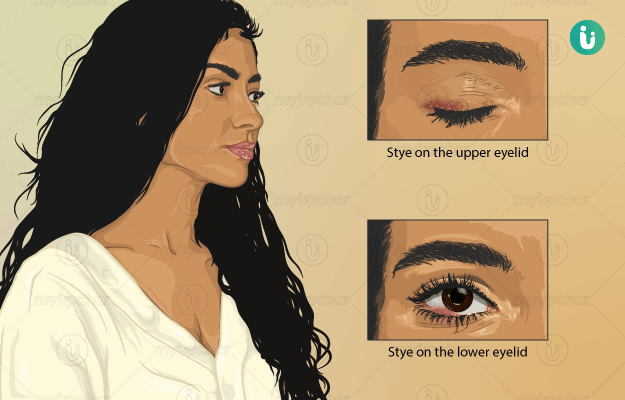
What is a stye?
A stye, also called a hordeolum, is an infection that affects the eyelids. It can be on the outer or inner surface of the eyelids and affects the gland of the lids. A stye appears as a small pimple or elevation on the eyelid.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
- A stye typically looks like a pimple near the eye.
- It is small and red in colour. Since it has pus, it will have a small yellow centre.
- The presence of a stye will cause pain in the region of the eye, which increases on closing and opening the eyes.
- The eyelids appear swollen, and there may be some discharge from this swelling.
- Eye movements are uncomfortable, the eyes water frequently, and there is a constant feeling of a foreign body in the eye.
What are the main causes?
- A stye can be caused by a bacterial infection.
- Risk factors include an immunocompromised state and a nutrient deficit diet.
- Since it is an infection, it can spread through contact, sharing napkins or other accessories.
- Poor personal hygiene is another factor that increases the risk of developing a stye.
- Sometimes, excessively dry eyes can also trigger the infection.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
- Diagnosing a stye is extremely simple and requires no investigative procedures.
- A doctor will diagnose it by just looking at it under a light.
- A stye resolves on its own in most cases, which takes a few days.
- If it persists or is increasingly painful, the doctor will advise treatment.
- If needed, antibiotics are given to cure the infection and eliminate the bacteria.
- If there is a lot of pressure build-up in the stye with the accumulation of pus, a small incision is made to relieve the pressure.
- It is advisable to maintain good personal hygiene, avoid sharing towels and refrain from touching the stye repeatedly.

 Doctors for Stye
Doctors for Stye