What are parasitic infections?
By definition, a parasite is an organism that lives inside a host and derives nourishment from it.
Parasites are responsible for causing infections in the body of the host, and these infections are called parasitic infections. Multiple different types of parasites, ranging from unicellular to multicellular types cause infections in humans.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Parasites can cause infections in almost any part of the body. Depending on the organism involved and the route of infection, the signs and symptoms may vary, which include the following:
- Some infections manifest as gastric discomfort, abdominal cramps and stomach ache.
- There may also be nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea along with a loss of appetite.
- Sexually transmitted parasitic infections can cause genital discharge, pain during urination, foul smell and itching or burning sensation.
- A person may also develop a fever or skin rashes in addition to the above-mentioned symptoms.
- Parasitic infections of the brain can lead to seizures and loss of alertness.
What are the main causes?
- Some parasites that cause infections include protozoa (single-celled organisms) and helminths (worms).
- Parasites can enter the body through different routes. Ingestion of contaminated food or water is the most common way by which humans can get an infection.
- Sexual contact with an infected person can also cause infection.
- Exposure to infected blood and contaminated clothing or household items can cause these infections.
- Infections are more common in areas with poor hygiene, overcrowded places and rural regions.
- Immigrants from underdeveloped countries and frequent travellers are also at high risk.
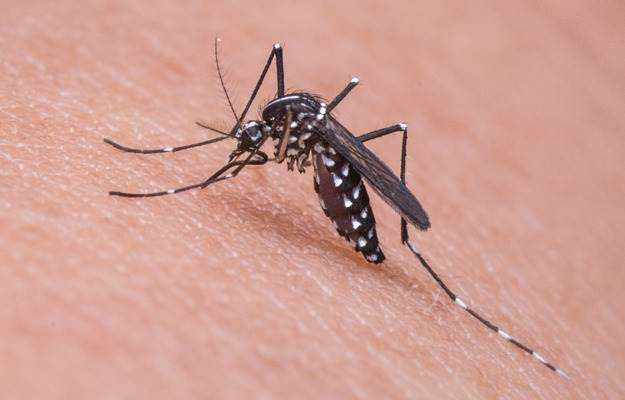
- Mosquitoes and other insects can also transmit these diseases in humans, as is the case in malaria.
- People with a weak immune system due to some other condition are at a greater risk of developing the infection. Cancer, HIV and diabetes are examples of such conditions.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
- When you have an infection in your body, a blood test will reveal a change in the number of blood cells and other indicators of infection.
- In addition, urine and stool samples may also be collected and microscopically examined for parasites.
- Imaging procedures check for any damage to the internal organs or tissues. These include X-rays, CT scans, ultrasounds and MRI.
- To check the health of the gastrointestinal tract, an endoscopy or colonoscopy may be carried out.
Medications are the primary form of treatment for infections. These are:
- Specific antimicrobials are prescribed to eliminate the parasite. The type of medicine depends on the organism that has caused the infection.
- If there is severe weakness along with fluid loss, fluid replacement is indicated.
- People with infection are advised to maintain good personal hygiene and consume well-cooked food prepared in clean environments.

 Doctors for Parasitic Infections
Doctors for Parasitic Infections  OTC Medicines for Parasitic Infections
OTC Medicines for Parasitic Infections