What is Hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood glucose or low blood sugar, is a major clinical problem for people suffering from diabetes mellitus. Hypoglycemia occurs when the level of blood glucose, which is the body’s main source of energy, goes below normal levels.
What are the main signs and symptoms?
- The mild to moderate symptoms include:
- An irregular heart rhythm.
- Fatigue.
- Shaky or jittery body.
- Pale skin.
- Anxiety.
- Sweating.
- Hunger.
- Irritability.
- Tingling sensation around the mouth.
- Confusion, disorientation, and dizziness.
- Weakness.
- The severe symptoms include:
- The symptoms that occur during sleep may include:
- Nightmares.
- Profuse sweating that drenches your clothes.
- Fatigue and weakness upon waking.
What are the main causes?
- The most common cause of hypoglycemia include
- Medications that are taken to treat diabetes mellitus, namely, sulfonylureas or meglitinides.
- Alcohol intake especially on an empty stomach.
- Tumour of the pancreas, which leads to low blood glucose levels due to excess insulin production (a hormone that reduces blood glucose levels).
- Hyperinsulinism and disorders of glucose metabolism.
- Risk factors include:
- Delayed or skipped meals.
- Inadequate intake of carbohydrates.
- Being ill.
- Increased physical activity.
- Kidney diseases.
- Liver diseases.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
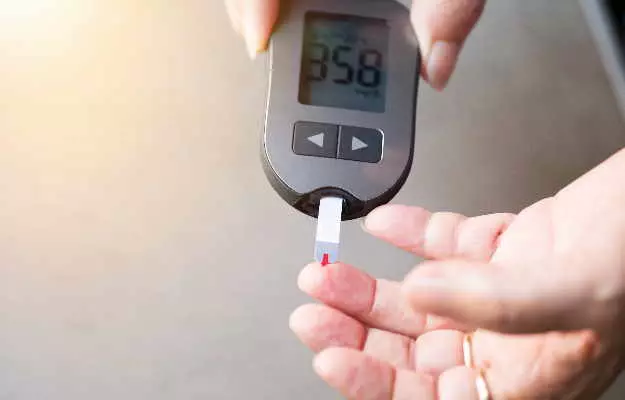
If taking medications for diabetes, one should always keep a check on the blood glucose levels using a glucometer. Your doctor will take a medical history along with a physical examination to diagnose hypoglycemia. However, the symptoms of severe hypoglycemia are quite evident, your doctor may immediately begin the treatment. If you do not have any symptoms during your initial visit to the doctor, you may be advised to do an overnight fast and then consult the doctor for an examination.
The investigations include:
- Tests to measure blood sugar levels before and after meals.
- Test to measure blood sugar level when symptoms occur.
Immediate treatment of hypoglycemia involves consumption of 15 to 20 grams of carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets, fruit juices, or sugar candies, honey, or plain sugar, which are easily converted to glucose.
In severe cases, an injection or intravenous glucose may be administered.
Blood sugar levels should be rechecked every 15 minutes after immediate treatment and maintained thereafter. The treatment of underlying precipitating factors involves an alteration in drugs taken for treating diabetes or removal of the tumour of the pancreas.

 Doctors for Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
Doctors for Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)  OTC Medicines for Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
OTC Medicines for Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
 Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar) articles
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar) articles News for Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
News for Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)

 First Aid for Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
First Aid for Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)







 Editorial Team
Editorial Team

 Dr. Nabi Darya Vali (AIIMS)
Dr. Nabi Darya Vali (AIIMS)











