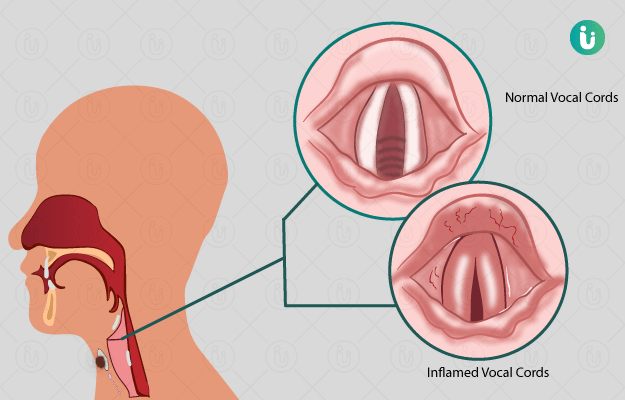
What is laryngitis?
Inflammation of the larynx and the vocal cords is referred to as laryngitis. The voice becomes hoarse due to improper vibration of the vocal cords. Studies show that the prevalence is highest in the age group of 30-50 years. The incidence of chronic laryngitis is 3.5 per 1000 population.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
The major symptoms include:
Complications can arise when stomach acids reach the larynx causing laryngitis due to acid reflux.
What are its main causes?
The major cause of laryngitis is a viral or bacterial infection, although cases of viral laryngitis are more. Straining the vocal cords can exacerbate this condition. When it continues for more than 3 weeks, it is said to be chronic. Other causes of laryngitis are:
- Use of cigarettes
- Overconsumption of alcohol
- Inhaled irritants like exhaust fumes, certain chemicals and smoke
- Excessive strain to the vocal cords
How is it diagnosed and treated?
It is usually diagnosed by an assessment of the symptoms and a physical examination. The medical history may reveal the reason behind laryngitis. The larynx is usually examined using a laryngoscope.
Generally, the condition is self-limiting and resolves on its own. Depending on the causative agent, treatment is given. Viral infection may be treated with anti-viral drugs. If it is due to acid reflux, then anti-acidity drugs may provide relief.
Self-care tips:
- Consume more fluids to flush out toxins
- Avoid exposure to smoke
- Gargle with warm saline
- Rest your voice and avoid talking loud
- Inhale steam to relieve a blocked nose
- Do not use nasal decongestants as they tend to dry your throat
If these remedies do not work, consult your physician.
In severe cases, laryngitis may cause difficulty breathing and require intensive therapy.

 Doctors for Laryngitis
Doctors for Laryngitis  OTC Medicines for Laryngitis
OTC Medicines for Laryngitis
 Laryngitis articles
Laryngitis articles
 Home Remedies for Laryngitis
Home Remedies for Laryngitis







 Editorial Team
Editorial Team











