Summary
Intestinal gas, also known as flatus, is a condition in which there is an accumulation of gas in the bowels. It can cause belching (burping), bloating (fullness), breaking wind (passing flatus) and even abdominal cramps. The term used for passage of gas is known as flatulence. Gas usually enters the body through the mouth when we eat and talk. Bacteria present in the large intestine break down food, which also leads to the production of gas. It is normal to pass flatus through the rectum or mouth. Causes might range from simple indigestion to more complex conditions like ulcerative colitis. Diagnosis is usually based on clinical signs and symptoms. In severe cases, your doctor might ask you to go for an abdominal X-ray, ultrasound, endoscopy or blood tests to confirm the underlying condition. Treatment of intestinal gas is rarely needed unless it causes severe discomfort or social embarrassment. Treating the underlying cause also provides relief. Avoiding certain foods that are associated with the production of intestinal gas might help too. Complications of intestinal gas are rarely heard of and the outcome is great with prompt treatment and diet modification.

 Doctors for Stomach Gas
Doctors for Stomach Gas  OTC Medicines for Stomach Gas
OTC Medicines for Stomach Gas
 Stomach Gas articles
Stomach Gas articles
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Stomach Gas
Ayurvedic Treatment of Stomach Gas
 Diet for Stomach Gas
Diet for Stomach Gas
 First Aid for Stomach Gas
First Aid for Stomach Gas
 Home Remedies for Stomach Gas
Home Remedies for Stomach Gas
 Homeopathic Treatment of Stomach Gas
Homeopathic Treatment of Stomach Gas
 Yoga for Stomach Gas
Yoga for Stomach Gas







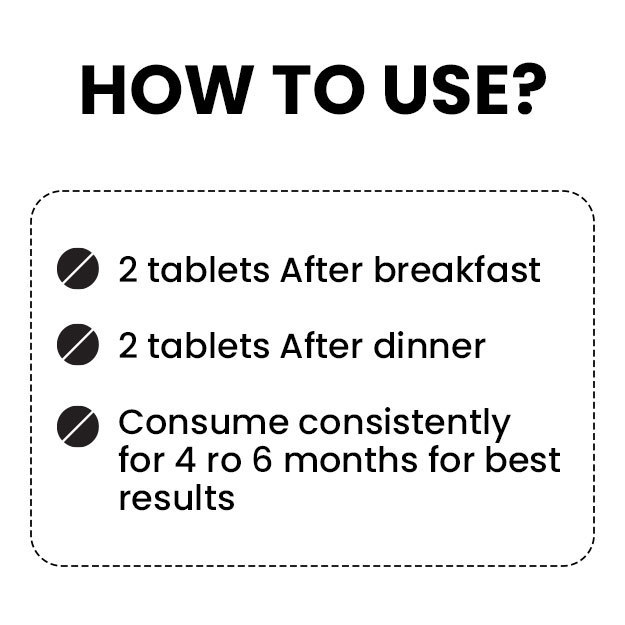








 Editorial Team
Editorial Team
















