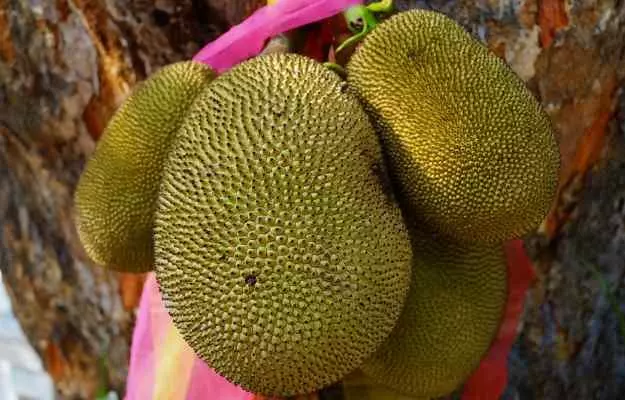
Jackfruit, commonly known as kathal, is a tree belonging to the Moraceae family. Its fruit is widely popular in tropical climates. It has a sweet taste when ripe and is fleshy on the inside. The fleshy part, also known as the bulb, can be eaten as such or used in various recipes. The fruit when still green in colour, ie unripe is remarkably similar in texture to chicken, which makes jackfruit a favoured vegetarian substitute for meat. Jackfruit is also canned in a brine solution which is sometimes referred to as vegetable meat.
The fruit has been popularly used in traditional Chinese medicine for various purposes.
The tree of jackfruit is about 50 to 60 feet in height and has a long lifespan, usually more than 100 years. It bears fruits in the rainy season between the months of May and August. A mature jackfruit tree can produce about to 100 to 200 fruits in a season. The fruits of the jackfruit tree are the largest tree-borne fruits and can weigh up to 55 kgs.
The ideal growing locations for the jackfruit tree are tropical lowlands. The tree is widely cultivated and is a popular food item throughout the tropical regions of the world. Jackfruit is a commonly used ingredient in South and South-east Asian cuisines. It is the national fruit of Sri Lanka and Bangladesh.
The state of Kerala in India is the largest producer of jackfruit in the world.
Some basic facts about jackfruit (kathal)
- Botanical Name: Artocarpus heterophyllus
- Family: Moraceae
- Common Name: Jack tree, fenne, jakfruit,
- Sanskrit Name: Kathal
- Parts Used: Fruits, seeds, fleshy flower petals
- Native Region and Geographical Distribution: Native to the tropical regions, especially South and South-east Asia
Jackfruit nutrition
Nutritional value of jackfruit is as follows:
| Nutrients | Value per 100g |
| Energy | 95 kcal |
| Water | 73.46 |
| Carbohydrate | 23.25 mg |
| Protein | 1.72 mg |
| Fats (Total lipids) | 0.64 mg |
| Fiber | 1.5 mg |
| Sugars | 19.08 mg |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A | 5 mg |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.105 mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.055 mg |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.920 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.329 mg |
| Vitamin B9 | 0.024 mg |
| Vitamin C | 13.7 mg |
| Vitamin E | 0.34 mg |
| Minerals | |
| Potassium | 448 mg |
| Calcium | 24 mg |
| Magnesium | 29 mg |
| Phosphorus | 21 mg |
| Sodium | 2 mg |
| Iron | 0.23 mg |
| Zinc | 0.13 mg |
| Fats | |
| Total | 0.195 mg |
| Monounsaturated | 0.155 mg |
| Polyunsaturated | 0.094 mg |
| Trans | 0 mg |
Jackfruit benefits
Jackfruit, in addition to being great in taste, is rich in a number of nutrients. The wide number of bioactive compounds found in the fruit imparts a variety of health benefits have been discussed in detail below.
Jackfruit for energy
Jackfruit has a substantial amount of carbohydrates which is ideal for a quick boost of energy without fat content. The fruit contains sucrose and fructose that can be easily digested by the body. The sugar content in this fruit is listed under the category called SAG (Slowly Available Glucose) which has the characteristic of releasing glucose in a slow pulsatile manner; hence, resulting in the low glycemic index of the fruit. This makes the fruit a favoured energy enhancer even for people with diabetes, as regulated amounts do not involve the risk of hyperglycemia.
Jackfruit for digestion
Jackfruit is an abundant source of dietary fibre. Fibres help in improving digestion and preventing constipation. Its ability to prevent constipation further helps in the prevention of haemorrhoids. Additionally, jackfruit makes for an effective laxative that softens stool by adding significant bulk, so that faecal waste can be eliminated efficiently. Studies have found that consuming jackfruit can keep conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome at bay.
Jackfruit for anaemia
Jackfruit contains a high amount of iron. Iron, as we all know, is required for the haemoglobin component of the red blood cells, which prevents anemia. The Vitamin C component of jackfruit helps iron absorption in the body as the body’s potential to absorb iron is increased in the presence of this vitamin. Additionally, jackfruit is also rich in magnesium and copper, both important minerals that aid in the blood building process.
Jackfruit for the heart
Another important nutrient found in jackfruit in sufficient amounts is potassium. This nutrient promotes overall cardiovascular health along with performing several other functions in the body. A deficiency in potassium can upset natural contractility of the heart and the flexibility of the blood vessels. Potassium also maintains proper muscle coordination and functioning of the heart. The body also needs potassium to maintain normal blood pressure. In addition, regulation of sodium and electrolyte balancing is also maintained by potassium. All these contribute towards maintaining a good heart health.
Jackfruit for asthma
Asthma is a respiratory problem that affects a large number of people ranging from children to adults. There is no known cure for the disease but its symptoms can be managed. Asthma can be triggered by air pollution and air debris, especially when your immune system is weak. Studies have found that inhaling the steam of boiled jackfruit can help alleviate symptoms of asthma, possibly by means of releasing the heat labile bioflavonoids found in the fruit.
Jackfruit for eye health
Consuming jackfruit can prove to be beneficial for the eyes. Jackfruit contains Vitamin A and certain other carotenoids which are essential for the eyes. Lutein, one of the carotenoids found in jackfruit, plays a role in regulating the amount of light that enters the eyes thus, helping to preserve the integrity of the retina and the optic nerve.
Vitamin A and related compounds aid in keeping the mucous membrane of the cornea intact. This membrane acts as a natural barrier against bacteria that are generally found in our surroundings. Additionally, studies have found that jackfruit consumption can slow down eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and help in protecting your vision.
Jackfruit for the skin
Jackfruit has anti-ageing properties owing to its rich antioxidant content which can work wonders for the skin. The process of ageing is contributed by factors such as pollution, exposure to harmful UV rays and an unhealthy lifestyle. Jackfruit delays the effects of ageing as antioxidants destroy and neutralise free radicals. The high water content of jackfruit also helps to keep the skin hydrated and moisturized. Keeping the skin hydrated makes it more supple and visually radiant.
The flavonoids present in jackfruit also help to reduce hyperpigmentation of the skin due to their ability to inhibit tyrosinase, the key enzyme that synthesizes the skin darkening pigment, melanin.
Jackfruit for the bones
Dietary intake of jackfruit can help to keep bones strong and healthy as it has high amounts of calcium. This is beneficial, especially for people with lactose intolerance. Calcium increases bone density, making them less prone to fracture and preventing the risk of diseases such as rickets and osteoporosis. The potassium component of jackfruit also minimizes the loss of calcium through the kidney.
Jackfruit as anti-inflammatory
Jackfruit has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties. Besides being rich in anti-oxidants, the other bioactive compounds present in jackfruits such as flavonoids, especially flavones, xanthones, isoflavones, chalcones, and prenylated stilbenes contribute to its anti-inflammatory properties.
Jackfruit for the immune system
Jackfruit hosts a wide variety of antioxidants. The body needs antioxidants to strengthen the immunity system and fight against common problems such as a runny nose and cold, along with slowing down the signs of ageing.
Jackfruit is an excellent source of the natural antioxidant, Vitamin C. This vitamin is water soluble and is not produced in the body naturally. It is, therefore, necessary that Vitamin C is consumed in the diet through fruits such as the jackfruit.
Antioxidants are required to neutralize the free radicals that damage cells. Eliminating free radicals from the body ensures that it functions as it should, and is not subjected to the effects of premature and accelerated damage.
Jackfruit for cancer
Jackfruit is healthy dietary inclusion because of its anti-oxidative and phytonutrient properties. Additionally, lectins, a type of bioactive compound present in jackfruit helps the body to get rid of toxins along with neutralising free radicals. Studies are suggestive of the fact that these compounds in jackfruit can contribute towards preventing cancer. Further studies are, however, required in this regard to establish this fact.
Side effects of jackfruit
The possible side effects of consumption of jackfruit have been mentioned below.
- People allergic to birch pollen or latex could also develop allergies upon jackfruit consumption. This is because of the similarity of the type of allergens present in jackfruit, natural latex, and pollen.
- Lectins found in the seeds of jackfruit can stimulate the immune system. This could, however, negatively impact patients with tissue transplants or immunosuppression therapy.
- Jackfruit may have an effect on blood coagulation and people with blood disorders should consume it with caution.
- Consumption of jackfruit may have certain negative effects on libido, sexual arousal, sexual vigour, and sexual performance in men.
- There are not enough studies on the effect of jackfruit during pregnancy and breastfeeding, so, its consumption in these stages can be avoided.
- Jackfruit may cause drowsiness if combined with medications when used during and after surgery. It is advisable to stop the consumption of jackfruit at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
References
- Hai Xuan Nguyen et al. Tyrosinase inhibitory activity of flavonoids from Artocarpus heterophyllous . Chem Cent J. 2016; 10: 2. PMID: 26834825
- Guillaume Poiroux et al. Plant Lectins Targeting O-Glycans at the Cell Surface as Tools for Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis and Therapy . Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun; 18(6): 1232. PMID: 28598369
- Xue Yao et al. Moracin C, A Phenolic Compound Isolated from Artocarpus heterophyllus, Suppresses Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Inflammatory Responses in Murine Raw264.7 Macrophages . Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug; 17(8): 1199. PMID: 27463712
- Vidyadhara Suryadevara et al. Studies on jackfruit seed starch as a novel natural superdisintegrant for the design and evaluation of irbesartan fast dissolving tablets . Integr Med Res. 2017 Sep; 6(3): 280–291. PMID: 28951842
- Yi-Tzu Fu et al. Extracts of Artocarpus communis Decrease α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone-Induced Melanogenesis through Activation of ERK and JNK Signaling Pathways . ScientificWorldJournal. 2014; 2014: 724314. PMID: 24737988
- Anubhuti Sharma, Priti Gupta, A. K. Verma. Preliminary nutritional and biological potential of Artocarpus heterophyllus L. shell powder . J Food Sci Technol. 2015 Mar; 52(3): 1339–1349. PMID: 25745202
- Maria A. Souza et al. The immunomodulatory effect of plant lectins: a review with emphasis on ArtinM properties . Glycoconj J. 2013; 30(7): 641–657. PMID: 23299509
- Akshatha Shrikanta, Anbarasu Kumar, Vijayalakshmi Govindaswamy. Resveratrol content and antioxidant properties of underutilized fruits . J Food Sci Technol. 2015 Jan; 52(1): 383–390. PMID: 25593373
- United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service. Basic Report: 09144, Jackfruit, raw . National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference Legacy Release [Internet]