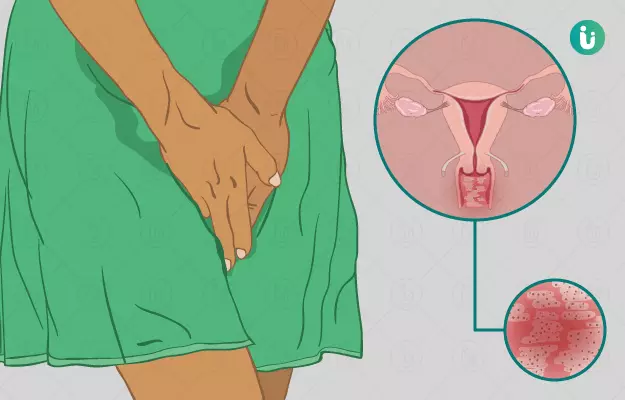
Have you ever felt an unusual burning or stinging sensation in your intimate area and wondered if something might be wrong? You're not alone. Vaginal burning is a common concern among women, yet it's rarely talked about openly. It can appear suddenly, after using a new hygiene product, during urination, or even without any obvious reason. Sometimes, the discomfort is mild and goes away quickly. Other times, it stays, becomes more intense, and leaves you feeling uneasy or anxious.
Vaginal burning can have many different causes. It could be something simple like irritation from clothing or soap, or it might be a sign of an infection, hormonal change, or sexually transmitted disease. While it’s important not to panic, it's equally important not to ignore the symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen.
This article will guide you through everything you need to know about vaginal burning. We’ll cover the common causes, signs to watch out for, when to seek help, and what you can do to prevent and manage the discomfort. The information is presented in simple and clear language to help you better understand your body and take the right steps toward your health and comfort.
- What is Vaginal Burning?
- Symptoms of Vaginal Burning
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Treatment Options
- Risk Factors
- Prevention of Vaginal Burning
- Diagnosis of Vaginal Burning
- Lifestyle Tips for Relief
-
FAQs on Vaginal Burning
- What causes a burning sensation in the vagina?
- Is vaginal burning always a sign of an infection?
- How can I relieve vaginal burning at home?
- When should I see a doctor for vaginal burning?
- Can stress or anxiety cause vaginal burning?
- Is vaginal burning during menopause normal?
- Can I prevent vaginal burning?
- Can I prevent vaginal burning?
- Does diet affect vaginal health?
- Can vaginal burning be a sign of cancer?
- Conclusion
What is Vaginal Burning?
Vaginal burning is among the most commonly experienced discomforts in women. There can be various types of discomfort in the vagina – some include irritation, pain and soreness. Vaginal burning may be an acute burning sensation or a pricking feeling in the vagina or the vulva and clitoris. It may sometimes be accompanied by itching. The burning may subside spontaneously. However, if it persists, it is important to seek medical help since the underlying condition may worsen.
In clinical practice, many women delay seeking help due to stigma, embarrassment, or the assumption that it will go away on its own. But understanding what this symptom means is key to early diagnosis and treatment.
(Read More: Tips on keeping your vagina healthy)
Symptoms of Vaginal Burning
While vaginal burning is a specific symptom in itself and can indicate a more complicated disorder, there are several tell-tale signs that you can look for when you experience a burning sensation in your vagina and are unsure of what it may be.
Vaginal burning may be experienced solely or there may be other accompanying symptoms that you can watch for, like:
- Redness, swelling or abrasion
- Unusual discharge from the vagina
- A distinct smell from the vagina and its secretions
- Pain or cramps in the vaginal region
- Painful urination
- Bleeding or spotting between periods
- Fish-like odour typically experienced after sex
Sometimes, the burning may come and go, while at other times, it remains constant and worsens during specific activities like urinating, exercising, or sitting for long periods. Keeping track of such patterns can help during diagnosis.
(Read More: Vaginal yeast infection symptoms)
Causes and Risk Factors
In some cases, vaginal burning may be due to a simple lack of hydration or sensitiveness to the underpants fabric. However, there are more serious problems, which could be showing themselves through this symptom. Here are some causes of burning in the vagina.
(Read More: Home remedies for UTIs)
Irritation
Sometimes vaginal burning is simply a reaction of the vagina experiencing irritation of some kind. It could be from synthetic or tight-fitting clothes and underwear, perfumes and other chemicals in soap, abrasion or friction of some kind or a minor injury. It can also be experienced because of residual parts of tampons or tissue from sanitary napkins remaining in or around the vagina.
Even new laundry detergents or certain wet wipes may trigger a reaction in some women, especially those with sensitive skin or allergies. Mild cases clear up once the irritant is removed.
(Read More: Parasitic infections symptoms)
Bacteria
Certain types of bacteria in the vagina may cause irritation and itching. All women have harmless bacteria present in their vagina, which is normal and helps maintain the pH of the vagina. When harmful bacteria grow, or if the normal bacteria present in the vagina grow into unusually large numbers, a burning sensation may develop. It is important to treat this immediately as it could cause STDs. Bacterial infections are most commonly experienced in women between the ages of 15 to 45 years.
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is the most common form, often triggered by douching, having multiple sex partners, or hormonal changes.
(Read More: How to wash your vagina)
Yeast
Yeast infections in the vagina may cause burning as one of the many symptoms. This condition is commonly called thrush. Thrush can be contracted in women who are pregnant, taking antibiotics or oral contraceptive pills, and have diabetes.
In warm, moist environments, the naturally occurring yeast (Candida albicans) can grow excessively. Women may notice thick, white, cottage cheese-like discharge along with burning and itching.
(Read More: Understanding Vaginal Pain)
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Burning is the most commonly experienced symptom in those who have UTIs. While this is easy to treat, the chances of recurrence are high.
Infections can affect any part of the urinary system – bladder, urethra, or kidneys. Women are more prone due to their shorter urethra. In many cases, vaginal burning is felt while urinating or shortly after.
(Read More: DIY Relief: Home Remedies for Managing Vaginal Pain)
Trichomoniasis
A parasite, Trichomonas, usually passed on to the partner while having sex, causes a common infection called Trichomoniasis and is the reason for burning sensation in the vagina, along with discomfort and itching.
It’s highly contagious and sometimes silent in men. In women, it may lead to frothy yellow-green discharge with a strong smell and inflammation.
(Read More: Home Treatments for Vaginal Burning)
Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhoea is a commonly transmitted STD in those between the ages of 15 to 25. The bacterial infection usually spreads into the cervix, fallopian tubes and uterus and may cause a burning sensation.
Often, symptoms appear within 10 days of exposure. It may also cause pelvic pain and irregular periods if left untreated.
(Read More: Chest Pain from Your Bra? What You Need to Know)
Chlamydia
While chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection, burning and itching make the most obvious of its symptoms; it is otherwise silent and shows no other signs.
In many women, chlamydia leads to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can cause long-term fertility issues if not treated early.
(Read More: Lump in Breast)
Genital Herpes
Herpes affects a large percentage of the female population and is among the most common reasons for experiencing vaginal burning.
Painful blisters, flu-like symptoms, and repeated outbreaks may occur. While there is no permanent cure, antivirals help reduce severity and frequency.
(Read More: Tubectomy Explained: Your Complete Guide)
Menopause
Women who are either approaching menopause or are already going through it may experience vaginal burning as a result of hormonal imbalance. While not every menopausal woman may experience burning, it is among the common physiological symptoms that are felt by menopausal women.
Declining estrogen levels cause vaginal thinning (atrophic vaginitis), dryness, and loss of elasticity, making the area more prone to discomfort and irritation.
(Read More: When To Have Sex After Tubectomy?)
Treatment Options
There are several courses of treatment that may be sought depending upon how the problem manifests and what the accompanying symptoms or conditions are. Women should seek help if the burning lasts for a prolonged period of time and doesn’t go away. The courses of treatment may include:
- A course of antibiotics to treat bacterial infections like chlamydia or gonorrhoea
- An antifungal cream and oral medication for fungal infections like thrush
- Antibiotics and repeat tests in the case of UTIs
- Oral metronidazole or tinidazole for trichomoniasis
- Anti-viral medication for herpes
- Hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women
Timely intervention is key. Left untreated, even common infections can lead to long-term complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease or recurrent discomfort.
(Read More: Home Remedies for Vaginal Yeast Infection)
Risk Factors
Here are some factors that predispose a woman to experience vaginal burning:
- Untreated bacterial infections
- UTIs spreading to the kidneys, urethra and bladder if untreated
- Poor personal hygiene
Other contributors include excessive sugar intake, immune disorders, hormonal imbalances, or chronic antibiotic use. Even psychological stress can indirectly worsen the risk.
(Read More: Navigating Vaginal Whitening: A Guide to Choices)
Prevention of Vaginal Burning
The following are some ways that vaginal burning can be prevented:
Make sure to keep the genital area clean. The best way to do so is using clean and cold water. Avoid using too many products or washing too frequently as it can dry the vaginal area and cause burning. Vagina has its own lubricating mechanism and using too many intimate care products may cause disbalance of the vaginal pH and healthy bacteria that inhabit the vagina.
- Avoid using soaps and chemicals to clean or opt for gentle feminine care products. Do not use regular soaps and gels to clean intimate areas. Avoid scented products. They have a higher amount of chemicals and may irritate your vaginal skin.
- Always use toilet paper from front to back while cleaning the intimate areas.
- Avoid using synthetic underwear, and ensure you change your underwear frequently. When washing your underwear, use only a mild non-scented detergent.
- Ensure your partner uses condoms during intercourse to prevent STDs.
- Stay away from sexual intercourse if you experience even minimal burning.
- If you have dryness, burning sensations could follow soon after. Use a mild vaginal moisturiser to keep your vagina hydrated, and use a lubricant before having sex.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to prevent dryness and irritation, which can, in turn, cause burning.
- Preventing relapses of UTIs by keeping your body clean and hydrated, and maintaining high levels of sanitisation.
- Wear loose-fitting clothes, especially in hot and humid climates
- Avoid prolonged sitting in damp workout clothes
- Opt for cotton menstrual products when possible
- Maintain a healthy gut to support immune health
(Read More: How to Keep Your Intimate Area Clean and Infection-Free)
Diagnosis of Vaginal Burning
A doctor will typically conduct a pelvic examination to check for the underlying cause of vaginal burning. This is usually followed by some simple blood or urine tests to confirm the diagnosis. A sample of the vaginal discharge may also be taken for examination in the case of suspected infections. Imaging tests are typically not needed to diagnose the cause of vaginal burning unless routine treatment doesn’t yield satisfactory results.
Doctors may also check your medical history, sexual habits, use of hygiene products, and recent stressors. In postmenopausal women, hormone levels might be checked to rule out atrophic vaginitis.
(Read More: Nourish from Within: The Top Foods for Optimal Vaginal Health)
Lifestyle Tips for Relief
Pointers to manage vaginal burning include:
- Avoid touching or scratching where burning is experienced. It will help the wound heal quickly
- Application of ice packs to help soothe the area
- Using petroleum jelly can also help soothe the area and reduce burning
- Taking probiotic supplements to restore vaginal flora
- Avoiding intercourse until fully healed
- Using sitz baths with plain water for 10–15 minutes
- Managing blood sugar levels if diabetic
- Practicing mindfulness or stress reduction, which helps hormonal balance
(Read More: Gokshura Benefits For Sexual Health)
FAQs on Vaginal Burning
Got questions!!
What causes a burning sensation in the vagina?
Burning in the vagina can be caused by infections (like yeast or bacterial vaginosis), irritation from soaps or clothing, sexually transmitted infections, or hormonal changes like menopause.
Is vaginal burning always a sign of an infection?
No. While infections are a common cause, it can also be due to non-infectious factors like dryness, friction, or allergic reactions.
(Read More: How to Take Care of a Woman After Delivery: Nutritional Tips)
How can I relieve vaginal burning at home?
Use cool compresses, wear breathable cotton underwear, avoid scented products, and stay hydrated. If symptoms last more than a few days, see a doctor.
When should I see a doctor for vaginal burning?
If the burning lasts longer than a couple of days, worsens, or comes with discharge, odor, or pain during urination or sex, it's best to consult a healthcare provider.
(Read More: Top Benefits of Aloe Vera for Radiant Facial Skin)
Can stress or anxiety cause vaginal burning?
Yes, chronic stress can weaken your immune system, making you more prone to infections or hormonal imbalances that may lead to burning sensations.
Is vaginal burning during menopause normal?
It can be. Hormonal changes during menopause can cause thinning and dryness in the vaginal walls, which may lead to burning or irritation.
(Read More: Nourish Your Body: Top Collagen-Rich Foods for Better Health)
Can I prevent vaginal burning?
Yes. Use gentle products, stay hydrated, wear breathable fabrics, and practice safe sex to help prevent irritation and infections.
Can I prevent vaginal burning?
Most cases are mild and easily treatable. However, if left unaddressed, it can lead to complications like infections, pain, or fertility issues.
(Read More: How to Lighten Dark Thighs at Home: Best Natural Solutions)
Does diet affect vaginal health?
Yes. A balanced diet with probiotics, sufficient water, and limited sugar can help maintain a healthy vaginal environment.
Can vaginal burning be a sign of cancer?
Rarely, persistent burning along with other symptoms like unexplained bleeding may warrant further investigation. Always consult a doctor if concerned.
(Read More: From Exfoliation to Hydration: The Benefits of Salt Scrubs)
Conclusion
Vaginal burning is a common yet often overlooked symptom that many women experience at some point in their lives. In most cases, it can be managed with simple self-care measures and lifestyle adjustments. However, when the burning sensation persists, becomes more intense, or is accompanied by unusual symptoms like discharge, odor, or pain, it should not be ignored. Seeking medical attention early can help identify the underlying cause—whether it's an infection, hormonal imbalance, or irritation—and ensure appropriate treatment. Left untreated, even seemingly mild symptoms can lead to complications such as reproductive tract infections, discomfort during intercourse, or increased risk of more serious infections. Maintaining good hygiene, using gentle products, staying hydrated, and being mindful of your sexual health can go a long way in preventing discomfort. Overall, listening to your body and not brushing off symptoms like vaginal burning is crucial for maintaining long-term reproductive health and well-being.
References
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention [internet], Atlanta (GA): US Department of Health and Human Services; Bacterial Vaginosis – CDC Fact Sheet
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention [internet], Atlanta (GA): US Department of Health and Human Services; Gonorrhea - CDC Fact Sheet
- Office on Women's Health [Internet] U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Vaginal yeast infections.
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention [internet], Atlanta (GA): US Department of Health and Human Services; Trichomoniasis - CDC Fact Sheet
- Office on Women's Health [Internet] U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Vaginal infections.
- Better health channel. Department of Health and Human Services [internet]. State government of Victoria; Vaginal thrush
- MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia: US National Library of Medicine; Vaginal itching and discharge - adult and adolescent
- MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia: US National Library of Medicine; Vaginal Diseases