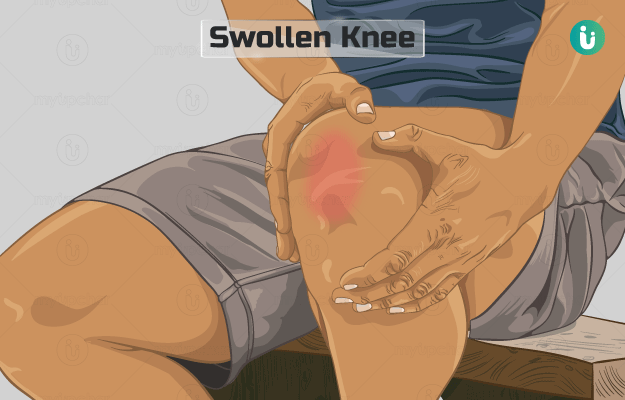
Swelling is a sign that there is an inflammation in the affected area, making it appear puffier and larger.
Inflammation is often the body’s response to trauma, including repetitive stress injuries such as bursitis.
Swelling in the knees is a common phenomenon, especially in middle-aged and older people. Sportspeople, dancers and people who are prone to falling or bumping their knees may also face this problem often.
Sometimes, applying RICE therapy—rest, ice, compression and elevation—to the affected knee is enough. In other cases, like swollen knees because of arthritis or because of an anterior cruciate ligament or ACL injury, patients may need greater medical attention and some tests.
Read on to know about the symptoms, types, causes, diagnosis and treatment of a swollen knee as well as when to see a doctor for a swollen knee and what to expect during this doctor's visit.

 Doctors for Swollen knee
Doctors for Swollen knee  OTC Medicines for Swollen knee
OTC Medicines for Swollen knee