up appointment to ensure everything is healing well, which is an excellent opportunity to ask any questions you might have. Remember, emotional support is also very important. Whether it's from friends, family, a counselor, or support groups, seeking help if you're struggling emotionally is always a healthy step.
Every individual's healing journey is unique, and safe, supportive care throughout the process is paramount.
When is The Best Time to Abort?
When considering the timing of an abortion, medical professionals generally agree that earlier is safer, as the risks tend to increase with advancing pregnancy.
The first trimester (up to about 12-13 weeks) is usually considered the safest period. During this time, both medical abortion (the abortion pill, typically up to 10-12 weeks) and in-clinic aspiration abortions are highly effective and have the lowest rates of complications. Medical abortion offers a more private experience, while aspiration is a quick in-clinic procedure.
As pregnancy moves into the second trimester (from 13 weeks onwards), procedures become more complex, usually involving surgical methods like dilation and evacuation (D&E). While still very safe when performed by skilled providers, the risk of complications, though low, is higher than in the first trimester.
Later abortions, especially after 21-22 weeks, are uncommon and typically reserved for serious medical reasons, requiring more involved procedures and specialized care.
How Many Abortions Can A Woman Have?
That's a very important question, and it's surrounded by a lot of discussion and misinformation. From a medical standpoint, there isn't a strict "limit" to the number of abortions a woman can have. However, it's essential to understand the nuances and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
Abortion, when performed safely by trained medical providers, is generally a very safe procedure, with risks typically lower than those associated with childbirth. This holds true even for individuals who have had more than one abortion.
However, like any medical procedure, there are always potential risks, and these risks can, in very rare cases, slightly increase with each subsequent procedure. For example:
-
Asherman's Syndrome: This is a very rare condition where scar tissue can form inside the uterus. It's more commonly linked to repeated uterine surgeries, but in rare instances, it can be a complication of multiple surgical abortions (specifically D&C procedures). If it occurs, it can sometimes make it harder to get pregnant in the future, but it is often treatable.
-
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): This is an infection of the reproductive organs. While it's far more commonly caused by untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs), there's a very small risk of it developing after an abortion if bacteria enter the uterus. If left untreated, PID can lead to scarring and potentially affect fertility or increase the risk of ectopic pregnancies. However, standard medical practice includes measures to prevent infection, such as antibiotics.
-
Preterm Birth: Some studies have suggested a potential, though small, increase in the risk of premature birth in future pregnancies after multiple surgical abortions. However, other research has not found this increased risk, and the evidence on this particular point is not entirely consistent across all studies. Medical abortions (the abortion pill) do not appear to carry this same potential risk.
It's really important to remember that these complications are rare. The vast majority of people who have one or even multiple abortions experience no long-term physical health issues or problems with future fertility. Many, many people have two or more abortions for various reasons and go on to have healthy pregnancies if they choose to.
The idea that there's a "limit" to how many abortions someone can have is often rooted more in social stigma or political agendas than in medical science. Healthcare providers prioritize your safety and well-being, and they will assess your individual health and circumstances each time to ensure you receive the best and safest care.
If you are concerned about avoiding future pregnancies, discussing effective contraception options with a healthcare provider is always a great step. There are many highly effective methods available that can help you plan your family according to your needs and preferences.
(Read More: Beyond the Basics: Your Definitive Guide to the Copper T)
Side Effects of Abortion
After getting the abortion done, you may experience a few of the following symptoms:
-
Nausea and Vomiting
It is usually experienced by women as a side effect of medical abortion using abortion pills. -
Heavy bleeding
Heavy bleeding results when the endometrium contracts and sheds its inner lining to remove the foetus from the womb. It may last up to two weeks. -
Pelvic cramps
The cramps in your pelvic area, which are felt after an abortion may sometimes be more severe than what you normally experience while on your period.
Read more: Pelvic pain causes
What Happens to a Woman’s Body After An Abortion?
After an abortion, a woman's body undergoes a range of physical and emotional changes as it recovers. The experience varies depending on the abortion type (medical or surgical), stage of pregnancy, and individual factors.
Bleeding and cramping are the most common physical effects. Medical abortions often involve heavier bleeding and more intense cramping, similar to a heavy period, lasting hours to days, with spotting for several weeks. Surgical abortions typically result in lighter bleeding or spotting for a few days to weeks. Cramping indicates the uterus is returning to its normal size.
Pregnancy symptoms like nausea and fatigue usually subside within 3 days, while breast tenderness may take up to 10 days. The menstrual cycle generally returns within 4 to 6 weeks, though initial cycles might be irregular. It's possible to become pregnant again quickly, as ovulation can occur soon after. Other temporary symptoms might include dizziness, headache, or diarrhea.
Emotional Responses
Emotional reactions are highly individual. Many women feel relief, but other emotions are also common, including sadness, grief, guilt, shame, anxiety, or fear. Hormonal shifts can lead to mood changes like tearfulness or irritability. These feelings are often temporary, resolving as the body recovers. However, if negative emotions are severe or persistent, seeking support from a healthcare provider or counselor is important.
Potential Complications
While generally safe, complications are possible. Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Heavy bleeding (soaking two or more maxi pads in an hour for two consecutive hours).
- Severe pain not relieved by medication.
- Fever of 38°C (100.4°F) or higher.
- Signs of infection (foul-smelling discharge, pus-like discharge, increasing abdominal pain).
Persistent pregnancy symptoms weeks after the abortion.
Self-Care During Recovery
Rest is crucial, especially in the first couple of days. Manage pain with over-the-counter relievers and a heating pad. Use sanitary pads instead of tampons until bleeding stops to prevent infection. Avoid baths, swimming, and sex for 1-2 weeks or as advised by your doctor. Focus on a balanced diet to support recovery. Emotional support from trusted individuals or professionals can also be very beneficial. Always attend any recommended follow-up appointments to ensure complete recovery and discuss contraception.
Risks or Complications of Abortion
Most abortions which are conducted in a healthcare facility may have some side effects as mentioned above, but in a few cases, severe complications may also be experienced. These include:
Fetal remains
In some cases, complete detachment of the foetus from the uterine lining may not occur. This is known as incomplete abortion. In such a case, further treatment with medications or surgery may be required.
Infections
Infection may occur in case of a surgical abortion. Antibiotics and painkillers are advised in such cases.
Damage to the organs
While performing the procedure, damage may occur to the cervix or the uterus. If this happens, the doctor may suggest another surgery.
Excessive blood loss
If the bleeding does not stop even after two weeks of medication or surgery, it may lead to anaemia. In such cases, a blood transfusion is required to restore the health of the woman.
Read more: How to have safe sex
Do Abortions Have Long-term Effects?
It's a very common and important question to consider whether abortions have long-term effects. The good news is that, for the vast majority of individuals, safe abortions do not lead to long-term physical health consequences. When performed by trained medical professionals in appropriate settings, abortion is a very safe procedure. However, like any medical intervention, understanding the nuances and rare potential risks is key.
Regarding physical health, research consistently shows that a safe abortion generally does not impact a person's future fertility. Many individuals who have undergone one or multiple abortions go on to have healthy pregnancies later in life. Furthermore, a safe abortion typically does not increase the risk of complications in future pregnancies, such as miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or stillbirth. While extremely rare complications like uterine scarring (Asherman's Syndrome) or, less definitively, a very slight increase in the risk of preterm birth in future pregnancies (more debated for surgical abortions and not associated with medical abortions) have been discussed in medical literature, these are highly uncommon, especially with modern, safe practices. It's also crucial to debunk the myth that abortion causes breast cancer; major medical and scientific organizations have extensively researched and refuted any such link.
Concerning mental and emotional health, the landscape is more varied and deeply personal. People experience a wide spectrum of emotions after an abortion, which can range from relief, to sadness, guilt, or even a mix of complex feelings. All these emotional responses are valid and normal. The consensus among leading medical and psychological organizations is that having an abortion does not inherently cause long-term mental health problems like depression or anxiety disorders for most individuals. Instead, a person's emotional well-being after an abortion is more likely to be influenced by factors such as their pre-existing mental health, the level of social support they receive, the presence of societal stigma or judgment, the personal circumstances that led to the abortion, and importantly, whether they were able to access the care they desired. In fact, studies have indicated that being denied a wanted abortion can sometimes lead to worse mental health outcomes than actually having the procedure.
In essence, for the majority of individuals, a safe abortion, when performed by a medical professional, does not result in long-term physical health issues or affect the ability to have children in the future. Emotional responses are diverse and are influenced by a multitude of personal and external factors. If you have any concerns about the potential physical or emotional effects, seeking personalized and accurate information from a healthcare provider is always the most beneficial approach.
Chances of Getting Pregnant After Abortion
Induced abortions do not affect your chances of getting pregnant in the future. In fact, it is possible to get pregnant after a short duration following an abortion procedure. But, it is advised to consult your gynaecologist for the right contraceptive method to prevent any unwanted pregnancy and abortions.
This is because spontaneous abortions if occurring repeatedly may put you at a higher risk of having a miscarriage in the future. Hence, a complete check-up and treatment of the underlying medical conditions is necessary to ensure a healthy full-term pregnancy.
Read more: Recurrent miscarriage causes
Survey Based On Abortion in India
This study, titled "Why do women abort their pregnancies? Evidence from the National Family Health Survey 2019–21 of India," was published on May 17, 2023. The authors of the study are Daisy Saikia and Manas Ranjan Pradhan from the Department of Fertility and Social Demography, International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai, India. The research assesses the reasons for induced abortion and their predictors in India, drawing insights from recent national data.
The study identified unintended pregnancy as the primary reason for induced abortions in India. Other reasons include medical complications and, in some cases, the undesired gender of the unborn child. A significant portion of abortions were found to be unsafe, with 31% prevalence reported in one finding, and 27% of women undergoing abortions without skilled healthcare providers, often at home. Factors strongly correlated with unintended pregnancies ending in abortion include gestational age, method and place of abortion, number of surviving children, religion, place of residence, and region. Sex-selective abortions continue to occur, particularly among women with higher parity, from the poorest households, and in central, eastern, and north-eastern regions of India.
The study primarily utilizes data from the National Family Health Survey-5 (NFHS-5), conducted between 2019 and 2021. This nationally representative survey is a crucial source of data on population, health, and nutrition in India. The analysis considered a sample of 5,835 women aged 15-49 who had terminated their last pregnancy by induced abortion in the five years preceding the survey. Multinomial logistic regression was employed to analyze the adjusted effects of socioeconomic predictors on abortion reasons.
The findings indicate that women were more likely to have abortions at home or outside the public health sector due to unintended pregnancies (Relative Risk (RR): 2.79) and sex-selective reasons (RR: 2.43) rather than life-threatening medical conditions. The study highlights significant socioeconomic, demographic, and geographic variations in the reasons for abortion across India. Despite legal provisions for abortion in India since 1971, unsafe abortion practices persist, contributing to maternal morbidity and mortality.
The study recommends several key interventions to address the issues surrounding abortions in India. A crucial recommendation is to enhance the understanding of contraception among women to reduce unintended pregnancies. Empowering women in reproductive decisions is also emphasized. Furthermore, there is a strong call for improving access to facility-based abortion services, especially in underserved rural areas, by ensuring adequate equipment, supplies, and trained providers, including the proper prescription and supervision of medication abortion methods. Sensitization of healthcare providers regarding ethical issues and women's reproductive rights is urgently needed to ensure safe, legal, and accessible abortion care. These measures are essential for improving women's health and reducing the incidence of induced and unsafe abortions.
The study underscores the complex interplay of socioeconomic, demographic, and geographical factors influencing abortion practices in India. Unintended pregnancies remain the leading cause, while sex-selective abortions, though illegal, continue. The findings highlight the critical need for comprehensive strategies that focus on increasing contraceptive knowledge, empowering women, and strengthening the healthcare infrastructure to provide safe, legal, and accessible abortion services while upholding women's reproductive rights.
Precautions After Abortion
Here are key precautions to take after an abortion:
- Prioritize Rest: Take it easy for a few days. Avoid strenuous activity, heavy lifting, and intense exercise for at least a week.
- Manage Pain: Use over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and a heating pad for cramps.
- Use Pads Only: Only use sanitary pads for bleeding. Do not use tampons or menstrual cups for at least one to two weeks, or as advised by your doctor, to prevent infection.
- Avoid Vaginal Insertion: Do not have vaginal intercourse, baths, hot tubs, or go swimming for at least one to two weeks, or as instructed by your provider. Showers are fine.
- Stay Hydrated & Eat Well: Drink plenty of fluids and maintain a nutritious diet to support healing.
- Attend Follow-Up: Go to your scheduled follow-up appointment to ensure you're healing properly and to discuss contraception if desired.
- Monitor for Complications: Be vigilant for signs of a problem. Immediately contact your healthcare provider if you experience very heavy bleeding (soaking more than two maxi pads an hour for two consecutive hours), severe pain not relieved by medication, a fever (over 100.4°F or 38°C), or foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
Seek Emotional Support: It's normal to experience a range of emotions. Talk to a trusted person or a counselor if you need support.
Indian Law of Abortion
According to Section 3 of the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971, an abortion can be conducted when:
- There is a health risk to the mother if she continues the pregnancy.
- The child has a high chance of being born with physical or mental disabilities.
- Pregnancy is caused due to a crime such as rape or in a case where the woman is mentally challenged.
Recently, the abortion limit has been extended up to 24 weeks for a rape victim.
According to Section 312 to 315 of the Indian Penal Code, a person who conducts an illegal abortion is liable for three-year imprisonment with or without a fine. A couple who indulges in a sex-selective abortion (abortion of the female child) is liable for seven-year imprisonment with or without a fine.
(Read More: Best Time To Get Pregnant - myUpchar)
Summary
This guide offers a detailed overview of the medical termination of pregnancy, covering its definition, types, safety, common causes, procedures, post-procedure care, potential long-term effects, and the legal aspects in India.
Abortion is defined as the termination of pregnancy, involving the removal or expulsion of the fetus from the womb. It distinguishes between spontaneous abortion (miscarriage), which occurs naturally due to pregnancy complications, and induced abortion, which is purposefully performed either medically or surgically, often due to health risks to the pregnant person or other personal and social considerations.
Regarding timing and safety, terminating a pregnancy is generally considered safe up to the second trimester (20 weeks) in India. Risks and complications increase significantly beyond this period. The safety of an abortion also heavily relies on the healthcare facility and the qualifications of the medical professional, stressing the importance of procedures being performed by authorized gynecologists in clinics adhering to strict sterilization protocols.
Various reasons for induced abortion are discussed, including child spacing, unwanted pregnancies (often from unprotected sex or contraceptive failure), financial difficulties, career aspirations, partner issues, very young age of the pregnant individual, pregnancies before marriage (especially where social taboos exist), health risks to the fetus or pregnant person, family or peer influences, and sadly, the illegal practice of sex-selective abortions. Causes for spontaneous abortions include genetic abnormalities, immunological factors, abnormal blood clots, hormonal disorders (like hypothyroidism and PCOS), faulty embryo development, unhealthy lifestyle choices, and uterine malformations.
The abortion procedure varies by trimester. For the first trimester (up to 13 weeks), options include medical abortion (abortion pills) and surgical abortion (suction-curettage). For the second trimester (13 to 20 weeks), medical abortion is performed in a clinic, and surgical abortion typically involves Dilatation and Evacuation (D&E).
After an abortion, common experiences include bleeding, cramping, and tiredness. In the weeks following, bleeding lessens, and the menstrual cycle usually resumes within four to eight weeks. It's important to note that safe abortions generally do not have long-term physical health effects or impact future fertility. Emotional responses are diverse, ranging from relief to sadness, and emotional support is vital.
From a medical standpoint, there isn't a strict "limit" to how many abortions a person can have. Safe abortions typically do not lead to long-term physical health issues or problems with future fertility, although very rare complications like uterine scarring or pelvic inflammatory disease are theoretical risks. The notion of a "limit" is often rooted more in social stigma than medical science.
Key precautions after an abortion include prioritizing rest, managing pain with over-the-counter medication, using only sanitary pads (avoiding tampons/cups), abstaining from vaginal intercourse, baths, and swimming for a specified period, staying hydrated, attending follow-up appointments, and monitoring for any signs of complications (like excessive bleeding or fever) that require immediate medical attention. Seeking emotional support is also encouraged.
In India, the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971, allows abortion under specific conditions up to 20 weeks (extended to 24 weeks for rape victims in some cases). The Indian Penal Code penalizes illegal abortions and sex-selective abortions with imprisonment and/or fines. Recent surveys highlight that unintended pregnancies are the primary reason for abortions in India, and underscore the persistence of unsafe practices and sex-selective abortions, emphasizing the need for better contraception awareness, women's empowerment, and improved access to safe, legal abortion services.
Find Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in cities
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in Bangalore
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in Mumbai
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in Ghaziabad
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in Chennai
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in Pune
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in Delhi
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in Hyderabad
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in New Delhi
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in Gwalior
- Obstetrician and Gynaecologist in Gurgaon
Surgery Cost In Your City
Doctors for Understanding Abortion: A Comprehensive Guide

Dr. Ayushi Gandhi
Obstetrics & Gynaecology
4 Years of Experience

Dr. Anjali
Obstetrics & Gynaecology
23 Years of Experience

Dr.Anuja Ojha
Obstetrics & Gynaecology
20 Years of Experience

Dr. Geeta Kulkarni
Obstetrics & Gynaecology
7 Years of Experience
References
- Elisabeth Clare Larsen et al. New insights into mechanisms behind miscarriage. BMC Med. 2013; 11: 154. PMID: 23803387
- Tae Yeong Choi et al. Spontaneous abortion and recurrent miscarriage: A comparison of cytogenetic diagnosis in 250 cases. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2014 Nov; 57(6): 518–525. PMID: 25469342
- Margreet Wieringa-de Waard et al. The natural course of spontaneous miscarriage: analysis of signs and symptoms in 188 expectantly managed women. Br J Gen Pract. 2003 Sep; 53(494): 704–708. PMID: 15103878
- National Health Service [Internet]. UK; Abortion.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists [Internet] Washington, DC; Induced Abortion
- National Health Service [Internet]. UK; Abortion.