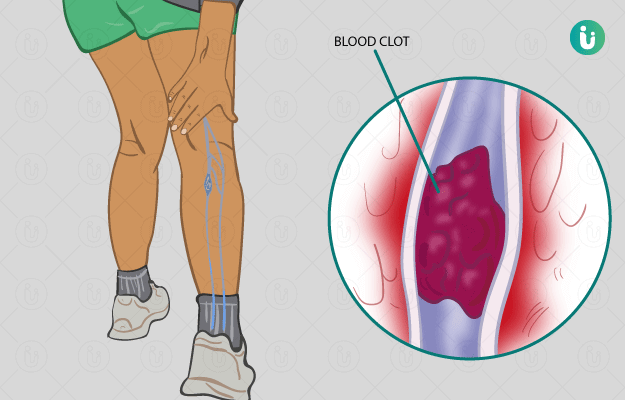
What is deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition wherein blood clots form in one of the deep veins, typically in the legs. It can affect anyone, typically above 60 years. The incidence rate in India is around 8%-20%.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The main symptom is swelling of the leg. Very rarely, swelling of both legs is seen.
Other symptoms include:
- Pain in the leg
- Reddish discolouration on the leg
- Feeling of warmth in the leg
If these symptoms are overlooked, the blood clot can dislodge, travel through the bloodstream to the lungs and block the blood flow, leading to pulmonary embolism.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism include:
- Sudden breathing difficulty
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing and cough
- Dizziness
- Fast pulse
- Coughing up blood
What are its main causes?
Anything that impedes blood flow can result in DVT. The main causes are as follows:
- Injury to a vein
- Surgery
- Major illnesses like cancer, heart disease or severe infection
- Certain medications
- Long periods of inactivity
Risk factors that can increase the chances of having DVT:
- Hereditary clotting disorder
- Pregnancy
- Use of birth control pills
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Heart failure
- Inflammatory bowel disease
How is it diagnosed and treated?
The diagnosis mainly relies on the medical history of the patient and physical examination of the affected limb. Medication history is also obtained. Other diagnostic steps include:
- D-dimer test
- Ultrasound
- Venography
- CT or MRI scans
- Pulmonary angiography
Tests that can detect the underlying cause for DVT:
- Blood test
- Chest X-ray
- ECG
Treatment goals for DVT include relief from pain and inflammation. Medications, especially blood- thinning agents, are preferred.
Preventive steps:
- If you have been on bed rest, move around as soon as possible. The sooner you do, the lesser the chances of DVT.
- Exercise the leg muscles to prevent stiffness from sitting for long periods of time.
- Use compression stockings to prevent clot formation.
- Choose loose-fitting clothes to avoid restriction to movement and blood circulation.
- Lead an active lifestyle.
- Keep a close watch for any bleeding episodes when on blood-thinning medicines.

 OTC Medicines for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
OTC Medicines for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)