Summary
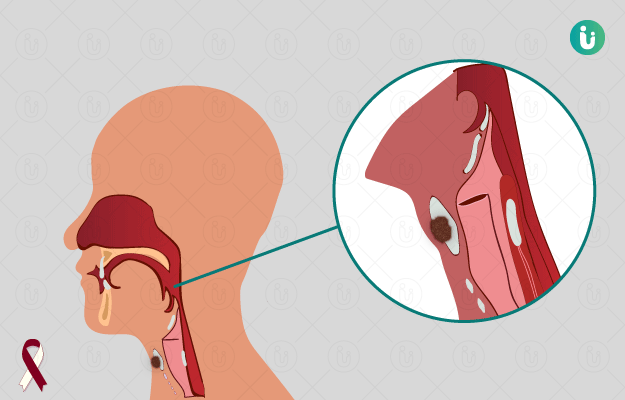
Throat cancer is a type of head and neck cancer, which includes an uncontrolled growth of cells in different regions of the throat. Throat cancer may have different names depending on the region of the throat that is affected. Its primary symptoms include difficulty in eating or swallowing, pain in the throat, speech difficulties and persistent coughing. Several risk factors, such as age, gender and even genetic vulnerabilities predispose an individual to develop throat cancer. Use of tobacco and excessive consumption of alcohol are also associated with throat cancer. Prevention is the key; avoiding risk factors like alcohol and tobacco are the main ways to avoid any type of throat cancer. Throat cancer can be diagnosed with a physical examination, blood tests, imaging tests and biopsy. The treatment options for throat cancer include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy and surgical intervention. Invasive cancer treatment is associated with several side effects. These side effects can be managed with help from doctors, counsellors and family members. There is a higher chance of survival if the cancer is detected early on.

 Doctors for Throat Cancer
Doctors for Throat Cancer  Throat Cancer articles
Throat Cancer articles
 Diet for Throat Cancer
Diet for Throat Cancer




































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team











