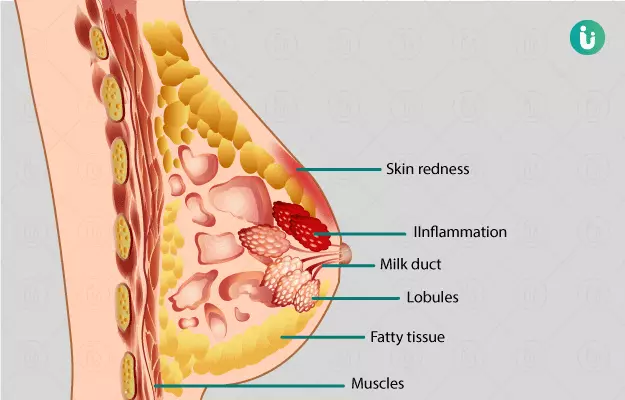
Breast infection is also called mastitis. This infection occurs in the tissues of the breast. This infection is the most common infection in breastfeeding women. When the baby breastfeeds, the bacteria present in his mouth go into the breast which causes infection. This is called lactation mastitis. Women who do not breastfeed are also at risk of infection, but it is not as common in them. The infection usually affects the fatty tissue present in the breast, causing swelling, lumps and pain in the breasts. Although most infections are caused by breastfeeding or blocked milk ducts. Very rarely, but sometimes breast infection is also related to breast cancer. Here are the symptoms, causes, treatment and prevention measures of breast infection -
(Read more - Breast Problems)
- Symptoms Of Breast Infection
- Causes Of Breast Infection
- How To Diagnose Breast Infection
- Treatment For Breast Infection
- Prevention For Breast Infection
- Summary
Symptoms Of Breast Infection
The symptoms of breast infection start suddenly and are as follows:
- Abnormal breast swelling, causing one breast to become larger than the other.
- Breast discomfort.
- Pain or burning while breastfeeding.
- Lumps in the breast, often painful.
- Itching in the breasts.
- Heat of the breasts.
- Feeling cold.
- Pus discharge from the nipple.
- Redness of the skin of the breasts in a wedge-shaped pattern.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the armpits or neck area.
- Fever over 101° Fahrenheit or 38.3° Celsius.
- Feeling sick or lethargic.
You may experience flu-like symptoms before noticing any changes in the breasts. Contact a doctor if you experience these types of symptoms.
(Read more - Breast pain)
Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Breast infection symptoms can also be caused by breast cancer. Although this happens in very few cases, if it does happen, it is a very serious disease. Breast cancer occurs when abnormal cells divide in the breast ducts. These abnormal cells then block the lymph vessels (the part of the lymphatic system that removes waste and toxins from the body) in the skin of the breast, causing redness and swelling in the skin and pain when touched. Inflammatory breast cancer symptoms can include:
- Breast thickening or one breast becoming larger.
- Feeling of unusual warmth in the affected breast.
- Change in the color of the breast, such as blue, purple or red.
- Discomfort and pain.
- Dimpling in the skin of the breast.
- Enlargement of lymph nodes under the arm or collarbone.
Unlike other forms of breast cancer, women suffering from inflammatory breast cancer do not develop lumps in their breasts. In this situation, there is often a dilemma of breast infection. Talk to the doctor if you feel any of these.
(Read more -Breast Engorgement)
Causes Of Breast Infection
Mastitis is an infection of the breast tissue that occurs most often during breastfeeding. This infection can occur when bacteria travel from the baby's mouth to the milk duct through the cracks in the nipple. Breast infections most often occur one to three months after delivery, but they can also occur in women who have not delivered immediately, or even after menopause. Other causes of infection can be chronic mastitis and another rare cancer called inflammatory carcinoma. In healthy women, mastitis is rare. However, it is more common in women suffering from diabetes, chronic disease, AIDS or immune system disorders.
About 1%-3% of breastfeeding women develop mastitis. Overfilling or emptying of the breasts can worsen the problem.Chronic mastitis occurs in women who do not breastfeed. In women who have gone through the menopause, breast infections are caused by chronic inflammation of the ducts under the nipple.Hormonal changes in the body cause the milk ducts to become clogged with dead skin cells and waste. These clogged ducts make the breasts more susceptible to bacterial infections. The infection can sometimes return even after treatment with antibiotics.
(Read more - How to relieve nipple pain)
How To Diagnose Breast Infection
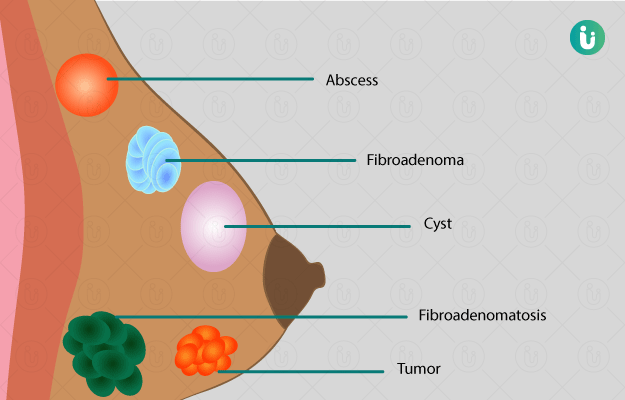
In breastfeeding women, the doctor diagnoses the problem based on a physical examination and the symptoms you describe. The doctor also checks if the infection has caused an abscess. If diagnosed, he or she drains it. If the infection keeps coming back, breast milk is sent to a laboratory to determine what type of bacteria is present in the infection.
If you have a breast infection and are not breastfeeding, other tests may be needed to check for other causes. Tests to check for breast cancer may include a mammogram or a biopsy of breast tissue. A mammogram is an imaging test. A breast biopsy involves taking a small tissue sample from the breast for laboratory testing to determine whether or not you have cancer.
(Read more - Breast pain in pregnancy)
Treatment For Breast Infection
Usually a 10 to 14 day course of antibiotics is the most effective treatment for this infection and most women feel relief within 48 to 72 hours. Always take the medicines advised by the doctor so that the infection does not recur. You can breastfeed while you're on antibiotics, but if nursing isn't possible, you can try pumping your breasts to remove excess milk. If your severe breast infection is caused by a breast abscess, it may need to be medically drained. This will help your breasts heal faster. You can breastfeed, but first consult a breast specialist or doctor about how to care for an abscess.
If your doctor finds inflammatory breast cancer, they will begin treatment based on the stage (severity) of the cancer. Treatment usually includes chemotherapy (a procedure to destroy cancer cells), radiation therapy (using high-powered X-rays to kill cancer cells) or surgery to remove the breast and nearby lymph nodes.
(Read more - How to breastfeed: positions, tips)
Prevention For Breast Infection
Some women are more susceptible to infection than others, especially those who are breastfeeding for the first time. In general, good habits to avoid breast cancer include:
- Breastfeed evenly from both breasts.
- Fully empty the breast to prevent overflowing and clogged ducts.
- Use good breastfeeding techniques to prevent sore or cracked nipples.
- Avoid dehydration by drinking plenty of fluids.
- Wash hands for hygiene, keep nipples clean and keep your baby clean.
(Read more - Breast changes in early and late pregnancy)
Summary
Breast infection, also known as mastitis, commonly occurs in breastfeeding women. It occurs when the milk ducts in the breast become blocked or bacteria enter the breast through the nipple. Its symptoms include breast pain, swelling, redness, feeling of warmth and sometimes fever. If left untreated, the condition can become more serious and lead to the formation of a breast abscess. Breast infections are treated with antibiotics, warm compresses and continued breastfeeding to keep the milk ducts clear. With timely treatment and proper care, this infection can be cured.