Mental disorders may be of several kinds. The most common types of mental disorders include:
- Anxiety-related Disorders
Phobias, post-traumatic stress disorders, panic attack, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- Mood Disorders
Depression, bipolar disorders, and others.
- Psychotic Disorders
Schizophrenia, delusional disorder, paraphrenia and more.
- Personality Disorders
Paranoid personality disorder, borderline personality disorder, antisocial personality disorder among others.
- Eating Disorders
Anorexia nervosa, bulimia, and more.
Some of the most commonly seen mental illnesses are:
Anxiety
Anxiety is experienced when there is a heightened feeling of tension that is accompanied by elevated blood pressure. Anxiety is also accompanied by an increase in worried thoughts. While a general opinion goes to show that moderate amounts of anxiety only help in building better defences and improve performance levels, anxiety disorders need to be treated medically.
Depression
Depression is a problem that more and more people are experiencing today. It is not just the rates of depression that are alarming, but the fact that it is a problem being experienced by younger people, including children is important.
Depression is often confused with sadness. The two differ not just in terms of intensity but also in what is being experienced. Depression is a brain disorder characterised by a feeling of great sadness, lack of interest in people and things, cluelessness regarding life situations, and persistently low moods.
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is characterised by an altered state of mind where things and situations are not perceived in the manner in which they exist. This mental disorder is most commonly seen in responses, relationships, perceptions, and interactions.
Autism
A neurobiological disorder that usually presents quite early in childhood, autism is marked by rigid behaviour patterns, which also tend to be repetitive. Those with autism are found to face challenges in social interactions and have somewhat inadequate communication skills.
Mental retardation
The condition where an individual’s brain has not developed to the desired extent is known as mental retardation. While mental retardation is a term that was conventionally used long ago, the more acceptable way of referring to this condition is Intellectual Disability or ID. An ID can be experienced as one of the four stages – mild, moderate, severe, or profound. While the more severe forms can be noticed at birth, in other forms, it may take longer to ascertain the condition. However, in almost all the cases, ID is detected before the individual has reached adulthood.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a mental condition that can be found in both adults and children. It is characterised by high levels of impulsivity and hyperactive behaviour, attention deficits, and lack of focus.
While there are several reported cases of ADHD that are worked upon, it is also a condition that goes undiagnosed in several cases because parents do not seek help or because of the lack of attention given to it when it is in very mild forms. Like most other conditions, there are different levels of ADHD. It is usually of three types – predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive, and both combined.

 Doctors for Mental Illness
Doctors for Mental Illness  OTC Medicines for Mental Illness
OTC Medicines for Mental Illness
 Mental Illness articles
Mental Illness articles

 Ayurvedic Treatment of Mental Illness
Ayurvedic Treatment of Mental Illness
 Home Remedies for Mental Illness
Home Remedies for Mental Illness
 Homeopathic Treatment of Mental Illness
Homeopathic Treatment of Mental Illness
 Yoga for Mental Illness
Yoga for Mental Illness








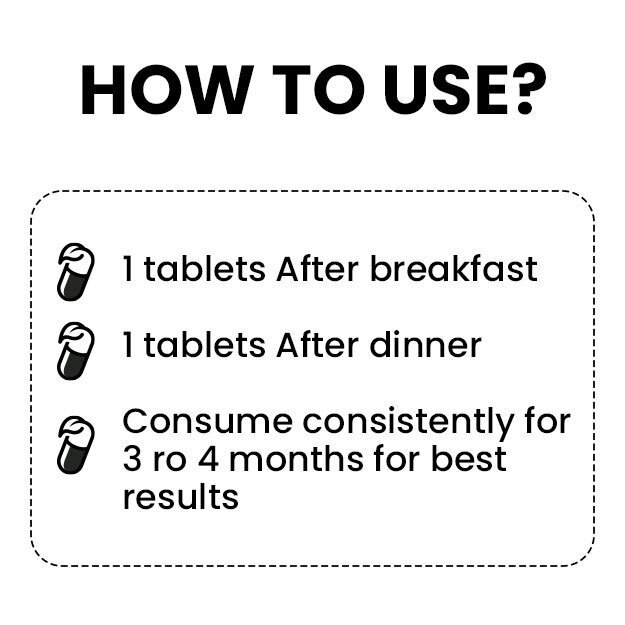








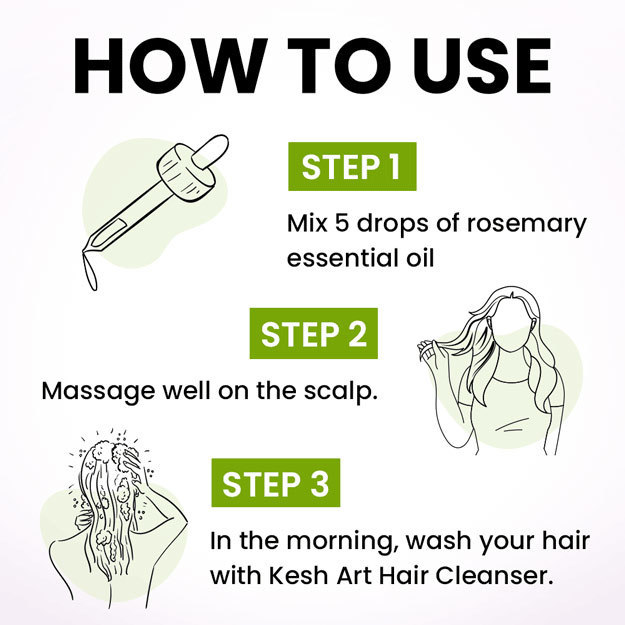











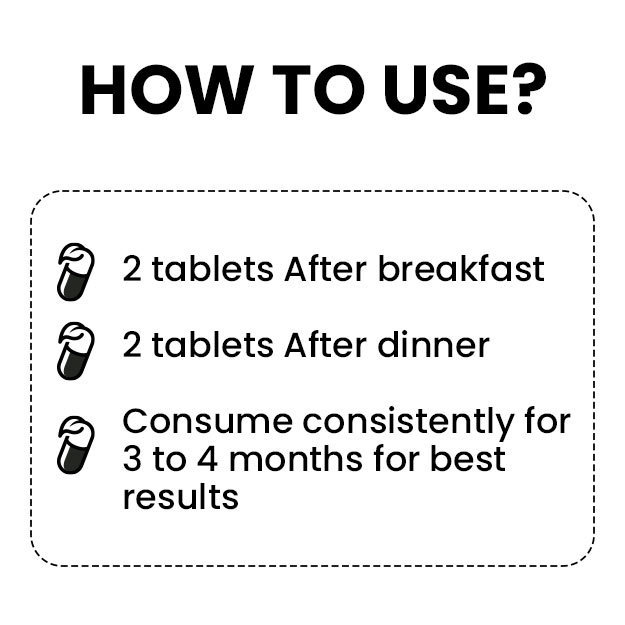







 Editorial Team
Editorial Team





 Dr. Nabi Darya Vali (AIIMS)
Dr. Nabi Darya Vali (AIIMS)











