Summary
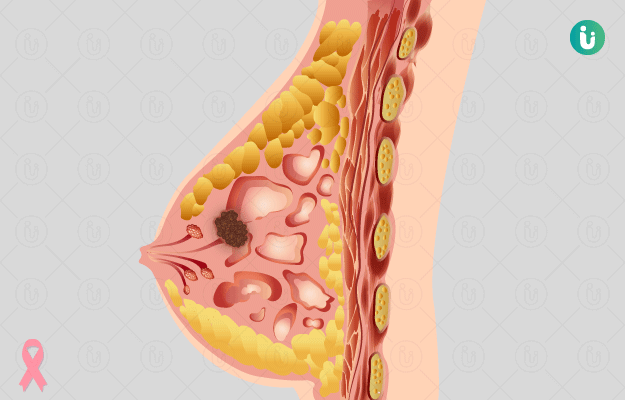
Globally, breast cancer is the most common cancer affecting women. The commonest symptom of breast cancer is the formation of a lump in the breast. However, not all women with breast cancer develop (present with) a lump in their breast. Other symptoms of breast cancer include peeling off of the skin on the breasts, oozing out of fluid from the nipples, and the presence of lumps in the neck and armpit. With the advances in medicine and technology, many novel diagnostic tools are now available, which facilitate early detection of breast cancer. Breast cancer progresses through four different stages, therefore, early detection of the disease enables prompt treatment, thus increasing the survival rate. The diagnostic tools include the screening of the breasts using mammography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI scan), and screening of the fluids and tissues present in the breasts. Breakthroughs in biotechnology have enabled diagnosis of faulty genes responsible for breast cancer. Studies on protein markers have made it easy to determine a proper treatment regimen for breast cancer.
Treatment of the disease ranges from conventional chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormonal therapy to novel nanotechnology-based formulations. Breast cancer can be prevented to some extent by regular exercise, controlling body weight, and breastfeeding the child for at least six months after delivery. However, a strong family history of breast cancer highly increases the risk of the disease in the next generations. Hence, in such cases, routine health check-ups can be helpful to screen for breast cancer. Complications arise when the cancerous tissue invades the body’s normal tissues e.g., pressure on adjacent tissues causing pain, blockage of adjacent blood vessels or nerves, and more. However, most complications arise due to adverse effects of breast cancer treatment e.g., hair loss, vomiting, lowered white blood cell count and others. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are key to improve survival rates in this dreaded disease. Radiation, chemotherapy using drugs and surgery remain the three most common methods of treatment, based on the severity and extent of spread of cancer.

 Doctors for Breast Cancer
Doctors for Breast Cancer  OTC Medicines for Breast Cancer
OTC Medicines for Breast Cancer
 Lab tests for Breast Cancer
Lab tests for Breast Cancer Breast Cancer articles
Breast Cancer articles News for Breast Cancer
News for Breast Cancer
 Diet for Breast Cancer
Diet for Breast Cancer
 Homeopathic Treatment of Breast Cancer
Homeopathic Treatment of Breast Cancer






































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team
















