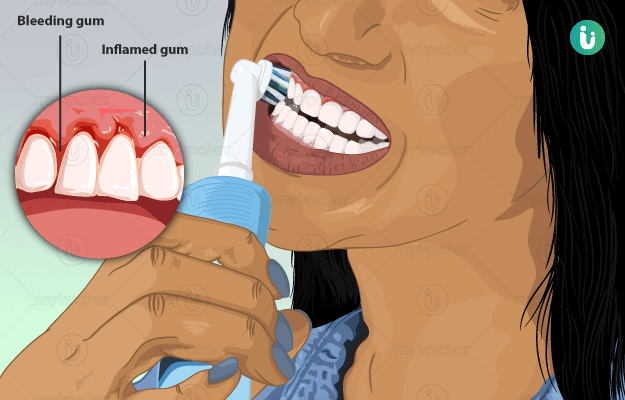
What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an inflammatory disease of the gums which happens due to the accumulation of dental plaque. Plaque is a naturally occurring colourless, sticky film (biofilm) over the surface of the teeth comprising of bacteria. Plaque can also accumulate between the teeth. If proper care is not taken, the condition can lead to severe gum damage and tooth loss.
What are its main associated signs and symptoms?
You may have gingivitis if you experience the following symptoms:
- Red and inflamed gums
- Bleeding gums
- Sore gums
- Foul smelling breath (Read more: Bad breath causes)
- Sensitivity to cold or hot food items and drinks (Read more: Tooth sensitivity treatment)
- Loosening of teeth
What are its main causes?
The main cause of gingivitis is plaque build-up. Bacteria present in plaque can affect the gums and cause inflammation and bleeding. This plaque can become hard and form a substance called tartar, which is firmer than a plaque.
Following factors increase the risk of gingivitis:
- Poor maintenance of oral hygiene
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Pregnancy
- Poor nutrition
- Stress
- Diseases like diabetes, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)- infection, and cancer
- Use of anti-epileptic drugs, cancer drugs, oral contraceptives, and steroid medications
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Regular visits to your dentist can help to identify gum disease early on since the condition is usually painless. Treatment involves removal of plaque from teeth by using special cleaning equipment.
If you feel pain, your dentist will recommend a painkiller (oral) to reduce pain. In some cases, antibiotic is also prescribed. Tooth removal is needed if the infection has affected the gums to a greater extent.
You can prevent gingivitis by following simple self-care tips like:
- Brush your teeth twice daily
- Proper flossing, once a day
- Using mouthwash regularly
- Regularly check your gums for any change in colour
- Regular dental check-up

 Doctors for Gingivitis
Doctors for Gingivitis  OTC Medicines for Gingivitis
OTC Medicines for Gingivitis
 Gingivitis articles
Gingivitis articles
 Home Remedies for Gingivitis
Home Remedies for Gingivitis







 Editorial Team
Editorial Team