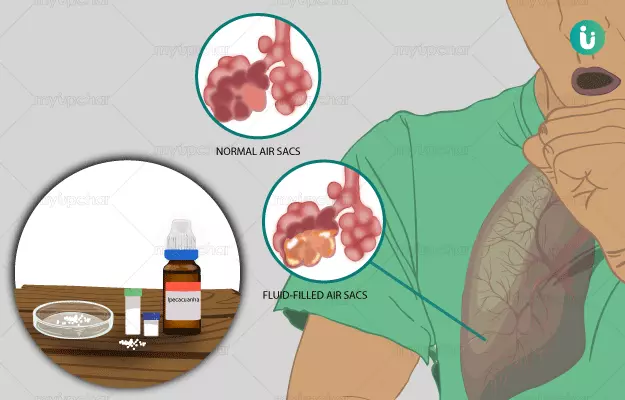
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of lungs that is caused by bacterial, viral or fungal infections. It usually results in filling up of air sacs or alveoli of the lungs with fluid or pus. The severity of pneumonia depends upon many factors, such as the type of microorganism involved, individual’s age and health.
It is the leading cause of death among children under the age of five, with approximately 2,400 deaths per day. According to the UNICEF reports, pneumonia accounted for 16% of the 5.6 million deaths of children under five in 2016. In addition, adults over the age of 65; people with medical conditions such as diabetes, heart failure, asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; and people with a weak immune system due to HIV/AIDS, transplantation, chemotherapy or long-term steroid use are also prone to pneumonia. The different types of pneumonia based on their causative agents are:
- Bacterial pneumonia: The most common type of bacterial pneumonia is pneumococcal pneumonia, caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Other bacteria that may cause pneumonia include Haemophilus influenzae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
- Viral pneumonia: Pneumonia can also be caused by viruses infecting the upper respiratory tract. Influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are the most common causes of viral pneumonia in adults and young children, respectively. Other viruses like rhinovirus, human parainfluenza virus (HPIV) and human metapneumovirus (HMPV) may also cause pneumonia.
- Fungal pneumonia: Fungal pnemonia occurs due to infection of Pneumocystis jirovecii, Histoplasma capsulatum, Cryptococcus neoformans and Coccidioides immitis.
- Aspiration pneumonia: This type of pneumonia is caused by breathing in a foreign or harmful substance, such as food, smoke or a chemical.
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia: As the name suggests, this pneumonia is aquired in hospitals while being operated or treated for some other condition.
Homeopathy, a form of alternative medicine used for the treatment of pneumonia, is based on the theory of individualisation. It takes into account the lifestyle, hereditary factors, personality as well as the medical history of a person and aims to treat the person as a whole including their psychological and physiological health.
Some of the homeopathic remedies that are effective against pneumonia are aconitum napellus, antimonium tartaricum, bryonia, ferrum phosphoricum, phosphorus, sulphur and veratrum viride.
- Homeopathic medicines for pneumonia
- Dietary and lifestyle changes for pneumonia patient as per homeopathy
- How effective are homeopathic medicines and treatments for pneumonia
- Side effects and risks of homeopathic medicine and treatments for pneumonia
- Takeaway
Homeopathic medicines for pneumonia
Some of the homeopathic medicines used in the treatment of pneumonia are discussed below. A homeopathic physician chooses a specific remedy for pneumonia based on the symptoms stated under each remedy.
- Aconitum Napellus
Common name: Monkshood
Symptoms: This remedy works best in case of a sudden onset of pneumonia symptoms and is effective for those in the early stages of pneumonia. The following symptoms can be relieved by monkshood:- Sleeplessness
- Restlessness with fear and anxiety
- Laboured breathing
- Hoarse and dry cough
- Red, hot and swollen face
- Shortness of breath
- Bloody cough
- Tingling sensation in chest after coughing
- Tachycardia or rapid abnormal heartbeat
- Alternating high fever and chilliness
- Symptoms worsen by lying on the affected side, tobacco smoke, dry and cold winds
- Antimonium Tartaricum
Common name: Tartar emetic, tartrate of antimony and potash
Symptoms: This remedy is particularly useful for aged people and very young children. It is given to patients who exhibit the following symptoms:- Cold and pale face
- An excessive rattling of mucus with little expectoration
- Burning in chest that reaches the throat
- Shortness of breath and difficulty in breathing
- Rapid, weak and trembling pulse
- Dizziness with cough
- Pain in larynx and chest
- Excessive mucus in bronchial tubes
- Difficulty in breathing, which is relieved by belching
- Irregularity in fever along with lethargy
- Symptoms worsen during the night while lying down, in warm and cold weather
- Bryonia Alba
Common name: Wild hops
Symptoms: Bryonia is strongly indicated for people suffering from pneumonia accompanied by chest pain. It is known to relieve the following symptoms:- Dry lips and mouth
- Irritability
- Splitting headache
- Yellow and pale skin
- Dry cough
- Stitching pain in chest
- Rust-coloured, jelly-like sputum
- Constant desire to take deep breaths
- Chest pain that worsens with movement, breathing and warm weather
- Pain in the chest relieved by lying on the painful side, applying pressure and by taking cold things
- Ferrum Phosphoricum
Common name: Phosphate of iron
Symptoms: Ferrum phosphoricum is helpful for people in the early stages of pneumonia. It is administered to individuals who show the following symptoms:- Flushed cheeks
- Restlessness
- Sleeplessness
- Lung congestion
- Coughing up of blood
- Short, tickling and painful cough
- Soreness in chest
- Fever with chills daily at 1 pm
- Symptoms worsen at night, by touch and movement
- Ipecacuanha
Common name: Ipecac-root
Symptoms: This remedy is recommended for individuals who have pneumonia along with nausea or vomiting. It helps relieve the following symptoms:- Irritability
- Blue rings around eyes
- Shortness of breath
- Persistent chest constriction
- Constant sneezing
- Wheezing cough
- Violent cough with each breath
- Bleeding lungs and nose
- Rattling cough
- Symptoms worsen with moist warm wind and lying down
- Phosphorus
Common name: Phosphorus
Symptoms: Individuals who benefit from phosphorus display some of the following symptoms:- Fearfulness and loss of memory
- Pale complexion with blue rings under eyes
- Extreme thirst for very cold water
- Hoarseness
- Tickly and painful larynx
- Hard and dry cough
- Sweet taste while coughing
- Lung congestion
- Cough worsens by exposure to cold air, reading, laughing and talking
- Tightness and heaviness in chest
- Sharp, stabbing chest pain
- Rapid and oppressed breathing
- Rusty, blood-coloured or purulent sputum
- Sulphur
Common name: Sublimated sulphur
Symptoms: Sulphur is frequently used for addressing the following symptoms:- Forgetfulness and difficulty in thinking
- Burning sensation in chest and eyes
- Difficulty breathing
- Red, brown spots on chest
- Greenish and pus-like expectoration
- Heaviness in chest
- Shortness of breath in the middle of the night, which is relieved by sitting upright
- Rattling of mucus
- Foul odour from discharges and bad breath
- Faster pulse in the morning than in evening
- Frequent flashes of fever
- Dry, scaly skin
- Symptoms aggravate with rest, warm bed, while standing, washing and bathing
- Veratrum Viride
Common name: White American hellebore
Symptoms: This remedy is useful for people during the congestive stage and initial signs of hepatisation. It is usually indicated for individuals who experience the following symptoms:- Bloated and flushed face
- Red streak in the middle of the tongue
- Lung congestion
- Difficulty in breathing
- Sensation of heaviness in chest
- Croup
- Slow and weak pulse
- Body temperature high in the evening and low in the morning
Dietary and lifestyle changes for pneumonia patient as per homeopathy
Do’s
- Exercise regularly in the open in all weathers
- Have nutritious foods and beverages
Don’ts
Homeopathic medicines are prepared in highl diuted doses, consequently, they easily react with certain foods and fragrant substances. It is best to avoid all of those substances. These include:
- Coffee and herb teas, liquor made with medicinal spices
- Spiced cakes and chocolates
- Chilled drinks and ice-creams
- Highly spiced foods and sauces
- Onions and celery
- Stale cheese and meat
- Strong-smelling perfumes, tooth powders and flowers
- Avoid sedentary lifestyle, smoking and passive exercises
- Refrain from taking long naps in the afternoon
- Unclean, damp and heated places must be avoided
- Avoid unnecessary mental and physical stress
How effective are homeopathic medicines and treatments for pneumonia
Homeopathic treatment can help in enhancing the general health of a pneumonia patient along with providing respite from symptoms. It stimulates the natural immune system of the body to fight the disease and hence does not pose a risk or side effect. Moreover, it can be safely and easily given to infants or patients who are seriously ill. However, it is important that the correct remedy is provided to ensure effective treatment.
A case study, involving a 15-year-old child who was suffering from pneumonia, reported the effectiveness of phosphorus, a homeopathic remedy, in relieving pneumonia symptoms.
Homeopathic medicines can also be taken concurrently with conventional medicines for a quicker recovery from pneumonia.
According to a study published in the Pacific Journal of Energy Medicine, homeopathic medicines are effective in improving the symptoms of Mycoplasma pneumonia infection when given independently or taken along with antibiotics.
Furthermore, the use of homeopathic medicines, instead of antibiotics has increasingly become significant due to the growing antimicrobial resistance.
A research study showed that the mortality rate of patients with pneumonia treated with homeopathy (3 out of 41 patients) was significantly less than the 30% mortality that would have been observed with conventional treatment.
Side effects and risks of homeopathic medicine and treatments for pneumonia
Homeopathic remedies are highly diluted preparations and are nonaddictive in nature. Thus, they are safe to use and have almost no side effects. In addition to this, the medicines, as well as the dosages given in homeopathic treatments, are based on the symptoms shown by the patient and individual miasms. So a medicine that works well for an individual may as well induce side effects in another. Hence, it is important to seek the advice of a registered homeopathic physician before consuming these medicines.
Takeaway
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition affecting lungs and is usually caused by infectious agents such as bacteria, virus or fungi. It leads to fluid accumulation in air sacs so your lungs are filled up with pus, making it difficult to breathe. Pneumonia can affect people of all ages, especially infants and the elderly. There is an increasing amount of scientific evidence citing that homeopathic remedies are safe and effective in the treatment of pneumonia. Homepathic medicines are prepared in highly potentised doses and are administered on the basis of individual symptoms and miasms. Therefore, homeopathy can be used along with conventional medicine for the treatment of pneumonia, without the risk of side effects. However, it is best to take these medicines under the supervision of a doctor.
Find Homeopathic Doctor in cities
Doctors for Homeopathic medicine, treatment and remedies for Pneumonia

Dr. Rutvik Nakrani
Homeopathy
6 Years of Experience

Dr. Jyothi
Homeopathy
23 Years of Experience

Dr. Urvashi Chaudhary
Homeopathy
8 Years of Experience

Dr. Anita Kumari
Homeopathy
12 Years of Experience
References
- National Health Service [Internet] NHS inform; Scottish Government; Overview - Pneumonia.
- United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund. [Internet]. New York, United States; Pneumonia.
- National Health Portal [Internet] India; Pneumonia .
- State of Victoria. [Internet]. Department of Health & Human Services. Homeopathy.
- National Center for Homeopathy. [Internet]. Mount Laurel NJ. A pneumonia case.
- Oliveira A, Lam FMK. Mycoplasma pneumonia. Pacific Journal of Energy Medicine. 2008; (2):58–64.
- Dean M. Comparative evaluation of homeopathy and allopathy within the Parisian hospital system, 1849–1851. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 2010;
- William Beoricke. Homeopathic Materia Medica. Kessinger Publishing. Médi-T 1999, Volume 1.
- British Homeopathic Association. [Internet]. United Kingdom. Is homeopathy safe?.