Deciding on family planning is a significant life choice, and for many women, tubectomy, or female sterilization, offers a permanent solution. This surgical procedure effectively prevents future pregnancies, providing peace of mind for those who are certain their family is complete. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about tubectomy, from how the procedure is performed and when is the ideal time to consider it, to understanding potential pain, recovery expectations, and important precautions. We'll also address common questions like its effect on periods and potential for weight gain, explore its numerous benefits, and delve into the rare risks and side effects, including insights from a clinical study on complications. Whether you're exploring long-term birth control options or preparing for the procedure, this information aims to empower you with a clear understanding of what tubectomy entails.
- What Is Tubectomy?
- How Is Tubectomy Done?
- When Should You Get A Tubectomy?
- Is Tubectomy Painful?
- Who Can Opt For A Tubectomy?
- When To Have Sex After Tubectomy?
- Can Tubectomy Stop Periods?
- What Are The Risks Of Tubectomy?
- What To Avoid After Tubal Ligation?
- How Much Rest Is Required After A Tubectomy?
- Is There Any Chance To Get Pregnant After A Tubectomy?
- Does Having Tubal Ligation Cause Weight Gain?
- Recovery After Tubectomy
- What Precautions Should Be Taken After A Tubectomy?
- Benefits Of Tubectomy
- Side Effects Of Tubectomy
- Study About The Complications Of Tubectomy
- Women’s Sterilization Scheme
- Summary
What Is Tubectomy?
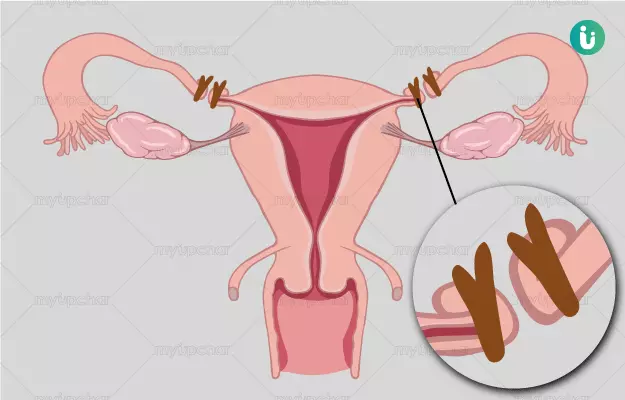
Tubectomy, often known as "female sterilization," is a surgical procedure for women that provides permanent contraception. It's a highly effective way to prevent pregnancy, designed for women who are sure they don't want to have any more children.
(Read More: Birth control methods)
How Is Tubectomy Done?
Before the procedure, your doctor will conduct a physical examination including a pelvic exam to rule out any problems in the organs in the abdomen and pelvic region. For example, if you have gallbladder stones, then surgery may have to be postponed till this is treated.
Tubectomy is usually carried out laparoscopically, that is, a small cut is made near the belly button or just above the pubic hairline. Then a stick-like instrument, with a camera attached to it, is inserted into the woman’s body. This instrument is called a laparoscope - it is used so the surgeon can see the fallopian tubes properly. Tubectomy can be done by various methods:
- The fallopian tube can be cut in half and then both the ends are tied together.
- The fallopian tubes can be blocked by clipping them (using clips) or tying them together.
- Electric current is used to char parts of the fallopian tube.
- The fallopian tube can be tied using a silastic (silicone) band.
- The surgeon may also remove the entire fallopian tube.
When Should You Get A Tubectomy?
"When is the right time to get a tubectomy?" it's a big life decision, kind of like deciding to buy a house or change careers, because it's meant to be permanent birth control. So, the first and most important thing is, you need to be 100% sure you don't want any more children in your life. No "maybe later," no "what if?" Just a solid "Nope, my family is complete."
Now, assuming you've got that certainty locked down, there are a few common times when women usually choose to have this procedure:
(Read More: Pubic Hair Removal: Safety Tips and Best Practices You Need)
Right After You've Just Had a Baby!
- If you had a vaginal delivery: Sometimes, within a day or two of giving birth naturally, a doctor can perform the tubectomy. Why then? Well, your uterus is still quite large and high up, which makes your fallopian tubes (the tubes we're talking about blocking) easier for the surgeon to reach through a tiny cut near your belly button. It's convenient because you're already in the hospital recovering from delivery.
- If you're having a C-section: This is super common! The doctor can perform the tubectomy right after they deliver your baby, using the very same incision they made for the C-section. It's like a two-in-one deal – you're already there, already under anesthesia, so it saves you from needing a separate surgery later.
Anytime You're Not Pregnant!
- You don't have to wait until after having a baby. Many women choose a separate time for their tubectomy. This is usually done using a "laparoscopic" method, which sounds fancy, but it just means the doctor makes very small "keyhole" cuts in your tummy.
- Often, doctors like to schedule this a week or so after your period starts. Why? Just to be absolutely sure you aren't secretly pregnant already. If you're planning this type of tubectomy, your doctor might even ask you to use another form of birth control right up until the surgery date, just to be extra safe.
After a Miscarriage or Abortion:
Yes, a tubectomy can also be done safely right after experiencing a miscarriage or having an abortion, as long as you're feeling medically stable.
(Read More: Best Time To Get Pregnant)
When Is YOUR Right Time?
Beyond the actual physical timing, think about these very important points:
-
Are you REALLY, truly done having kids? Seriously, take your time with this thought. Life changes, and sometimes people regret permanent decisions if they made them too quickly or when they were very young.
-
Have you talked it over with your partner? If you have one, this is a shared decision that impacts both of you.
-
What does your doctor say? They'll check your overall health to make sure surgery is safe for you and discuss all the pros, cons, and other birth control options too.
Ultimately, the best time is when you feel completely ready, well-informed, and absolutely sure that your family is complete, and you're looking for a permanent birth control solution.
Is Tubectomy Painful?
That's a very common and understandable question! When people think about surgery, "pain" is often the first concern.
During the Procedure:
No Pain During Surgery. You will absolutely not feel any pain during the tubectomy itself. This is because you'll be given anesthesia. Most commonly, this is general anesthesia, meaning you'll be completely asleep throughout the surgery. In some cases, especially if it's done right after childbirth (like after a C-section or with an epidural), you might receive regional anesthesia (like a spinal or epidural), which numbs the lower part of your body so you're awake but feel nothing from the waist down. The goal of anesthesia is to make sure the procedure is entirely painless for you.
(Read More: Beyond the Basics: Your Definitive Guide to the Copper T)
After the Procedure (During Recovery):
Some Discomfort is Normal: Like any surgery, you can expect some pain and discomfort as the anesthesia wears off and you begin to heal. This is generally manageable, not usually severe, and improves over a few days.
Where you might feel pain:
Incision Sites: You'll likely feel soreness, tenderness, or mild pain around the small cuts (incisions) the surgeon made. These can be a bit bruised too.
Abdominal Cramping: Many women describe this as similar to menstrual cramps. It's due to the manipulation of organs during surgery.
Bloating and Gas Pain: If you had a laparoscopic procedure (the "keyhole" method), gas (like carbon dioxide) is often used to inflate your abdomen to give the surgeon room to see. This gas can sometimes cause discomfort, bloating, and even referred pain in your shoulders or neck for a day or two as your body absorbs it. This is normal and usually subsides.
Fatigue: You might feel very tired and drowsy from the anesthesia and the healing process itself.
Managing the Pain:
Your doctor will usually prescribe pain medication, or recommend over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, to help manage any discomfort.
Applying a heating pad to your abdomen can also help soothe cramps.
Gentle movement, like walking, can help the gas discomfort resolve faster.
Recovery Time:
Most women feel well enough to resume light daily activities within a few days.
Full recovery, including avoiding strenuous activity and heavy lifting, usually takes about 1-2 weeks, depending on the type of tubectomy you had (laparoscopic recovery is often quicker than a mini-laparotomy if done separately).
When to Contact Your Doctor:
While some pain is normal, you should contact your doctor if you experience:
- Severe pain that doesn't get better with medication or gets worse.
- Fever (100.4°F or 38°C or higher).
- Heavy bleeding, foul-smelling discharge, or increasing redness/swelling at the incision sites.
- Fainting or severe dizziness.
Who Can Opt For A Tubectomy?
- Tubectomy is another name for female sterilization, any of the following people can go for a tubectomy:
- Women who do not want to get pregnant and want a permanent solution for contraception.
- Women who already have a child and do not wish to get pregnant again.
- Women who are likely to have a high-risk pregnancy. For example, women who are older than 35 or those who have a pre-existing medical condition like high blood pressure or those who have had recurrent miscarriages.
(Read More: Abortion: types, causes, pills, procedure, side effects)
When To Have Sex After Tubectomy?
This is a common question, and the good news is you typically don't have to wait too long! Most doctors recommend waiting about one to two weeks after your tubectomy before resuming sexual activity.
Why the wait? It's mainly to allow your body to heal and to reduce the risk of infection or discomfort. Your incisions (the small cuts made during the procedure) need a little time to close up and start healing properly. Listen to your body – if you feel pain or discomfort, it's a sign to wait a bit longer. When you do resume, take it easy and gentle at first.
(Read More: When To Have Sex After Tubectomy?)
Can Tubectomy Stop Periods?
This is a really important point to clarify: No, tubectomy does not stop your periods.
Tubectomy is a procedure that blocks or seals your fallopian tubes. These tubes are like pathways for the egg to travel from your ovary to your uterus. By blocking them, sperm and egg can't meet, preventing pregnancy.
Your menstrual cycle (periods) is controlled by your ovaries and hormones. Your ovaries still release eggs and produce hormones even after a tubectomy.
So, you'll continue to have your regular periods just as you did before the procedure. If you experience changes in your periods after a tubectomy, it's best to consult your doctor to rule out any other causes.
What Are The Risks Of Tubectomy?
While tubectomy is widely considered a safe and highly effective method of birth control, like any surgical procedure, it carries some potential risks that you should be aware of. These can include general risks associated with anesthesia, such as allergic reactions or breathing difficulties. There's also a small risk of infection at the incision sites or internally, which is why following post-operative care instructions is crucial. Minor bleeding is normal, but in rare cases, excessive bleeding can occur. Very rarely, there could be accidental damage to nearby organs like the bladder or bowel during the procedure. Although tubectomy is extremely effective in preventing pregnancy, if a pregnancy does occur (which is exceedingly rare), there's a higher chance it could be an ectopic pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube, requiring immediate medical attention. Some women also report experiencing chronic pelvic pain, though this is not common. Lastly, there's a very slight possibility that the tubes might reconnect over time, leading to a rare chance of pregnancy, which is why the procedure is around 99% effective, not 100%. Your doctor will thoroughly discuss all these potential risks with you before the procedure to ensure you are fully informed and comfortable with your decision.
(Read More: Navigating Vaginal Whitening: A Guide to Choices)
What To Avoid After Tubal Ligation?
To ensure a smooth recovery, here's what you should generally avoid after a tubectomy:
- Heavy Lifting: For the first few weeks, avoid lifting anything heavy. This can strain your abdominal muscles and potentially affect your incision sites. Think light housework, nothing strenuous.
- Strenuous Exercise: Give your body time to heal. Avoid intense workouts, running, or any activities that put a lot of pressure on your abdomen for at least 2-4 weeks, or as advised by your doctor.
- Douching or Tampons: It's often recommended to avoid douching and using tampons for a short period after surgery to prevent infection. Stick to sanitary pads if you have any bleeding.
- Baths: For the first few days to a week, stick to showers instead of baths. Soaking in a bathtub could increase the risk of infection at the incision sites.
- Intercourse: As mentioned earlier, wait for at least one to two weeks, or until your doctor gives you the green light and you feel comfortable.
- Wearing Tight Clothing: Opt for loose, comfortable clothing, especially around your abdomen, to avoid irritation of the incision sites.
- Ignoring Pain or Unusual Symptoms: Don't hesitate to contact your doctor if you experience severe pain, fever, redness or pus at the incision site, or any other concerning symptoms.
How Much Rest Is Required After A Tubectomy?
The amount of rest needed after a tubectomy can vary slightly among individuals, but there are general guidelines to follow. Immediately after the procedure, you will likely feel groggy from the anesthesia and should plan to rest for the remainder of that day. For the first two to three days, it's advisable to take it easy, which means avoiding any heavy lifting or strenuous activity and ensuring you get plenty of sleep. During this period, you might experience some mild pain, discomfort, or fatigue. Most women are able to resume light activities and return to work (if it's not physically demanding) within about a week. However, even then, it's important to continue avoiding any activities that put significant strain on your abdomen. Complete healing of the internal tissues typically takes about two to four weeks. Your doctor will provide you with specific instructions tailored to your individual recovery. Most importantly, listen to your body; if you feel tired or in pain, it's a clear signal that you need more rest, and you should avoid pushing yourself too hard too soon.
Is There Any Chance To Get Pregnant After A Tubectomy?
While tubectomy is one of the most effective forms of permanent birth control, it's crucial to understand that there is a very small chance of getting pregnant after a tubectomy. No birth control method, short of complete abstinence, is 100% effective, and tubectomy is no exception. The effectiveness rate for preventing pregnancy is typically cited as over 99%.
How can this happen? In very rare instances, the fallopian tubes that were blocked or sealed during the procedure might spontaneously reconnect or an alternative pathway might form, allowing sperm and egg to meet. When a pregnancy does occur after a tubectomy, there's a higher risk that it could be an ectopic pregnancy. This is a serious condition where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube itself. Ectopic pregnancies cannot proceed to term and require immediate medical attention. Because of this very small risk, if you have had a tubectomy and experience symptoms of pregnancy (like a missed period), it's important to contact your doctor right away for evaluation.
(Read More: Oligomenorrhea: causes, symptoms, prevention, treatment)
Does Having Tubal Ligation Cause Weight Gain?
This is a common concern for many women, but the good news is that there is no scientific evidence to suggest that having a tubal ligation directly causes weight gain.
Weight gain is typically related to factors such as:
- Diet: Changes in eating habits or calorie intake.
- Activity Level: A decrease in physical activity.
- Hormonal Changes: Natural hormonal fluctuations associated with aging, menopause, or other medical conditions.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause weight gain as a side effect.
- Lifestyle: Stress, sleep patterns, and other lifestyle factors can influence weight.
Since tubal ligation does not affect your hormone levels (your ovaries continue to function normally), it does not inherently lead to weight gain. If you experience weight gain after the procedure, it's more likely due to other concurrent life changes or factors, rather than the tubectomy itself. If you're concerned about weight changes, it's always best to discuss it with your healthcare provider to identify the underlying cause.
Recovery After Tubectomy
Recovery after a tubectomy is generally straightforward, though it does require some rest and care. Immediately after the procedure, you'll typically be monitored for a few hours as you recover from the anesthesia. You might feel groggy, experience some mild abdominal pain, cramping, or discomfort, and possibly shoulder pain (due to the gas used in laparoscopic procedures irritating the diaphragm).
For the first 24-48 hours, it's important to rest significantly and avoid any strenuous activity. You might be advised to take pain relievers as needed. Most women can resume light daily activities within a few days to a week. However, complete recovery, where the internal tissues are fully healed and you can return to all normal activities, usually takes about two to four weeks. During this time, it's crucial to avoid heavy lifting, vigorous exercise, or anything that puts strain on your abdomen. Your doctor will provide specific instructions on wound care, bathing, and when you can resume activities like driving or sexual intercourse. Listening to your body and not pushing yourself too soon is key for a smooth recovery.
What Precautions Should Be Taken After A Tubectomy?
Prioritize Rest: Get plenty of rest, especially in the first few days, and avoid strenuous activities or heavy lifting for 2-4 weeks as advised by your doctor.
Proper Wound Care: Keep incision sites clean and dry, following your doctor's specific instructions. Avoid scrubbing the area.
Avoid Submerging Incisions: Take showers instead of baths for at least a week to prevent infection; do not use hot tubs or go swimming.
Avoid Vaginal Insertion: Refrain from using tampons, douching, or having sexual intercourse for 1-2 weeks, or until cleared by your doctor, to prevent infection.
Pain Management: Take prescribed pain medication as directed, without exceeding the recommended dosage.
Monitor for Complications: Watch out for fever (above 100.4°F or 38°C), severe or worsening abdominal pain, redness/swelling/pus/odor from incisions, heavy bleeding, or persistent nausea/vomiting. Contact your doctor immediately if these occur.
Wear Loose Clothing: Opt for loose, comfortable clothing around your abdomen to avoid irritating incision sites.
Attend Follow-up Appointments: Keep all scheduled appointments with your doctor to ensure proper healing and address any concerns.
(Read More: Bleeding After Abortion: What to Expect and When to Get Help)
Benefits Of Tubectomy
Tubectomy offers several significant benefits for women seeking permanent birth control. It is a highly effective permanent contraception method, with a very low failure rate (over 99% effective), providing great peace of mind for women who are certain they do not want future pregnancies. As a one-time procedure, once performed, you do not need to think about birth control methods daily, weekly, or monthly; there are no pills to remember, patches to change, or injections to receive. Crucially, it has no impact on hormones, meaning it will not affect your menstrual cycle, mood, sex drive, or cause hormonal side effects like weight gain, as your ovaries continue to function normally. Tubectomy also does not affect sexual function or pleasure, as it does not interfere with a woman's sexual desire, ability to have orgasms, or overall sexual pleasure. While there is an upfront cost, it is generally cost-effective in the long term compared to ongoing expenses for other birth control methods. Lastly, it offers immediate effectiveness once confirmed successful, allowing for immediate peace of mind regarding pregnancy prevention.
Side Effects Of Tubectomy
While the benefits are clear, it's also important to be aware of the potential side effects and what to expect after a tubectomy. Common short-term side effects during the recovery period include mild to moderate abdominal pain, cramping, or soreness at the incision sites. You might also experience shoulder pain due to the gas used in laparoscopic procedures, general fatigue from the anesthesia and healing, possible nausea or vomiting, abdominal bloating, and light vaginal spotting for a few days. Beyond these temporary effects, there are rare but serious side effects that align with the risks discussed previously. These include infection at the incision site or internally, excessive bleeding (hemorrhage), accidental damage to other organs during surgery, and a higher risk of ectopic pregnancy if a pregnancy does occur after the procedure. Some women also report chronic pelvic pain, though this is rare, and there's a very slight chance of the procedure failing if the tubes reconnect. It's crucial to understand the distinction between common, temporary discomfort during recovery and these rare, more serious complications. Most women experience a straightforward recovery with only minor, temporary discomfort. If you have concerns about any side effects, always consult your healthcare provider.
Study About The Complications Of Tubectomy
(Clinical study of tubectomy and its complications)
This article presents a clinical study on tubectomy and its complications. The study aimed to investigate complications associated with different types of tubal ligation. It was a prospective analytical study conducted over an 18-month period, including all cases of female sterilization complications that were reported or referred to the study institute. The article was published on May 27, 2020. The specific writer or authors are not mentioned in the extracted information.
During the 18-month study period, a total of 50 cases of tubectomy complications were observed. A significant majority, 80% of these complications, were linked to the abdominal method of sterilization, while the remaining 20% were associated with the laparoscopic method. Furthermore, in 66% of the reported cases, the sterilization procedure was performed at a primary health center. The study also reported three deaths.
The results indicate a higher incidence of complications with the abdominal tubal ligation method compared to the laparoscopic method. A notable proportion of complications originated from procedures performed at primary health centers.
Women’s Sterilization Scheme
In India, both female sterilization (tubectomy) and male sterilization (vasectomy) programs are offered on a voluntary basis, allowing couples to choose the procedure they deem most suitable. During the 2013-14 fiscal year, a total of 4,092,806 sterilization operations were performed in India.
The government's scheme provides compensation to families in cases of death or failed operations:
- If death occurs within 7 days of the operation, the family receives ₹200,000.
- If death occurs between 8 and 30 days after discharge from the hospital, the compensation is ₹50,000.
- In case of a failed operation, a compensation of ₹30,000 is provided.
- The government also covers all operation costs within the hospital and any expenses incurred due to complications arising from the operation for up to 60 days from the date of discharge, with a maximum limit of ₹25,000.
(Read More: Periods diet)
Summary
Tubectomy, a permanent contraception method for women, involves surgically blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. The procedure is typically performed laparoscopically, using minimal incisions, and can involve various techniques like cutting and tying, clipping, charring with electric current, or using a silastic band, sometimes even involving the removal of the entire fallopian tube. The ideal time for a tubectomy is when a woman is absolutely certain she desires no more children, and it can be conveniently performed immediately after childbirth (vaginal or C-section) or as a separate procedure anytime a woman is not pregnant, often a week after her period starts to ensure no existing pregnancy. It can also be safely done after a miscarriage or abortion, provided the woman is medically stable.
Regarding the experience of tubectomy, there is no pain during the procedure itself due to anesthesia (general or regional). Post-procedure, mild pain, cramping, soreness at incision sites, and gas-related discomfort (including shoulder pain) are common but manageable with prescribed pain relief. Recovery typically involves significant rest for the first 24-48 hours, with most women resuming light activities within a few days to a week, and full recovery taking 2-4 weeks, requiring avoidance of heavy lifting and strenuous exercise during this period.
Crucially, tubectomy does not stop menstrual periods as it doesn't affect ovarian hormone production. While highly effective (over 99%), there's a very small chance of pregnancy if tubes reconnect, with a higher risk of ectopic pregnancy if it occurs. It's important to note that tubal ligation does not cause weight gain directly, as it doesn't interfere with hormones related to metabolism.
Key precautions post-tubectomy include prioritizing rest, meticulous wound care, avoiding submerging incisions in baths, refraining from vaginal insertion (tampons, douching, intercourse) for a recommended period, diligent pain management, monitoring for any signs of complications, wearing loose clothing, and attending all follow-up appointments. The benefits are significant, offering a highly effective, one-time, non-hormonal, and long-term cost-effective birth control solution that doesn't impact sexual function. However, potential side effects include common short-term discomforts during recovery and rare, serious risks such as infection, excessive bleeding, organ damage, and ectopic pregnancy. A clinical study highlighted that abdominal tubal ligation carried a higher incidence of complications compared to the laparoscopic method, with many originating from procedures at primary health centers. In India, female sterilization is offered voluntarily, with government schemes providing compensation for rare instances of death or failed operations, covering operation costs and complication-related expenses for up to 60 days post-discharge.