Summary
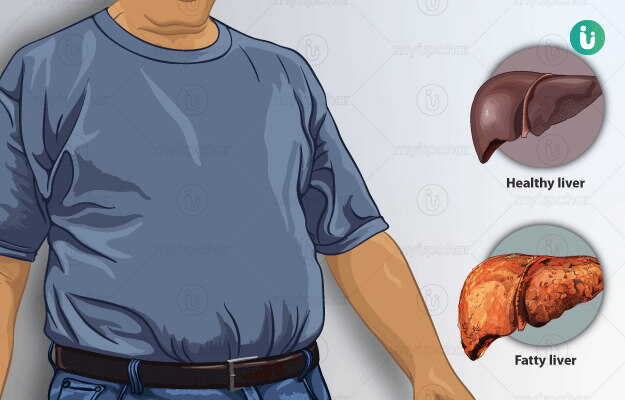
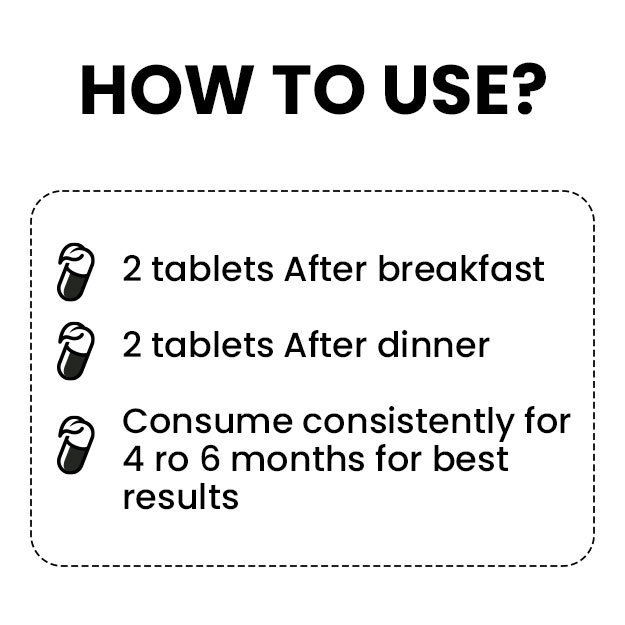
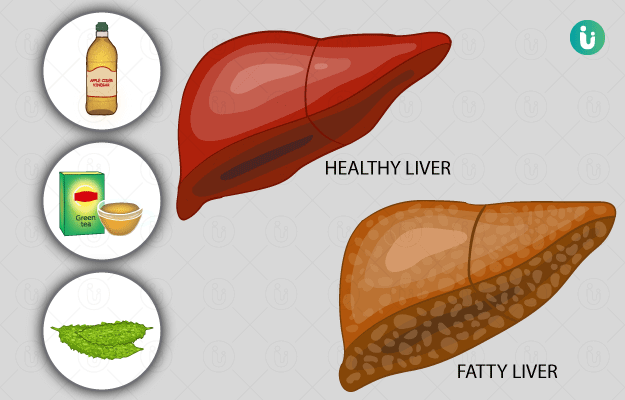
Fatty liver disease is a disease in which there is excess fat accumulation in the liver. It is of two types, alcoholic fatty liver disease that occurs due to excessive intake of alcohol and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that occurs due to the build-up of fat deposits in the liver. The exact causes of NAFLD are unknown, though, it is associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD is one the most common liver conditions to affect the western world. The disease may exist without any symptoms other than an enlarged liver or it may suddenly manifest itself with serious symptoms that require immediate medical intervention and indicate a complete liver failure. Timely diagnosis and intervention are key in preventing and possibly reversing or arresting the progression of the disease. At present, the treatment is aimed at managing the liver health through weight loss and exercises. There are no approved medicines for the condition through several promising drugs are on the horizon. More serious conditions require a surgery.

 Doctors for Fatty Liver
Doctors for Fatty Liver  OTC Medicines for Fatty Liver
OTC Medicines for Fatty Liver
 Lab tests for Fatty Liver
Lab tests for Fatty Liver Fatty Liver articles
Fatty Liver articles
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Fatty Liver
Ayurvedic Treatment of Fatty Liver
 First Aid for Fatty Liver
First Aid for Fatty Liver
 Home Remedies for Fatty Liver
Home Remedies for Fatty Liver
 Homeopathic Treatment of Fatty Liver
Homeopathic Treatment of Fatty Liver


















 Editorial Team
Editorial Team



 Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Dt. Akanksha Mishra

 Dr. Ayush Pandey
Dr. Ayush Pandey
 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla