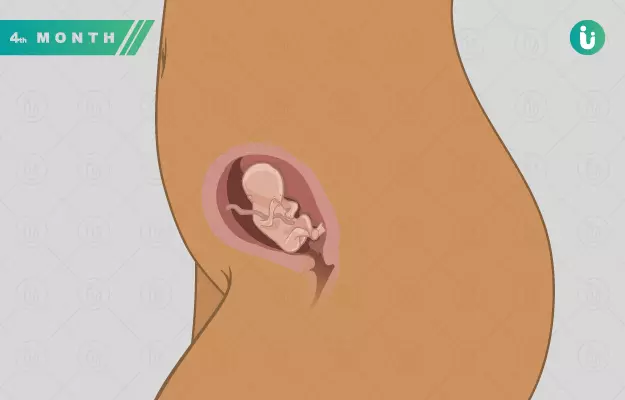
You have successfully advanced the first trimester of pregnancy and are entering the second trimester, beginning at the fourth month. This is the time you have finally accepted some of the body changes and very well reconcile with the fact that you are pregnant. With that comes a lot of gratification, all that the fourth month of pregnancy is about. It marks the month when ‘morning blues’ diminish and you feel a lot better physically and mentally.
The fourth month is a comfortable time for you and your pregnancy buddy, but it also witnesses some major foetal developments, which necessitate taking care of your health, particularly your diet. To help you with it, this article will share some diet tips, pregnancy tests, ultrasounds and all that you need to comfortably swing through this month. It also gives you an insight into the growth and development of the foetus during this month. So, get exploring
(Read more: Pregnancy month by month)
- 4 months pregnant symptoms
- 4 months pregnancy baby
- 4th month of pregnancy diet
- Exercise during the 4th month of pregnancy
- Diagnostic tests during the fourth month of pregnancy
- Vaccination during the 4th month of pregnancy
- Pregnancy fourth month: Dos and don’ts
4 months pregnant symptoms
While the annoying symptoms of morning sickness do not bother you anymore, it’s not that you do not experience any changes. Your body is still constantly evolving and adapting to host the baby in your womb. This is what happens in the fourth month of pregnancy:
- Nausea finally goes away but leaves behind heartburn, constipation and bloating.
- By now you have already put on some weight, and will continue to gain some more during this month at a faster rate. During the whole first trimester, you may have gained around 2 kgs of weight, but you are likely to gain an equal number during the fourth month itself. This obviously will make your belly look a bit bigger, giving a slight ‘pregnancy bump’. You may also feel a bit sore.
- This feeling of soreness may also be felt in your behind, which is usually a matter of concern. The risk of haemorrhoids or piles is high during the fourth month, so, it will be good if you see a doctor in case of any symptoms.
- As you gain weight, your breasts also continue to grow. You again need to go shopping for some better innerwear to support your growing breasts. During the fourth month, your nipples get darker and more tender. Your breasts also feel more tender and sore. (Read more: Breast changes in pregnancy)
- Shortness of breath may also be experienced by some and others may experience a nosebleed or bleeding gums or nasal stuffiness. The latter ones mainly due to an improved blood flow.
- Due to vascular changes, you may also feel dizzy sometimes.
The bright side
- Since nausea and fatigue step back, you will surely feel more energised. Now is the time, you will be able to do away without several day naps and can finally give more time to yourself. Join a club, read a book, go for a walk, exercise, whatever you like.
- With better energy, comes the feeling of euphoria. You are finally happy (and sure) that you are becoming a mother, and all your friends and family know that by now. Also, since nausea is gone, food aversions would also not stay, welcoming more food cravings.
- The new vigour and energy are also likely to affect your sex drive, of course in a good way. You may have more and better sex with your partner, which is good, right? Oh, you need not worry about the baby. It is safe within your uterus and the thickened linings are protecting it.
(Read more: Benefits of sex during pregnancy) - You feel more motherly and start awaiting the baby. You start buying baby stuff and clothes and foods and whatever you see. Wait, are you already thinking of baby names?
4 months pregnancy baby
After spending 3 months in your body, the baby is already quite comfortable. It is almost fully formed. The major organs have developed, it has a proper nutritional supply from the placenta; blood vessels of its own; it has also developed its muscles, tiny bones and limbs. Even the sex organs have formed and sex can be determined at this stage, but, that is a criminal offence in India. Let’s have a virtual look at your baby’s development during the fourth month.
(Read more: Symptoms of having a baby boy)
4-month pregnant baby size
The foetus at the beginning of four months is around 7 centimetres in length and grows doubly by the end of the 4th month, to achieve a size of 14 cm.
Baby development 4 months
Your baby is growing and maturing at 4 months. While his/her major organs have already formed, they just continue to differentiate more. The baby's eyelids form in this month, though they will remain fused above the eyes for a while. He/she will also develop eyebrows and eyelashes along with other body hair.
Your baby's fingers and toes, which were already formed, start growing nails and the foetus develops taste buds. The body of the baby continues to develop and differentiate, which reduces the appearance of a larger head and a smaller body.
Also, the sound of the foetal heartbeat is quite pronounced at this time and may be heard with the help of an ultrasound scanner.
(Read more: Fetal development month by month and week by week)
4 months pregnant baby movements
Does the foetus start moving during the fourth month? Yes. it definitely does. Although you may or may not feel it yet.
The foetus is quite in an active state in the fourth month, just like you. The minutest movements of the foetus include activities like thumb sucking, which is an essential skill to be developed for sucking milk after birth. Foetus can also perform vigorous movements like swimming within your womb.
Some other functions of the foetus may also be developed during the fourth month, like, faint crying or hiccups.
4th month of pregnancy diet
Diet is an important aspect to take care of during the fourth month so that all the foetal developments occur normally. Your body is constantly changing during pregnancy and so your diet must also. Following are a few diet essentials for month 4:
Increase calorie intake
During the first trimester of pregnancy, you must be having almost an equal amount of calories as your non-pregnant self (minus the food cravings). But, during the fourth month, marking the beginning of the second trimester, it is important to increase your calorie intake.
You are recommended to take a minimum of 2200 daily calories in your fourth month and may require even more based on your body needs.
To ensure this, it is advisable to have a balanced diet with increased calorie intake from healthy sources and a particular inclusion of the foods discussed in sections ahead.
(Read more: Pregnancy diet)
Increase fibre intake
Since constipation is a major problem during the fourth month, it is important to include more dietary fibres, both soluble and insoluble. Fibres have been evidenced to improve digestion and prevent constipation by adding bulk to your faeces. Also, they help in keeping you full for longer since they possess a better satiety index. This will help with the unmindful food cravings. To include more fibres in your diet, simply add more whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables with skin, whenever possible.
(Read more: Fibre-rich foods)
Have more water
This will help with the assimilation of fibres and will also help in keeping you energetic throughout the day. It is recommended to consume at least 2-3 litres each day. You may need more depending upon your weight and levels of physical activity.
(Read more: How much water to drink in a day)
Include more iron in your diet
Iron is essential during pregnancy for the avoidance of iron deficiency anaemia. Iron is important for blood formation, which is essential for foetal nourishment and prevention of abnormalities. Also, a deficiency of iron is associated with preterm birth, low birth weight and other anomalies.
WHO suggests taking 30 to 60 mg of iron during pregnancy to meet the growing needs.
This can be achieved by including dietary sources like green leafy vegetables, nuts, lentils, whole grains and legumes in your diet.
When increasing the consumption of iron through these natural plant sources, you must include more vitamin C in the diet to facilitate iron absorption.
(Read more: Vitamins and minerals you need during pregnancy)
Consume proteins
Proteins are the building blocks of life, which makes them an essential component of diet during pregnancy.
Research evidence suggests that milk and proteins promote foetal growth during pregnancy and their deficiency causes growth retardation. Since the baby is rapidly growing in size during the fourth month, it is important that you take enough proteins.
It is, however, recommended to include proteins in moderation in your diet and not eat more than 65 gm each day. This is because excess protein consumption during pregnancy can delay foetal growth.
(Read more: When to start protein powder during pregnancy)
Folic acid
Folic acid is involved in the formation of the neural tube and a deficiency of this vitamin causes neural tube abnormalities. However, it is usually not required in the fourth month of pregnancy since the development has already been completed.
Calcium
It is essential to include calcium in your diet to facilitate foetal bone growth, but additional supplementation is may not be required unless advised by the doctor.
Foods to avoid
You must refrain from the consumption of raw or undercooked eggs and raw or cold processed meats like pepperoni, salami, hotdogs etc since they carry parasites and cause infections. Also, seafood, sushi, tuna, cheese, raw milk, liver, fish oil supplements must be avoided. Other than this, excess caffeine or green tea/herbal tea consumption should be monitored as excess caffeine intake holds the risk of low birth weight. So, more than 4 cups of tea or coffee must not be consumed per day.
(Read more: Reasons for underweight baby)
Exercise during the 4th month of pregnancy
Exercising is completely safe during the fourth month of pregnancy. Since you feel more energised now, you can opt for a variety of physical activities like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, jogging or even yoga. If you were physically active before pregnancy, you can resume the same routine with your trainer’s consult. However, if you are new to exercising, begin your routine by starting a 30-minute session daily and then increase gradually.
Exercising will help in avoiding excess weight gain reducing the risk of gestational diabetes and gestational hypertension. It will also help in improving digestion ridding you of constipation and other digestive issues.
However, if symptoms like pain, headache, dizziness, shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling, muscle weakness or vaginal discharge are observed, you must stop exercising and see a doctor.
(Read more: Exercises during pregnancy)
Diagnostic tests during the fourth month of pregnancy
A combined screening test is recommended for the fourth month, if not already done at week 12. Performed at week 16, it consists of an ultrasound and a maternal blood test to detect foetal abnormalities and infections respectively. Ultrasound will also help in detecting the position of the baby.
During the fourth month, foetal heart sound can also be detected with the help of these ultrasounds.
(Read more: Ultrasound during pregnancy)
Vaccination during the 4th month of pregnancy
It is important to get vaccinated during pregnancy if you have not been vaccinated before. This will help in protecting you and your baby since antibodies will be passed to the foetus. Though it is safe during pregnancy, vaccination can cause complications like swelling, pain or fever, so, it is best to consult with your doctor about it.
It is recommended to get vaccinated for flu (influenza) and whooping cough at the earliest to prevent these in infants. This will protect infants till the time they can get vaccinated. Flu shot additionally protects infants from the risk of serious complications like pneumonia.
(Read more: Vaccination during pregnancy)
Pregnancy fourth month: Dos and don’ts
Here is a list of dos and don’ts, which can act as a guide on what to do and avoid during pregnancy.
Dos
- Eat a balanced diet
- Exercise regularly
- Go to work
- Have sex
- Be physically active
- Opt for your favourite hobby
- Go out with friends
- Wear a supportive bra
- Get ultrasound and blood test
- See your doctor regularly
- See your doctor in case of soreness in the stomach and the behind
- Go baby shopping
Don’ts
- Calorie restriction
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Performing intense physical activities
- Wearing the wrong size of bra
- Skipping doctor’s appointments
- Taking unprescribed supplements like vitamins or folic acid
- Going overboard with protein consumption
- Consuming a predominantly non-vegetarian diet consisting of raw meats, fish and eggs
- Not washing fruits before eating
- Prenatal sex determination
- Employing home remedies or herbal remedies
References
- Planned Parenthood Federation of America. What happens in the fourth month of pregnancy?. [Internet]
- Better health channel. Department of Health and Human Services [internet]. State government of Victoria; Pregnancy - week by week
- World Health Organization [Internet]. Geneva (SUI): World Health Organization; Daily iron and folic acid supplementation during pregnancy.
- Fatemeh Borazjani et al. Milk and Protein Intake by Pregnant Women Affects Growth of Foetus . J Health Popul Nutr. 2013 Dec; 31(4): 435–445. PMID: 24592584
- Karen M Switkowski et al. Maternal protein intake during pregnancy and linear growth in the offspring. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016 Oct; 104(4): 1128–1136. PMID: 27581477
- Roger L. Hammer et al. Exercise During the Childbearing Year. J Perinat Educ. 2000 Winter; 9(1): 1–14. PMID: 17273187
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists [Internet] Washington, DC; Exercise During Pregnancy