Ever wondered why everyone keeps talking about Vitamin D, or why getting a little sun feels so good? It's not just a fad! Vitamin D, often dubbed the "sunshine vitamin," is a powerhouse nutrient crucial for far more than just healthy bones. From bolstering your immune system and enhancing your mood to even influencing hair growth and muscle strength, its impact on our overall well-being is truly astounding.
But how exactly do we get this vital vitamin? Is it just about soaking up some rays, or are there other reliable sources? And once we have it, what incredible benefits does it unlock for every stage of life, from a child's growing bones to an elder's resilience? Let's dive in and explore the multifaceted world of Vitamin D, understanding its sources, its widespread benefits for different age groups and body systems, and importantly, how to ensure you're getting just the right amount to thrive.
- How Do I Get Vitamin D From the Sun?
- How Much Sun Exposure is Enough?
- Sources of Vitamin D
- Study About the Overall Health Benefits of Vitamin D
-
Benefits Of Vitamin D
- Benefits of Vitamin D for Children
- Benefits of Vitamin D For Elders
- Benefits Of Vitamin D For Women
- Does Vitamin D Help Skin?
- Is Vitamin D Good for Bones?
- Does Vitamin D Helps With Fracture?
- Does Vitamin D Help Heal Injuries?
- Vitamin D for Healthy Teeth - Vitamin D deficiency
- Is Vitamin D Good for Hair?
- Does Vitamin D Improves Muscle Growth?
- Does Vitamin D Increase Stamina?
- Can Vitamin D Help in Weight loss?
- Benefits of Vitamin D for Cancer Patients
- Dosage of Vitamin D
- Side Effects of Vitamin D
- Summary
How Do I Get Vitamin D From the Sun?
Getting Vitamin D from the sun is a natural and efficient process, as your skin produces this vital vitamin when exposed to specific ultraviolet B (UVB) rays. Here's how it works and what factors influence it:
When sunlight hits your skin, the UVB photons are absorbed by a compound called 7-dehydrocholesterol, which is present in your skin cells. This compound is then converted into pre-vitamin D3. Pre-vitamin D3 rapidly transforms into Vitamin D3 within your skin's plasma membrane. This Vitamin D3 then travels to your liver and kidneys, where it undergoes further conversions to become the active form of Vitamin D (calcitriol) that your body can use.
Several factors influence how much Vitamin D your body produces from sun exposure:
- Time of Day
- Season
- Skin Pigmentation
- Latitude
- Amount of Skin Exposed
- Cloud Cover and Pollution
- Glass and Clothing
How Much Sun Exposure is Enough?
There's no single universal recommendation because it varies so much by individual and environmental factors. However, a general guideline is to expose a good portion of your skin (e.g., arms, legs, face) to direct sunlight for 10-30 minutes, 2-3 times per week, during the peak UVB hours for your location and season. People with darker skin may need longer exposures.
Read More: (Effective Home Remedies for Sun Tan Removal)
Sources of Vitamin D
The most natural and efficient way to obtain Vitamin D is through natural sunlight exposure. Your skin produces Vitamin D when exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) rays. While natural sunlight is ideal, it's not always practical or safe for everyone. Therefore, it's important to consider other reliable sources:
Other Sources of Vitamin D:
Food Sources:
- Egg yolk
- Fishes like tuna, herring and salmon
- Cheese
- Beef Liver
- Cod liver oil
- Oysters
- Shrimp
- Milk, soy milk, and their products.
- Certain packaged food,s like cereals and oatmeal.
Supplements:
- Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol)
- Vitamin D2 (Ergocalciferol)
Study About the Overall Health Benefits of Vitamin D
This article, written by William B. Grant and Michael F. Holick and published in 2005, is basically a deep dive into why Vitamin D is so important for our health. It explains that having enough Vitamin D isn't just a good idea; it's absolutely necessary for our bodies to work their best at any age. They really highlight how Vitamin D helps our bodies take in calcium, which is super important for strong bones.
The authors looked at a lot of research from the twenty years before their paper came out. This research showed that Vitamin D does a lot more than just help bones. It can lower the risk of getting serious diseases like cancer, multiple sclerosis, and a type of diabetes. They also mentioned that at the time, experts in the United States were thinking about saying we need more Vitamin D than previously thought, especially because of its benefits for soft parts of our bodies, not just bones. The study makes it clear what "enough" Vitamin D means in your blood: if your levels are below 20 ng/mL, you're deficient; between 20-32 ng/mL, you have some but not enough; and anything above 33-80 ng/mL is considered good. They found that many people in places like the UK and Europe don't have enough Vitamin D, which leads to many early deaths from cancer. In the U.S. alone, they estimated that tens of thousands of people die prematurely from cancer each year because they don't have enough Vitamin D.
So, what should we do? The article strongly suggests that getting some sunlight is the main way most people get their Vitamin D. They say that getting a moderate amount of sun is generally good for you and the benefits usually outweigh any risks. But if you can't get enough sun, then you can get Vitamin D from foods that have it added (like some milk or cereals), oily fish, supplements, or even special lights that mimic the sun. The main message is that public health efforts should really focus on making sure everyone gets enough Vitamin D, because it's so important for staying healthy.
To wrap it up, this study clearly states that having enough Vitamin D is vital for good health and for protecting us from various diseases. It urges that governments and health organizations should understand how crucial Vitamin D is and take steps to help people get enough of it.
Benefits Of Vitamin D
Benefits of Vitamin D for Children
Due to its astounding effects on bone health, vitamin D is essential during the stages of bone growth and formation, that is, among infants and children. Children are often prescribed vitamin D supplements to promote stronger bones and to reduce the likelihood of developing rickets, which develops during the growing stage of an individual.
Vitamin D has other unexpected benefits for the health of your infant/child. Supplementation with vitamin D has been evidenced to reduce the incidence of childhood diseases like eczema, atopic dermatitis and asthma, by enhancing the infant’s immunity. Supplementation with 2000 IU daily has been known to be helpful in the management of steroid-resistant asthma.
Read more: (Sunburn symptoms)
Benefits of Vitamin D For Elders
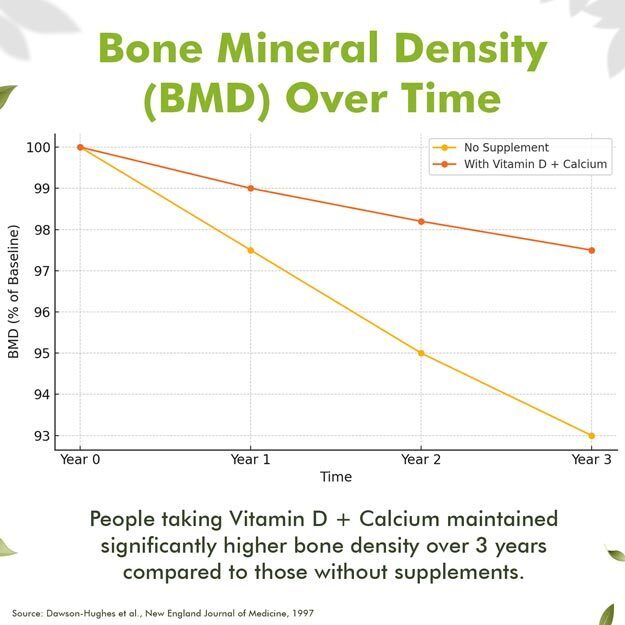
It is believed that peak bone mass is attained by the third decade of life through nutrition, genetics, lifestyle and physical factors. Following this, bone loss or reduction in bone mass density occurs beginning in the fourth decade. Researchers have proven that insufficient consumption of vitamin D during these phases can accelerate the process of bone mineralisation and loss. Thus, vitamin D supplementation is often prescribed during advancing age to prevent massive bone loss.
Benefits Of Vitamin D For Women
Vitamin D offers a wide array of benefits particularly important for women's health throughout their lives. Primarily, it's indispensable for strong bones. It facilitates the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, vital minerals for bone formation and density. This is especially crucial for women, who face a higher risk of osteoporosis, especially post-menopause, due to hormonal shifts. Adequate vitamin D, often alongside calcium, helps prevent bone loss and reduces the likelihood of debilitating fractures.
Beyond bone health, vitamin D significantly supports the immune system, helping the body defend against infections like colds and flu. It also plays a role in regulating immune responses, which may lessen the risk of autoimmune conditions.
For women, its impact on hormonal balance is noteworthy. Vitamin D receptors are found in reproductive tissues, and it's involved in processes that can influence menstrual regularity and alleviate period pain due to its anti-inflammatory properties. During pregnancy, sufficient vitamin D levels are linked to healthier outcomes for both mother and baby, supporting fetal development and potentially reducing risks of complications like preeclampsia and gestational diabetes. For women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), vitamin D supplementation has shown promise in improving insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance.
Furthermore, vitamin D contributes to mental well-being. Low levels have been associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety, and some research suggests that supplementation can help improve mood symptoms. It's also vital for proper muscle function, which is particularly beneficial for older women in maintaining mobility and reducing the risk of falls.
Read more: (Early menopause and premature menopause)
Does Vitamin D Help Skin?
Vitamin D plays a significant and multifaceted role in maintaining healthy skin. While often recognized for its role in bone health, its influence on the skin is substantial, making it a key player in dermatological well-being.
One of the primary benefits is its contribution to skin barrier function. Vitamin D regulates the production and differentiation of keratinocytes, the main cells in the outermost layer of the skin (epidermis). These cells are critical for forming a strong and intact skin barrier, which acts as a protective shield against harmful microbes, toxins, and environmental stressors, while also preventing excessive moisture loss and maintaining skin hydration.
Vitamin D also has potent anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. It helps regulate the skin's immune responses, which is crucial in managing inflammatory skin conditions. This is why topical vitamin D analogues are often prescribed for conditions like psoriasis, where it helps control the rapid and abnormal proliferation of skin cells and reduces inflammation. Similarly, it shows promise in alleviating symptoms of atopic dermatitis (eczema) by strengthening the skin barrier and reducing inflammation. Its anti-inflammatory effects can also help to soothe general skin irritation and redness.
The vitamin exhibits antimicrobial effects on the skin. It activates certain receptors that help kill harmful microorganisms on the skin's surface, contributing to the skin's natural defense against infections. This can be beneficial in managing conditions like acne, where bacterial overgrowth plays a role.
Furthermore, vitamin D is involved in regulating sebum production by influencing the function of sebaceous glands. These glands produce the natural oils that keep skin moisturized and supple. Balanced sebum production can lead to clearer skin and fewer breakouts.
In terms of anti-aging and photoprotection, research suggests that vitamin D may offer benefits. It induces antioxidant responses, helps inhibit DNA damage, and promotes DNA repair mechanisms within skin cells, which can attenuate premature skin aging caused by UV radiation. While not a substitute for sunscreen, some studies indicate that topical application of vitamin D3 may help reduce UV-induced cell death and redness. It also plays a role in collagen synthesis and inhibits enzymes (matrix metalloproteinases, or MMPs) that break down collagen, which helps maintain skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. It also supports the skin's regenerative processes, potentially promoting faster and more effective healing of damaged skin.
Is Vitamin D Good for Bones?
The most well-known effects and benefits of vitamin D are on your bone health. Vitamin D aids the absorption of calcium and phosphate in your body from food sources and supplements. Now, as we all know, calcium is very essential for the formation of a healthy bone structure. Vitamin D thus regulates and promotes healthy bone growth in your body, making your bones stronger and giving them the right frame.
This mechanism can be disturbed in case of deficiency of vitamin D, which can lead to soft or malformed bones and an increased risk of rickets (in children) or osteomalacia (in adults). To avoid this and enhance bone mineralization particularly if you experience bone pain, supplementation with vitamin D is often suggested.
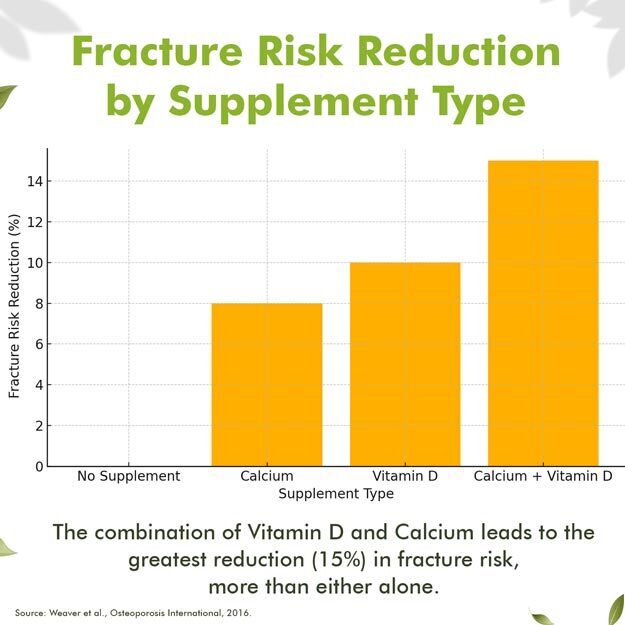
Does Vitamin D Helps With Fracture?
As discussed above, a reduction in bone mass density occurs with an advancing age, which makes the bones weaker and more prone to fractures. Researchers have claimed that a deficiency of vitamin D leads to a reduction in calcium absorption, which causes the release of calcium ions from the bone to maintain normal concentrations of calcium in the blood. Studies have also demonstrated a direct relationship between a decrease in bone mass density and an increased risk of fractures, which can be prevented by taking vitamin D in sufficient quantities either from dietary sources or as supplements. if so prescribed by your physician.
Does Vitamin D Help Heal Injuries?
Yes, Vitamin D plays a crucial role in the healing process of various injuries, from mending broken bones to repairing damaged skin and soft tissues. Its beneficial influence spans multiple stages of recovery, largely due to its involvement in inflammation control, immune response, cell growth, and tissue regeneration.
In the healing of skin and soft tissue wounds, Vitamin D exerts several key effects. It helps regulate the initial inflammatory response, preventing excessive inflammation that could impede healing. It also aids the immune system in fighting off infections within the wound, which is critical for proper closure. Furthermore, Vitamin D influences the growth and differentiation of cells essential for wound repair, such as skin cells (keratinocytes) and collagen-producing cells (fibroblasts), thereby promoting the formation of new tissue. While Vitamin C is a direct cofactor for collagen synthesis, Vitamin D indirectly supports this by influencing cellular pathways and fostering a regenerative environment. Some research also suggests Vitamin D might promote angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients to healing tissues.
For muscle injury recovery, Vitamin D is vital for optimal muscle function and repair. Deficiency can lead to muscle weakness and potentially prolong recovery time after injuries. It's believed to impact muscle protein synthesis and reduce inflammation, both of which are beneficial for muscle healing.
More broadly, Vitamin D is involved in overall tissue regeneration processes. It influences various genes related to cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue remodeling, all of which are essential for repairing and rebuilding damaged tissues throughout the body.
Vitamin D for Healthy Teeth - Vitamin D deficiency
Dental caries or tooth decay refers to demineralization and destruction of the tooth structure, which can or cannot be painful depending upon the structures affected. Once initiated, the disease is irreversible but treatable with the help of dental drills and filling materials. Since it is not possible to reverse tooth decay, it is essential to prevent it from happening.
While maintaining your oral hygiene and consuming less sugar is the key to prevention, research evidence also suggests that vitamin D helps to reduce the risk of dental caries when given to children and adults. Since the tooth structure is majorly made of calcium ions (calcium phosphate), dietary supplementation with vitamin D at this stage will help to channelize calcium ions, resulting in stronger teeth that are more resistant to decay.
Read more: (Five foods to make your teeth and gums stronger)
Is Vitamin D Good for Hair?
Yes, Vitamin D is indeed very beneficial for hair health, and surprisingly, a common contributor to hair loss and thinning is often an overlooked deficiency in this vitamin. The direct link between Vitamin D and hair stems from its influence on hair follicles and their growth cycle.
Hair follicles, the tiny structures from which hair grows, constantly cycle through phases of growth, transition, and rest. Vitamin D plays a critical role in regulating this cycle. Hair follicles contain specific Vitamin D receptors, and when Vitamin D binds to these, it helps stimulate the production of new hair follicles and activates the anagen, or growth, phase. This is the stage where hair actively grows and achieves its thickness. If Vitamin D levels are inadequate, this crucial cycle can be disrupted, leading to a shortened growth phase and an extended resting phase, which ultimately results in increased shedding and thinner-looking hair.
Beyond regulating the existing cycle, Vitamin D is also directly involved in the formation of brand new hair follicles. These new follicles are essential for maintaining hair density and preventing premature hair loss, and sufficient Vitamin D ensures a healthy supply of these new growth sites.
Does Vitamin D Improves Muscle Growth?
Vitamin D has a positive impact on muscle strength and mass and also on the physical strength, capabilities and performance of an individual. It regulates the calcium levels of the body, which help in regulating muscle strength and functioning and deficiency of this vitamin causes muscle cramps. Several studies have also reported a significant reduction in the rate of falls among individuals, which is suggestive of improved muscle mass and balance. The impact of vitamin D on muscle fibres and its morphology is yet to be studied.
Does Vitamin D Increase Stamina?
Yes, Vitamin D can significantly contribute to increased stamina and overall energy levels, particularly if you have a deficiency. Its impact on stamina is multifaceted, stemming from its crucial roles in muscle function, oxygen utilization, and reducing fatigue.
One of the primary ways Vitamin D affects stamina is through its influence on muscle function. Vitamin D receptors are present in skeletal muscle tissues, and the vitamin plays a vital role in muscle protein synthesis, muscle strength, and muscle fiber growth and differentiation (especially fast-twitch fibers, which are important for power and explosive movements). If you're deficient in Vitamin D, you might experience muscle weakness, aches, and reduced physical performance, all of which directly impact your stamina during physical activity. Correcting a deficiency can lead to improved muscle strength and faster recovery after exercise, thereby boosting endurance.
Beyond direct muscle impact, Vitamin D is also thought to play a role in oxygen utilization. Some studies suggest that adequate Vitamin D levels are associated with a higher oxygen consumption rate (VO2 max), which is a key indicator of aerobic fitness and endurance capacity. This means your body might be able to use oxygen more efficiently during prolonged activity, contributing to better stamina.
Furthermore, Vitamin D's ability to reduce fatigue is a major factor in perceived stamina. Fatigue is a common symptom of Vitamin D deficiency, and numerous studies have shown that correcting low Vitamin D levels can significantly improve self-perceived fatigue and overall energy levels. This can make a substantial difference in an individual's ability to sustain physical or mental effort for longer periods.
Lastly, Vitamin D's anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties also indirectly contribute to stamina. By reducing inflammation and supporting a robust immune system, Vitamin D helps the body recover more effectively from the stress of exercise and reduces the likelihood of illness. When you're less prone to inflammation or infections, your body can allocate more energy towards physical performance and maintaining stamina.
Can Vitamin D Help in Weight loss?
Foods rich in vitamin D often have appetite suppressant actions, which helps in weight loss. Individuals who are already on a restrictive diet for weight reduction are often recommended to add vitamin D rich foods in their diet, to boost their energy levels, which prevents fatigue and dizziness and enhances their exercise performance. This ensures that the journey of weight loss is healthy and less stressful.
Read more: (Seven common weight loss mistakes)
Benefits of Vitamin D for Cancer Patients
It has been a common observation that people living in areas of sunshine are less likely to develop certain cancers. Researchers have often debated the relationship of this observation with higher levels of vitamin D in them. In fact, lower levels of vitamin D have been suggestive of certain types of cancers. Majority of studies have proven the protective relationship of vitamin D on the body for reducing the risk of cancer, particularly colorectal cancer. Thus, vitamin D supplements have often been suggested to reduce cancer risk and mortality.
Dosage of Vitamin D
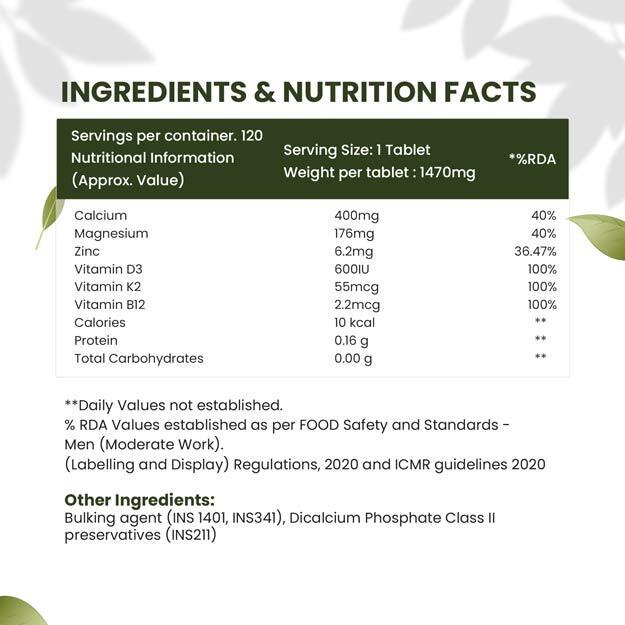
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has recently released a report on how much vitamin D should be taken daily? This report has been prepared keeping in mind the needs and health of the Indian population. Vitamin D aids in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the body, strengthens bones and strengthens the immune system. In the new report of FSSAI, the required daily amount of vitamin D for different age groups has been divided into the following categories:
1. Children (1-9 years)
Vitamin D is important for the growth of children and proper bone formation. According to FSSAI, children aged 1-9 years need 400 IU (international units) of vitamin D daily. This amount helps in strengthening the growing bones of children.
2. Teenagers (10-18 years)
Bone growth occurs rapidly in adolescence, so the need for vitamin D is higher for this age group. FSSAI recommends 600 IU of vitamin D daily for adolescents aged 10-18 years. This amount is essential for bone development and overall health.
3. Adults (19-70 years)
It is important for adults to maintain adequate vitamin D levels to maintain bone strength and immune system power. According to FSSAI, adults aged 19-70 years need 600 IU of vitamin D daily.
4. Senior citizens (above 70 years)
Senior citizens are at a higher risk of bone weakness and vitamin D deficiency. Therefore, senior citizens above 70 years of age should take 800 IU of vitamin D daily, this amount helps in maintaining strong bones and reducing the risk of falls.
5. Pregnant and lactating women
Pregnant and lactating women need adequate vitamin D for their and their baby's health. 600 IU of vitamin D per day is essential for the bone development of the baby and the health of the mother.
Side Effects of Vitamin D
While Vitamin D is essential for good health, taking too much can lead to adverse effects, primarily due to a condition called Vitamin D toxicity, also known as hypervitaminosis D. This condition is almost exclusively caused by excessive intake of Vitamin D supplements, not by sun exposure or dietary intake.
The main problem with Vitamin D toxicity is that it leads to hypercalcemia, which is an abnormally high level of calcium in the blood. This occurs because Vitamin D's primary role is to help your body absorb calcium from food. When Vitamin D levels are excessively high, calcium absorption goes into overdrive, leading to a dangerous buildup of calcium in the bloodstream.
Here are the key side effects and symptoms associated with Vitamin D toxicity and hypercalcemia:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Stomach pain
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Kidney stones
- Kidney damage and failure
- Drowsiness and lethargy
- Confusion and disorientation
- Apathy
- Irritability
- Arrhythmias
- Muscle weakness
- Unexplained weight loss
Read More: (Melasma or dark spots on the skin)
Summary
We've explored the fascinating journey of Vitamin D, from its natural synthesis in your skin through sun exposure to its crucial roles across various aspects of health. The sun remains our most natural source, with specific timings and factors like skin tone and latitude influencing how much we produce. When sun exposure isn't enough, we learned about valuable dietary sources like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods, along with the convenience of supplements (Vitamin D3 being generally more effective than D2).
The discussed Vitamin D's profound benefits across the lifespan: vital for children's bone growth and immunity (reducing risks of rickets, eczema, and asthma), and essential for elders in maintaining bone density and reducing fracture risk. For women, it's a key player in bone health, immune function, hormonal balance (aiding menstrual health and pregnancy outcomes), and even mental well-being. We also delved into its significant contributions to skin health (barrier function, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging), bone strength (preventing osteomalacia and rickets), and its direct role in healing various injuries by regulating inflammation, supporting cell growth, and aiding tissue regeneration. Beyond that, Vitamin D is crucial for healthy teeth, invigorates hair growth by influencing follicle cycles, boosts muscle strength and physical performance, and can even contribute to increased stamina by enhancing muscle function, oxygen utilization, and reducing fatigue. Its potential role in weight management and as a protective factor against certain cancers was also discussed.
Finally, we covered the recommended dosages by FSSAI for different age groups in India, emphasizing the need for personalized consultation with a healthcare professional. Crucially, we examined the side effects of Vitamin D toxicity, primarily due to excessive supplementation leading to high calcium levels, manifesting in symptoms like nausea, kidney issues, and neurological changes. The key takeaway? Embrace diverse sources, prioritize responsible intake, and remember that professional guidance is paramount to safely harness the immense power of Vitamin D for your optimal health.
Find Nutritionist in cities
Doctors for Vitamin D Sources, Benefits and Side Effects and dosage

Dr. Dhanamjaya D
Nutritionist
16 Years of Experience

Dt. Surbhi Upadhyay
Nutritionist
3 Years of Experience

Dt. Manjari Purwar
Nutritionist
11 Years of Experience

Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Nutritionist
8 Years of Experience
References
- Y. Lhamo, Preeta Kaur Chugh, C. D. Tripathi. Vitamin D Supplements in the Indian Market. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2016 Jan-Feb; 78(1): 41–47. PMID: 27168680
- Cedric F. Garland et al. The Role of Vitamin D in Cancer Prevention. Am J Public Health. 2006 February; 96(2): 252–261. PMID: 16380576
- Song M et al. Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D and colorectal cancer risk according to tumour immunity status. Gut. 2016 Feb;65(2):296-304. PMID: 25591978
- National Cancer Institute [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Vitamin D and Cancer Prevention
- Lisa Ceglia. Vitamin D and Its Role in Skeletal Muscle. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2009 Nov; 12(6): 628–633. PMID: 19770647
- Lars Rejnmark. Effects of Vitamin D on Muscle Function and Performance: A Review of Evidence from Randomized Controlled Trials. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2011 Jan; 2(1): 25–37. PMID: 23251739
- Khosravi ZS, Kafeshani M, Tavasoli P, Zadeh AH, Entezari MH. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Weight Loss, Glycemic Indices, and Lipid Profile in Obese and Overweight Women: A Clinical Trial Study. Int J Prev Med. 2018 Jul 20;9:63. PMID: 30123437
- Erin S. LeBlanc et al. Vitamin D levels and menopause-related symptoms. Menopause. 2014 Nov; 21(11): 1197–1203. PMID: 24736200
- Daniel D. Bikle. Vitamin D and Bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2012 Jun; 10(2): 151–159. PMID: 22544628
- Eamon Laird, Mary Ward, Emeir McSorley, J.J. Strain, and Julie Wallace. Vitamin D and Bone Health; Potential Mechanisms. Nutrients. 2010 Jul; 2(7): 693–724. PMID: 22254049
- Yoshida T, Stern PH. How vitamin D works on bone. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2012 Sep;41(3):557-69. PMID: 22877429
- Marwaha RK. Regional and seasonal variations in ultraviolet B irradiation and vitamin D synthesis in India.. Osteoporos Int. 2016 Apr;27(4):1611-1617. PMID: 26630977