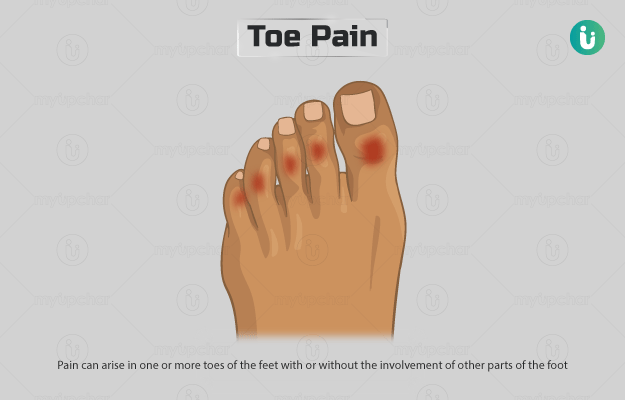
Pain can arise in one or more toes of the feet with or without the involvement of other parts of the foot. Toes can be affected in isolation, like big toe pain or second toe pain, or with more widespread involvement of other digits. The most frequent causes of pain in the toes involve mechanical injury or age-related wear and tear, and subsequent inflammation of the skin, toenails, muscles, bones, joints, tendons and ligaments of the toe. Sometimes, the pain of the toes can be neuropathic (stemming from the breakdown, injury or other diseases of the nerves of the foot) and presents with tingling, burning, a feeling of pins and needles pricking the skin or loss of sensation. While mechanical injuries of the forefoot and toe are common, some systemic diseases (diseases affecting the whole body) also affect the toes in a telltale manner. For example, an acute attack of gout typically presents with a swollen painful big toe that often wakes the patient up in the middle of the night. Gouty arthritis of the big toe is called podagra. Another cause of toe pain can be infection of any of the components of the digit. Some orthopaedic conditions that affect the toes arise due to a similar pattern of injury in susceptible individuals (like athletes and dancers). Pain may arise with or without noticeable physical changes. Although pain can subside spontaneously, if severe or accompanied by other signs and symptoms, it is wise to seek medical care.
One can approach their primary physician with their complaints and can then be referred to an orthopedician, rheumatologist or podiatrist as per the need of the situation. Overall, the medical practitioner begins by making an assessment of the patient by taking a thorough medical history, conducting an extensive physical examination, ordering laboratory investigations, and radiological imaging of the foot. After reaching an accurate diagnosis, treatment is carried out through lifestyle changes, medicines, physiotherapy, occupational therapy or even surgery when necessary.

 Doctors for Toe pain
Doctors for Toe pain  Toe pain articles
Toe pain articles
 Home Remedies for Toe pain
Home Remedies for Toe pain
























 Editorial Team
Editorial Team